Abstract
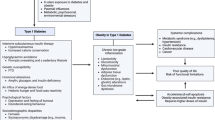
Obesity is a major risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes and is an important obstacle to the management of this disease. The increasing incidence of both obesity and type 2 diabetes makes management of these related conditions particularly important. Conventional approaches to the management of type 2 diabetes that focus primarily on improving glycaemic control—notably insulin or sulphonylurea treatment—often lead to weight gain, which is particularly detrimental to patients with type 2 diabetes. By contrast, reducing body weight in such patients improves glycaemic control and other cardiovascular risk factors associated with the metabolic syndrome. This suggests that weight reduction is a rational option in the management of obese patients with type 2 diabetes. While reductions in body weight of approximately 10% have been achieved in some studies, this is difficult to achieve in real life, especially for patients with type 2 diabetes. Weight management agents such as sibutramine and orlistat, used as part of an integrated programme of diet, physical activity and behavioural therapy, are thus an attractive early option for the management of type 2 diabetes in obese patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, G. Obesity and type 2 diabetes: a conflict of interests?. Int J Obes 23 (Suppl 7), S2–S4 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800954
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800954
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Obesity: under-diagnosed and under-treated in hospital outpatient departments
International Journal of Obesity (2002)