Abstract
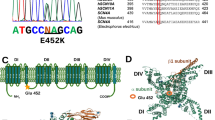
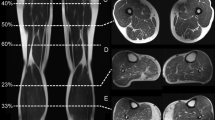
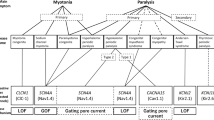
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (hyperPP), paramyotonia congenita (PC) and PC with myotonia permanens are closely related muscle disorders of genetic origin due to allelic mutations in the muscle sodium channel gene, SCN4A. Seven families of French origin with hyperPP were studied. Five of these had the Thr704Met mutation, but 2 families, genetically linked to SCN4A, failed to show any of the known mutations of SCN4A. Correlations between the phenotype and the genotype were made for patients with the Thr704Met mutation. All 12 patients over 30 years old with the Thr704Met mutation presented muscle weakness due to degeneration of muscle fibers in addition to periodic paralysis. Only approximately 12.5% of patients with the Thr704Met mutation presented with clinical myotonia and about 50% with hyperkalemia. One family with PC displayed the Gly 1306Val mutation with a phenotype similar to the one already reported for this mutation. Five families with either PC or PC with myotonia permanens had the Thr 1313Met mutation indicating that the severity of myotonia and its permanence were variable. Two mutations of SCN4A were found to be predominant in these 13 families: the Thr704Met and the Thr1313Met mutations. Only 2 families with the Thr704Met mutation and 3 families with the Thr1313Met shared the same SCN4A haplotype determined with intragenic dinucleotide repeats. Recurrent mutations of SCN4A may contribute to the predominance of these two mutations in the French population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Koch MC, et al: The skeletal muscle chloride channel in dominant and recessive human myotonia. Science 1992;257:797–800
George AL Jr, Crackower MA, Abdalla JA, Hudson AJ, Ebers GC: Molecular basis of Thomsen’s disease (autosomal dominant myotonia congenita). Nature Genet 1993;3:305–309
Ptàcek U, Trimmer JS, Agnew WS, Roberts JW, Petajan JH, Leppert M: Paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis map to the same sodium channel gene locus. Am J Hum Genet 1991;49:851–854
Koch MC, Ricker K, Otto M, Grimm T, Bender K, Zoll B, Harper PS, Lehmann-Horn F, Rudel R, Hoffman EP: Linkage data suggesting allelic heterogeneity for paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis on chromosome 17. Hum Genet 1991,88:71–74.
Ebers GC, George AL, Barchi RL, Ting-Pasador SS, Kallen RG, Lathrop GM, Beckman JS, Hahn AF, Brown WF, Campbell RD, Hudson AJ: Paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis are linked to the adult muscle sodium channel gene. Ann Neurol 1991;30:810–816
Fontaine B, Trofatter J, Rouleau GA, Khurana TS, Haines J, Brown R, Gusella JF: Different gene loci for hyperkalemic and hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Neuromusc Disord 1991;1:235–238
Casley WL, Allon M, Cousin HK, Ting SS, Crackower MA, Hashimoto L, Cornells F, Beckman JS, Hudson AJ, Ebers GC: Exclusion of linkage between hypokalemic periodic paralysis (Hokpp) and three candidate loci. Genomics 1992;14:493–494
Buruma OJS, Schipperheyn JJ: Periodic paralysis; in Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds): Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Amsterdam, North Holland Publishing, 1979, vol 41, pp 147–174.
Rüdell R, Ricker K: The primary periodic paralyses. Trends Neurosci 1985;8:467–470
Lehmann-Horn F, Rüdel R, Ricker K: Workshop report: Non-dystrophic myotonias and periodic paralyses. Neuromusc Disord 1993;3:161–168
McKusick VA: Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Baltimore, Johns Hopkins University Press, 1990.
Bradley WG, Taylor R, Rice DR, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I, Adelman LS, Jenkison M, Jedrzejowska H, Drac H, Pendleburry WN: Progressive myopathy in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Arch Neurol 1990;47:1013–1017
Noda M, Ikeda T, Kayano T, Suzuki H, Takeshima H, Kurasaki M, Takahashi H, Numa S: Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature 1986;320:188–192
Catterall WA: Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science 1988;242:50–61
Strühmer W: Structure-function studies of voltage-gated ion channels. Annu Rev Biophys Chem 1991;20:65–78
Barchi RL: Sodium channel gene defects in the periodic paralyses. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1993;6:40–47
Trimmer JS, Cooperman SS, Tomiko SA, Zhou J, Crean SM, Boyle MB, Kallen RG, Sheng Z, Barchi RL, Sigworth FJ, Goodman RH, Agnew WS, Mandel G: Primary structure and expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron 1989;3:33–49
George AL, Komosarof J, Kallen RG, Barchi RL: Primary structure of the adult human skeletal muscle voltage-dependent sodium channel. Ann Neurol 1992;31:131–137
Wang J, Rojas CV, Zhou J, Schwartz LS, Nicholas H, Hoffman EP: Sequence and genomic structure of the adult skeletal muscle sodium channel a subunit gene on 17q. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992;182:794–801
Ptàcek LJ, Johnson KJ, Griggs RC: Genetics and physiology of the myotonic muscle disorders. N Engl J Med 1993;328:482–489
Fontaine B: Periodic paralysis, myotonia congenita and sarcolemmal ion channels: A success of the candidate gene approach. Neuromusc Disord 1993;3:101–107
Lehmann-Horn F, Küther G, Ricker K, Grafe P, Ballanyi K, Rüdel R: Adynamia episodica hereditaria with myotonia: A non-inactivating sodium current and the effect of extracellular pH. Muscle Nerve 1987;10:363–374
Lehmann-Horn F, Rüdel R, Ricker K: Membrane defects in paramyotonia congenita (Eulenburg). Muscle Nerve 1987;10:363–374
Lehmann-Horn F, Iazzo PA, Hatt H, Franke C: Altered gating and conductance of Na+ channels in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Pflügers Arch 1991;418:297–299
Cannon SC, Brown RH, Corey DP: A sodium channel defect in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis: Potassium-induced failure of inactivation. Neuron 1991;6:619–626
Lerche H, Heine R, Pika U, George AL Jr, Mitrovic N, Browatzki M, Weiss T, Rivet-Bastide M, Franke C, Lomonaco M, Ricker K, Lehmann-Horn F: Human sodium channel myotonia: Slowed channel inactivation due to substitutions for a glycine within the III/IV linker. J Physiol 1993;470:13–22
Fontaine B, Khurana TS, Hoffman EP, Bruns GAP, Haines JL, Trofatter JA, Hanson MP. Rich J, McFarlane H, Yasek DM, Romano D, Gusella JF, Brown RH Jr: Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and the adult muscle sodium channel α-subunit gene. Science 1990;250:1000–1002
Ptàcek LJ, George AL, Griggs RC, Tawil R, Kallen RG, Barchi RL, Robertson M, Leppert MF: Identification of a mutation in the gene causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Cell 1991;67:1021–1027
Rojas CV, Wang J, Schwartz LS, Hoffman EP, Powell BR, Brown RH Jr: A Met to Val mutation in the skeletal muscle Na+ channel α-subunit in hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Nature 1991;354:387–389
Ptàcek LJ, George AL Jr, Barchi RL, Griggs RC, Riggs JA, Robertson M, Leppert MF: Mutations in an S4 segment of the adult skeletal muscle sodium channel causes paramyotonia congenita. Neuron 1992;8:891–897
McClatchey AI, Van den Berg P, Pericak-Vance MA, Raskind W, Verellen C, McKenna-Yasek D, Rao K, Haines JL, Bird T, Brown RH Jr, Gusella JF: Temperature-sensitive mutations in the III-IV cytoplasmic loop region of the skeletal muscle sodium channel gene in paramyotonia congenita. Cell 1991;68:769–774
Cummins TR, Zhou J, Sigworth FJ, Ukomadu C, Stephan M, Ptàcek LJ, Agnew WS: Functional consequences of a Na+ channel mutation causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Neuron 1993;10:667–678
Cannon SC, Strittmatter SM: Functional expression of sodium channel mutations identified in families with periodic paralysis. Neuron 1993;10:317–326
Rudolph JA, Spier SJ, Byrns G, Rojas CV, Bernoco D, Hoffman EP: Periodic paralysis in quarter horses: A sodium channel mutation disseminated by selective breeding. Nature Genet 1992;2:144–147
McClatchey AI, McKenna-Yasek D, Cros D, Worthen HG, Kuncl RW, De Silva SM, Cornblath DR, Gusella JF, Brown RH Jr: Novel mutations in families with unusual and variable disorders of the skeletal muscle sodium channel. Nature Genet 1992;2:148–152
Ptàcek LJ, Gouw L, Kwiecinski H, McManis P, Mendell JR, Barohn RJ, George AL, Barchi RL, Robertson M, Leppert MF: Sodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita and hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Ann Neurol 1993;33:300–307
Feero WG, Wang J, Barany F, Zhou J, Todorovic SM, Convit R, Galloway G, Hartlage P, Hayakawa H, Hoffman EP: Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis: Rapid molecular diagnosis and relationship of genotype to phenotype in 12 families. Neurology 1993;43:668–673
Gusella JF: DNA polymorphism and human diseases. Ann Rev Biochem 1986;55:831–854
McClatchey AI, Trofatter J, McKenna-Yasek D, Raskind W, Bird T, Pericak-Vance M, Gilchrist J, Arahata K, Radosavljevic D, Whorthen HG, Van den Bergh P, Haines JL, Gusella JF, Brown RH Jr: Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the SCN4A locus suggest allelic heterogeneity of hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and paramyotonia congenita. Am J Hum Genet 1992;50:896–901
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, ed 2. Cold Spring Harbor, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1989.
Ott J: Analysis of Human Genetic Linkage. Baltimore, Johns Hopkins University Press, 1991.
Jennings HS: The numerical result of diverse systems of breedings with respect to two pairs of characters. Genetics 1917;2:97–106
McClatchey AI, Lin CS, Wang J, Hoffman EP, Rojas C, Gusella JF: The genomic structure of the human skeletal muscle sodium channel gene. Hum Mol Genet 1992;1:521–527
George AL Jr, Iyer GS, Kleinfeld R, Kallen RG, Barchi RL: Genomic organization of the human skeletal muscle sodium channel gene. Genomics 1993;15:598–606
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T: Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989;86:2766–2770
Thomas C, Schweitzer R, Isch F, Collin H, Fardeau M: Données nouvelles sur la généalogie, la clinique et l’histologie d’une famille atteinte de paralysie périodique hyperkahémique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1978,134: 45–58.
Serratrice G, Desnuelle C: Paramyotonie congénitale, adynamie épisodique héréditaire ou paralysie périodique familiale paramyotonique et hyperkaliémique. Semaine Hôp Paris 1982;58:841–848
Lehmann-Horn F, Heine R, Pika U, Steinbach P, Golla A, Dobler M, Ricker K: The same SCN4A mutation is present in non-myotonic and in myotonic hyperkalemic and normokalemic periodic paralysis patients. Neuromusc Disord 1993, in press.
Wang J, Zhou J, Todorovic SM, Feero WG, Barany F, Conwit R, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I, Fidzianska A, Arahata K, Wessel HB, Sillen A, Marks HG, Hartlage P, Galloway G, Ricker K, Lehmann-Horn F, Hayakawa H; Hoffman EP: Molecular genetic and genetic correlations in sodium channelopathies: Lack of founder effect and evidence for a second gene. Am J Hum Genet 1993;52:1074–1084
Weber JL: Informativeness of human (dC-dA)n polymorphism. Genomics 1990;7:524–530
Weissenbach J, Gyapay G, Dib C, Vignal A, Moricette J, Millasseau P, Vaysseix G, Lathrop M: Second generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature 1992;359:794–801
Weber JL, Wong C: Mutation of human short tandem repeats. Hum Mol Genet 1993;2:1123–1128
Oudet C, Mornet E, Serre JL, Thomas F, Lentes-Zengerling S, Kretz C, Deluchat C, Tejada I, Boué J, Boué A, Mandel JL: Linkage disequilibrium between the fragile X mutation and two closely linked CA repeats suggest that fragile X chromosomes are derived from a small number of founder chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet 1993;52:297–304
Ozelius LJ, Kramer PL, de Leon D, Risch N, Bressman SB, Schubach DE, Brin MF, Kwiatkowski DJ, Burke RE, Gusella JF, Fahn S, Breakefield XO: Strong allelic association between the torsion dystonia gene (DYT1) and loci on chromosome 9q34 in Ashkenazi jews. Am J Hum Genet 1992;50:619–628
Sirugo G, Keats B, Fujita R, Duclos F, Purohit K, Koenig M, Mandel JL: Friedreich ataxia in Louisania Acadians. Demonstration of a founder effect by analysis of microsatellitegenerated extended haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet 1992;50:559–566
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support of the Association Française contre les Myopathies, the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale, the Ministère de la Recherche, the Laboratoires Servier, and the Assistance Publique-Hôpitaux de Paris. We thank Généthon for helping us with DNA sequencing; Dr. A.I. McClatchey and Prof. J.F. Gusella for sending primers at the initial stages of this work, and Prof. C. Van Broekhoven for sending DNA from 2 patients; Prof Y. Agid, Prof. O. Lyon-Caen and Dr. N. Baumann for their constant support; Dr. L. Maurs for referring a family; V. Müller for helping to collect DNA samples from the families; patients and their families for their help and their support; Dr. Nicole Feingold (INSERM U-155 and University of Paris VII) for revising the statistics used for the genetic analysis; Dr. Alexis Brice (INSERM U-289, Paris) for critically reading the manuscript, and Dr. Marc Del Bigio and Dr. Merle Ruberg for revision of the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plassart, E., Reboul, J., Rime, CS. et al. Mutations in the Muscle Sodium Channel Gene (SCN4A) in 13 French Families with Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis and Paramyotonia Congenita: Phenotype to Genotype Correlations and Demonstration of the Predominance of Two Mutations. Eur J Hum Genet 2, 110–124 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1159/000472351
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000472351
Key Words
This article is cited by
-
Periodic paralysis and voltage-gated ion channels
Kidney International (1996)