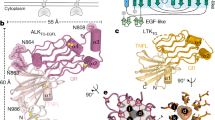
Abstract
The transcription factors p53 and E2F-1 play important roles in the control of cell cycle progression. In transient transfection experiments, expression of E2F-1, other E2F family members, or p53 squelched transcription from cotransfected plasmids in a dose-dependent manner. Although the proteasome inhibitors MG-132 and lactacystin markedly increased the level of expression of E2F-1 and p53, these inhibitors completely alleviated squelching by both proteins. Several observations indicate MG-132 alleviates squelching by influencing the conformation of newly synthesized p53 and E2F-1: MG-132 increased the fraction of wild type p53 bound by a monoclonal antibody which preferentially recognizes mutant conformers of p53, increased binding of hsp70 to p53 and inhibited nuclear accumulation of both p53 and E2F-1, but not the pocket protein p107. The protease inhibitors ALLN and ALLM did not influence expression of E2F-1 or p53, nor did they alleviate squelching by either transcription factor. Because MG-132 and lactacycstin are highly specific inhibitors of the proteasome protease, our results suggest that the proteasome influences post-translational processes involved in proper folding and cytoplasmic clearing of E2F-1 and p53.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magae, J., Illenye, S., Tejima, T. et al. Transcriptional squelching by ectopic expression of E2F-1 and p53 is alleviated by proteasome inhibitors MG-132 and lactacystin. Oncogene 15, 759–769 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201251
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1201251
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Development of HER2-antagonistic peptides as novel anti-breast cancer drugs by in silico methods
Breast Cancer (2008)
-
Caspase-dependent apoptosis by ectopic expression of E2F-4
Oncogene (2000)
-
NPDC-1, a regulator of neural cell proliferation and differentiation, interacts with E2F-1, reduces its binding to DNA and modulates its transcriptional activity
Oncogene (2000)
-
BMPs inhibit neurogenesis by a mechanism involving degradation of a transcription factor
Nature Neuroscience (1999)