Abstract
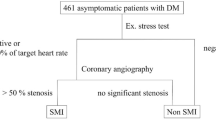
The concomitant presence of diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension significantly impairs myocardial function through a direct negative effect on cardiac myocytes, coronary microvessels and precipitation of atherosclerosis in major coronary arteries. The purpose of the present study was to establish to what extent non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) modified silent myocardial ischaemia (SMI) in patients with essential hypertension and without documented coronary artery disease (CAD). The study population consisted of 41 patients with essential arterial hypertension associated with NIDDM, treated with diet and oral hypoglycaemic agents (group I) and 40 patients with essential arterial hypertension without diabetes mellitus (group II). Both groups were comparable with respect to age, gender, duration, severity and complications of hypertension. A mean duration of diabetes mellitus in group I was 6.8 years. Conventional and automatic blood pressure and heart rate measurements, continuous ECG recordings, echocardiograms and laboratory tests were obtained in all patients. SMI was more frequent in group I than in group II (29.3% vs 12.5%, P < 0.05). in group i the total duration of smi was longer (37.3 vs 2.8 min, P < 0.001) and the total number of silent episodes was larger (15.5 vs 2.6, P < 0.001). no inter-group differences were seen in conventional and automatic blood pressure and heart rate measurements. both groups did not differ significantly in left ventricular mass index (lvmi) or the proportion of patients with left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh) (75.6% vs 60%). Lipid profile in both groups indicated an increased risk of CAD, but without significant differences. In conclusion, in patients with essential arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus, the incidence and severity of SMI were clearly higher than in hypertensives with normal carbohydrate metabolism. Employment of modern diagnostic techniques in hypertensives permits identification of those at greater risk, which may have further clinical implications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lubaszewski, W., Kawecka-Jaszcz, K., Czarnecka, D. et al. Silent myocardial ischaemia in patients with essential arterial hypertension and non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Hum Hypertens 13, 309–313 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000813
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000813
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The diabetic, hypertensive heart: epidemiology and mechanisms of a very high-risk situation
Journal of Human Hypertension (2009)