Abstract
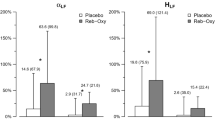
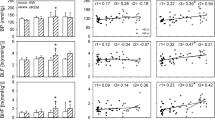
The objective of this study was to examine the effects of dihydropyridine calcium antagonist therapy on 24-h baroreflex sensitivity. Twenty-three patients with moderate essential hypertension were studied before and during acute (10 patients) and chronic (21 patients) treatment with a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist (nifedipine, nicardipine or felodipine) as monotherapy in a dose titrated to produce a fall in mean cuff pressure of at least 10%. Twenty-four hour unrestricted ambulatory intra-arterial blood pressure (IABP) and heart rate (R-R interval) were monitored. Baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) was assessed throughout the 24-h period by off-line computer analysis of spontaneous variations in IABP and R-R interval. During acute first dose treatment with a calcium antagonist there was a significant fall in blood pressure (BP), increase in heart rate and reduction in BRS. With chronic therapy (6–16 weeks) there was a continued reduction in mean BP of 11% (P < 0.001), but heart rate had returned to control levels and brs was significantly increased over the 24 h by 14% (P < 0.01). the increase in brs was evident during both the waking and sleeping periods, but the greatest increase was during sleep (awake 12% P = 0.02, asleep 28% P = 0.003). In conclusion, although dihydropyridine calcium antagonists acutely cause a reflex tachycardia associated with a reduced BRS, there is no such effect with chronic therapy. BRS was significantly increased after chronic treatment, with exaggeration of the diurnal pattern.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaile, J., Jordan, P., Stallard, T. et al. The effects of acute and chronic dihydropyridine calcium antagonist therapy on baroreflex sensitivity: a re-analysis using the sequence method. J Hum Hypertens 14, 189–194 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000962
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1000962
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of peritoneal dialysis fluid biocompatibility on baroreflex sensitivity
Kidney International (2008)