Abstract
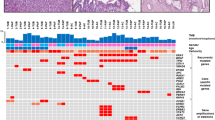
The ARP gene encodes a highly conserved arginine-rich protein from chromosomal band 3p21.1. At the cytogenetic level this region is frequently deleted in a variety of different solid tumors, although not in pancreatic cancer. We have reported the presence of a specific mutation (ATG50→AGG) or deletion of codon 50 of the ARP gene in different tumor types (Shridhar et al., 1996, 1996a). In the present study, we have observed mutations involving codon 50 in 11 of 37 pancreatic tumors. The frequency of codon 50 mutation is roughly the same in pancreatic tumors as in the other types of tumors previously examined. In addition, we have detected mutations at codon 51 in multiple PCR subclones in two other pancreatic tumors. Mutations in the ARP gene are thus commonly observed in pancreatic cancer, as well as many other cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shridhar, V., Rivard, S., Wang, X. et al. Mutations in the arginine-rich protein gene (ARP) in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 14, 2213–2216 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201054
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201054
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotropic factor is an important factor in chondrocyte ER homeostasis
Cell Stress and Chaperones (2019)
-
Tumor suppressor genes on chromosome 3p involved in the pathogenesis of lung and other cancers
Oncogene (2002)