Abstract
OBJECTIVE: Insulin inhibition of insulin secretion has been described in normal lean subjects. In this study, we examined whether this phenomenon also occurs in the morbidly obese who often have severe peripheral insulin resistance.
SUBJECTS: Twelve obese patients, normotolerant to glucose (8 F/4 M, body mass index (BMI)=54.8±2.5 kg/m2, 39 y) and 16 lean control subjects (10 F/6 M, BMI=22.0±0.5 kg/m2, 31 y).
DESIGN AND MEASUREMENTS: An experimental study using various parameters, including an euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp (280 pmol/min/m2 of body surface), an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), electrical bioimpedance and indirect calorimetry.
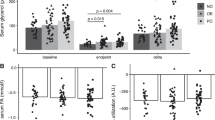
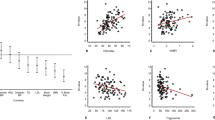
RESULTS: The obese subjects were insulin resistant (M=19.8±1.6 vs 48.7±2.6 μmol/min kg FFM, P<0.0001) and hyperinsulinemic in the fasted state and after glucose ingestion. Fasting plasma C-peptide levels (obese 1425±131 pmol/l vs lean 550±63 pmol/l; P<0.0001) decreased less during the clamp in the obese groups (−16.9±6.9% vs −43.0±5.6% relative to fasting values; P=0.007). In the lean group, the C-peptide decrease during the clamp (percentage variation) was related to insulin sensitivity, M/FFM (r=0.56, P=0.03), even after adjustment for the clamp glucose variation.
CONCLUSION: We conclude that, in lean subjects, insulin inhibits its own secretion, and this may be related to insulin sensibility. This response is blunted in morbidly obese patients and may have a role in the pathogenesis of fasting hyperinsulinemia in these patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perry IJ, Wannamethee SG, Walker MK, Thomson AG, Whincup PH . Prospective study of risk factors for development of non-insulin dependent diabetes in middle aged British men Br Med J 1995 310: 560–564.
Chan JM, Rimm EB, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willet WC . Obesity, fat distribution, and weight gain as risk factors for clinical diabetes in men Diabetes Care 1994 17: 961–969.
Manson JE, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Willet WC, Rosner B, Monson RR, Speizer FE, Hennekens CH . A prospective study of obesity and risk of coronary heart disease in women New Engl J Med 1990 322: 882–889.
Lissner L, Odell PM, D'Agostino RB, Stokes J, Kreger BE, Belanger AJ, Brownell KD . Variability of body weight and health outcomes in the Framingham population New Engl J Med 1991 315: 1839–1844.
Olefsky JM, Kolterman OG, Scarlett JA . Insulin action and resistance in obesity and non insulin-dependent type I diabetes mellitus Am J Physiol 1982 243: E15–E30.
Bonadonna RC, Groop L, Kraemer N, Ferrannini E, Del Prato S, De Fronzo RA . Obesity and insulin resistance in humans: a dose–response study Metabolism 1990 39: 452–459.
Muscelli E, Camastra S, Catalano C, Quinones G, Ciociaro D, Baldi S, Ferrannini E . Metabolic and cardiovascular assessment in moderate obesity: effect of weight loss J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 2937–2943.
Cohen P, Barzilai N, Barzilai D, Karnieli E . Correlation between insulin clearance and insulin responsiveness: studies in normal, obese, hyperthyroid and Cushing's syndrome patients Metabolism 1986 35: 744–749.
Polonsky KS, Given BD, Hirsch L, Shapiro ET, Tillil H, Beebe C, Galloway JA . Quantitative study of insulin secretion and clearance in normal and obese subjects J Clin Invest 1988 81: 435–441.
Meistas MT, Margolis S, Kowarski, A . 1983 Hyperinsulinemia of obesity is due to decreased clearance of insulin Am J Physiol 1983 245: E155–E159.
Bonora E, Zavaroni I, Bruschi F, Alpi O, Pezzarossa A, Guerra L, Dall'aglio E, Coscelli C, Butturini U . Peripheral hyperinsulinemia of simple obesity: pancreatic hypersecretion or impaired insulin metabolism J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1984 59: 1121–1127.
Polonsky KS, Given BD, Van Cauter E . Twenty-four hour profiles and pulsatile pattern of insulin secretion in normal and obese subjects J Clin Invest 1988 81: 442–448.
Willer AK, Pacini G, Ludvik B, Schernthane G, Prager R . β-Cell hypersecretion and not reduced hepatic insulin extraction is the main cause of hyperinsulinemia in obese nondiabetic subjects Metabolism 1992 41: 1304–1312.
Ferrannini E, Natali A, Bell P, Cavallo-Perin P, Lalic N, Mingrone G . Insulin resistance and hypersecretion in obesity. European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR) J Clin Invest 1997 100: 1166–1173.
Liljenquist JE, Horwitz DL, Jennings AS, Chiasson JL, Keller U, Rubenstein AH . Inhibition of insulin secretion by exogenous insulin in normal man as demonstrated by C-peptide assay Diabetes 1978 27: 563–570.
Kraegen EW, Lazarus L, Campbell LV . Failure of insulin of infusion during euglycemia to influence endogenous basal insulin secretion Metabolism 1983 32: 622–627.
Peiris AN, Stagner JI, Vogel RL, Samols E, Nakagawa A . Lack of insulin feedback inhibition in non-obese and obese men Metabolism 1993 42: 371–375.
Cavallo-Perin P, Bruno A, Boine L, Cassader M, Lenti G, Pagano G . Insulin resistance in Graves' disease: a quantitative in-vivo evaluation Eur J Clin Invest 1988 18: 607–613.
Cavallo-Perin P, Bruno A, Scaglione L, Gruden G, Cassader M, Pagano G . Feedback inhibition of insulin and glucagon secretion by insulin is altered in abdominal obesity with normal or impaired glucose tolerance Acta Diabet 1993 30: 154–158.
Baynes C, Anyaoku V, Johnston G, Elkeles RS . Feedback inhibition of insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes Clin Sci 1991 81: 685–690.
Hirota M, Shima K, Tanaka A, Tahara Y, Ikegami H, Kumahara Y . Failure of human insulin to influence endogenous basal insulin secretion in mild diabetics Metabolism 1987 36: 303–307.
Kulkarni RN, Bruning JC, Winnay JN, Postic C, Magnuson MA, Kahn R . Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pancreatic β-cells creates an insulin secretory defect similar to that in type 2 diabetes Cell 1999 96: 329–339.
Elahi D, Nagulesparan M, Hershcopf RJ, Muller DC, Tobin JD, Blix PM, Rubenstein AH, Unger RH, Andres R . Feedback inhibition of insulin secretion by insulin: relation to the hyperinsulinemia of obesity New Engl J Med 1982 306: 1196–1202.
Robertson DA, Singh BM, Hale PJ, Nattrass M . Effects of morbid obesity on insulin clearance and insulin sensitivity in several aspects of metabolism as assessed by low-dose insulin infusion Metabolism 1992 41: 604–612.
The fifth report of the Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC V) Arch Intern Med 1993 153: 154–183.
National Diabetes Data Group Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance Diabetes 1979 28: 1039–1057.
Fulcher GR, Farrer M, Walker M, Rodham D, Clayton B, Alberti KGM . A comparison of measurements of lean body mass derived by bioelectrical impedance, skinfold thickness and total body potassium. A study in obese and non-obese normal subjects Scand J Lab Invest 1991 51: 245–253.
De Fronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R . Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance Am J Physiol 1979 237: E214–E223.
McGuire EAH, Heldermann JH, Tobin JD, Andres R, Berman M . Effects of arterial versus venous sampling on analysis of glucose kinetics in man J Appl Physiol 1976 41: 1312–1318.
Ferrannini E, Cobelli C . The kinetics of insulin in man. General aspects Diabetes Metab Rev 1987 3: 335–363.
Cobelli C, Mari A, Ferrannini E . On the linearity of insulin kinetics Am J Physiol 1986 251: E247–E250.
Polonsky K, Jaspan J, Pugh W, Cohen D, Schmeider M, Schwartz T, Moossa AR, Tager H, Rubenstein AH . Metabolism of C-peptide in dogs: in vivo demonstration of the absence of hepatic extraction J Clin Invest 1983 72: 1114–1124.
De Fronzo RA, Binder C, Wahren J, Felig P, Ferrannini E, Faber OK . Sensitivity of insulin secretion to feedback inhibition by hyperinsulinaemia Acta Endocrinol 1981 98: 81–86.
Wu MS, Ho LT . The pancreatic glucagon and C-peptide secretion during hyperinsulinemia in euglycemic glucose clamp with or without somatostatin infusion in normal man Horm Metabol Res 1987 19: 253–256.
Bratusch-Marrain PR, Waldhäusl W . Suppression of basal, but not glucose stimulated secretion by human insulin in healthy and obese hyperinsulinemic subjects Metabolism 1985 34: 188–193.
Bonora E, Moghetti P, Zancarano C, Cigolini M, Querena M, Cacciatori V, Zenere M, Corgnati A, Muggeo M . Normal inhibition by somatostatin of glucose-stimulated β-cell secretion in obese subjects Horm Metab Res 1990 22: 584–588.
Schusdziarra V, Lawecki J, Ditschuneit HH, Lokas B, Maier E, Pfeiffer F . Effect of low dose somatostatin infusion on pancreatic and gastric function in lean and obese non diabetic human subjects Diabetes 1985 34: 595–601.
Boden G, Chen X, Desantis R, Kolaczynski J, Morris M . Evidence that suppression of insulin secretion by insulin itself is neurally mediated Metabolism 1993 42: 786–789.
Stagner J, Samols E, Polonsky K, Pugh W . Lack of direct inhibition of insulin secretion by exogenous insulin in the canine pancreas J Clin Invest 1986 78: 1193–1198.
Anderson EA, Hoffman RP, Balon TW, Sinkey CA, Mark AL . Hyperinsulinemia produces both sympathetic neural activation and vasodilatation in normal humans J Clin Invest 1991 87: 2246–2252.
Muscelli E, Emdin M, Natali A, Pratali L, Camastra S, Gastaldelli A, Baldi S, Carpeggiani C, Ferrannini E . Autonomic and hemodynamic responses to insulin in lean and obese humans J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998 83: 2084–2090.
Scherrer U, Randin D, Tappy L, Vollenweider P, Jéquier E, Nicod P . Body fat and sympathetic nerve activity in healthy subjects Circulation 1994 89: 2634–2640.
Grassi G, Serravalle G, Cattaneo BM, Bolla GB, Lanfranchi A, Colombo M, Giannattasio C, Brunani A, Cavagnini F, Mancia G . Sympathetic activation in obese normotensive subjects Hypertension 1995 25: 560–563.
Velloso LA, Carneiro EM, Crepaldi SC, Boschero AC, Saad MJA . Glucose and insulin-induced phosphorylation of the insulin receptor and its primary substrates IRS-1 and IRS-2 in rat pancreatic islets FEBS Lett 1995 377: 353–357.
Rothemberg PL, Willison LD, Simon J, Wolf BA . Glucose induced receptor tyrosine phosphorylation in insulin-secretion beta-cells Diabetes 1995 44: 802–809.
Goodyear LJ, Giorgino F, Sherman LA, Carey J, Smith RJ, Dohm GL . Insulin receptor phosphorylation, insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphorylation, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity are decreased in intact skeletal muscle strips from obese subjects J Clin Invest 1995 95: 2195–2204.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP); Fundação de Apoio ao Ensino e Pesquisa (FAEP, UNICAMP) and Consella Nacional de Pesquisa (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muscelli, E., Pereira, J., Lazarin, M. et al. Lack of insulin inhibition on insulin secretion in non-diabetic morbidly obese patients. Int J Obes 25, 798–804 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801607
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801607
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Intact cross-talk between insulin secretion and insulin action after postgastroplasty recovery of ideal body weight in severely obese patients
International Journal of Obesity (2004)
-
Restored insulin inhibition on insulin secretion in nondiabetic severely obese patients after weight loss induced by bariatric surgery
International Journal of Obesity (2003)