Abstract
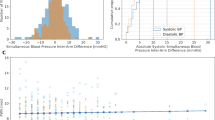
Blood pressure (BP) variability is estimated as the standard deviation of 24-h ambulatory BP. The present study was performed to determine the effect of the mean 24-h ambulatory BP values and standard deviations on arterial wall stiffness assessed by brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV). Brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity, carotid intima–media thickness (IMT), urinary albumin excretion (UAE) and 24-h ambulatory BP were measured before the start of antihypertensive therapy in 203 newly diagnosed hypertensive patients (53.3±0.7 years old; clinic systolic/diastolic BP: 154±1/98±1 mm Hg), and univariate and multivariate regression analyses of these clinical and biological parameters were performed. Univariate regression analyses revealed a significant association between mean baPWV values and the standard deviations of ambulatory systolic/diastolic BP. Mean ambulatory systolic/diastolic BP values were also associated with UAE, and the standard deviations of ambulatory systolic BP were associated with maximum carotid IMT. Quintile analyses showed that patients with a mean 24-h ambulatory mean BP value and standard deviation below 110 and 20 mm Hg, respectively, had the lowest baPWV. Moreover, the multivariate regression analyses confirmed a significant correlation between baPWV and the standard deviation of 24-h ambulatory systolic BP. In conclusion, untreated hypertensive patients with a higher 24-h ambulatory systolic BP variability had stiffer arterial walls. Ambulatory systolic BP variability may be involved in stiffening of the arteries of hypertensive patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blacher J, Asmar R, Djane S, London GM, Safar ME . Aortic pulse wave velocity as a marker of cardiovascular risk in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 1999; 33: 1111–1117.
Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Asmar R, Gautier I, Laloux B, Guize L et al. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2001; 37: 1236–1241.
Asmar RG, London GM, O'Rourke ME, Safar ME . Improvement in blood pressure, arterial stiffness and wave reflections with a very-low-dose perindopril/indapamide combination in hypertensive patient. A comparison with atenolol. Hypertension 2001; 38: 922–926.
Boutouyrie P, Tropeano AI, Asmar R, Gautier I, Benetos A, Lacolley P et al. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of primary coronary events in hypertensive patients. A longitudinal study. Hypertension 2002; 39: 10–15.
Amar J, Ruidarets JB, Chamontin B, Drouet L, Ferrieres J . Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a population-based study. J Hypertens 2001; 19: 381–387.
Ichihara A, Hayashi M, Koura Y, Tada Y, Hirota N, Saruta T . Long-term effects of intensive blood-pressure lowering on arterial wall stiffness in hypertensive patients. Am J Hypertens 2003; 16: 959–965.
Perloff D, Sokolow M, Cowan R . The prognostic value of ambulatory blood pressures. JAMA 1983; 249: 2792–2798.
Verdecchia P, Porcellati C, Schillaci G, Borgioni C, Ciucci A, Battistelli M et al. Ambulatory blood pressure. An independent predictor of prognosis in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1994; 24: 793–801.
Ohkubo T, Imai Y, Tsuji I, Nagai K, Watanabe N, Minami N et al. Prediction of mortality by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring versus screening blood pressure measurements: a pilot study in Ohasama. J Hypertens 1997; 15: 357–364.
Staessen JA, Thijs L, Fagard R, O'Brien ET, Clement D, de Leeuw PW et al. Predicting cardiovascular risk using conventional vs ambulatory blood pressure in older patients with systolic hypertension. Systolic Hypertension in Europe Trial Investigators. JAMA 1999; 282: 539–546.
Bjorklund K, Lind L, Zethelius B, Andren B, Lithell H . Isolated ambulatory hypertension predicts cardiovascular morbidity in elderly men. Circulation 2003; 107: 1297–1302.
O'Sullivan C, Duggan J, Lyons S, Thornton J, Lee M, O'Brien E . Hypertensive target-organ damage in the very elderly. Hypertension 2003; 42: 130–135.
Parati G, Pomidossi G, Albini F, Malaspina D, Mancia G . Relationship of 24-h blood pressure mean and variability to severity of target-organ damage in hypertension. J Hypertens 1987; 5: 93–98.
Frattola A, Parati G, Cuspidi C, Albini F, Mancia G . Prognostic value of 24-h blood pressure variability. J Hypertens 1993; 11: 1133–1137.
Pickering TG, James GDJ . Ambulatory blood pressure and prognosis. J Hypertens 1994; 12 (Suppl 8): S29–S33.
Verdecchia P, Borgioni C, Ciucci A, Gattobigio R, Schillaci G, Sacchi N et al. Prognostic significance of blood pressure variability in essential hypertension. Blood Press Monit 1996; 1: 3–11.
Kikuya M, Hozawa A, Ohokubo T, Tsuji I, Michimata M, Matsubara M et al. Prognostic significance of blood pressure and heart rate variabilities: the Ohasama study. Hypertension 2000; 36: 901–906.
Ichihara A, Hayashi M, Ryuzaki M, Handa M, Furukawa T, Saruta T . Fluvastatin prevents development of arterial stiffness in hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2002; 17: 1513–1517.
Ichihara A, Hayashi M, Koura Y, Tada Y, Kaneshiro Y, Saruta T . Long-term effects of statins on arterial pressure and stiffness of hypertensives. J Hum Hypertens 2005; 19: 103–109.
Ichihara A, Hayashi M, Kaneshiro Y, Takemitsu T, Homma K, Kanno Y et al. Low doses of losartan and trandolapril improve arterial stiffness in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 2005; 45: 866–874.
Sun K, Daimon M, Watanabe S, Komuro I, Masuda Y . The relation of pulse wave velocities measured by oscillometric and tonometric methods and clinical application studies. Jpn J Appl Physiol 2002; 32: 81–86.
Yamashina A, Tomiyama H, Takeda K, Tsuda H, Arai T, Hirose K et al. Validity, reproducibility, and clinical significance of noninvasive brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity measurement. Hypertens Res 2002; 25: 359–364.
Cuspidi C, Meani S, Fusi V, Valerio C, Catini E, Magrini F et al. Isolated ambulatory hypertension and changes in target organ damage in treated hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens 2005; 19: 471–477.
Imai Y, Aihara A, Ohkubo T, Nagai K, Tsuji I, Minami N et al. Factors that affect blood pressure variability. A community-based study in Ohasama, Japan. Am J Hypertens 1997; 10: 1281–1289.
Kobayashi K, Akishita M, Yu W, Hashimoto M, Ohni M, Toba K . Interrelationship between non-invasive measurements of atherosclerosis: flow-mediated dilation of brachial artery, carotid intima–media thickness and pulse wave velocity. Atherosclerosis 2004; 173: 13–18.
Yokoyama H, Aoki T, Imahori M, Kuramitsu M . Subclinical atherosclerosis is increased in type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria evaluated by intima–media thickness and pulse wave velocity. Kidney Int 2004; 66: 448–454.
Mule G, Cottone S, Vadala A, Volpe V, Mezzatesta G, Mongiovi R et al. Relationship between albumin excretion rate and aortic stiffness in untreated essential hypertensive patients. J Int Med 2004; 256: 22–29.
Smith A, Karalliedde J, De Angelis L, Goldsmith D, Viberti G . Aortic pulse wave velocity and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 16: 1069–1075.
Kario K, Pickering TG, Umeda Y, Hoshide S, Hoshide Y, Morinari M et al. Morning surge in blood pressure as a predictor of silent and clinical cerebrovascular disease in elderly hypertensives. A prospective study. Circulation 2003; 107: 1401–1406.
Kario K, Pickering TG, Hoshide S, Eguchi K, Ishikawa J, Morinari M et al. Morning blood pressure surge and hypertensive cerebrovascular disease: role of the alpha adrenergic sympathetic nervous system. Am J Hypertens 2004; 17: 668–675.
Redon J, Liao Y, Lozano JV, Miralles A, Pascual JM, Cooper RS . Ambulatory blood pressure and microalbuminuria in essential hypertension: role of circadian variability. J Hypertens 1994; 12: 947–953.
Kario K, Matsuo T, Kobayashi H, Imiya M, Matsuo M, Shimada K . Nocturnal fall of blood pressure and silent cerebrovascular damage in elderly hypertensive patients. Advanced silent cerebrovascular damage in extreme dippers. Hypertension 1996; 27: 130–135.
Asmar R, Benetos A, Topouchian J, Laurent P, Pannier B, Brisac AM et al. Assessment of arterial distensibility by automatic pulse wave velocity measurement. Validation and clinical application studies. Hypertension 1995; 26: 485–490.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan (16790474 and 17390249). We acknowledge the skilful secretarial work of Ms Mahoko Uchimura of Keio University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ichihara, A., Kaneshiro, Y., Takemitsu, T. et al. Ambulatory blood pressure variability and brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity in untreated hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens 20, 529–536 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002023
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1002023
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Relationships between 24-h blood pressure variability and 24-h central arterial pressure, pulse wave velocity and augmentation index in hypertensive patients
Hypertension Research (2017)
-
Plasma levels of natriuretic peptides and year-by-year blood pressure variability: a population-based study
Journal of Human Hypertension (2017)
-
Average real variability of 24-h systolic blood pressure is associated with microalbuminuria in patients with primary hypertension
Journal of Human Hypertension (2016)
-
Association of long-term blood pressure variability and brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity: a retrospective study from the APAC cohort
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Arterial stiffness, fatty liver and the presence of coronary artery calcium in a large population cohort
Cardiovascular Diabetology (2013)