Abstract
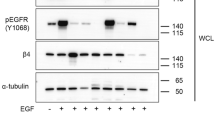
Integrin-mediated signalling has been implicated in asbestos-induced carcinogenesis. In studies here, we examined signal transduction events associated with integrin-directed cell reactions triggered by crocidolite asbestos in the pleural mesothelial cell line 4/4 RM-4. Crocidolite fibres induced a significant time- and dose-dependent activation of the extracellular-signal-regulated kinases ERK1 and ERK2. ERK activation was specifically inhibited by integrin-blocking agents, that are integrin-binding peptides containing the sequence arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD), and monoclonal antibodies against the integrin ß1-chain. Integrin-dependent activation of ERK1/2 in response to asbestos appeared to be independent of focal adhesion kinase pp125FAK (FAK) since FAK autophosphorylation remained unaffected in crocidolite-exposed mesothelial cells. Instead, we observed striking similarities in the kinetics of asbestos-induced ERK1/2 responses and phosphorylation of protein kinase B (AKT) at serine 473, a possible target residue for integrin-linked kinase. As with ERK activation, asbestos-induced AKT stimulation was significantly blocked by both the RGD-peptide and the ß1-integrin antibodies. These studies are the first to establish that in mesothelial cells ERK1/2 and AKT are simultaneously phosphorylated upon asbestos exposure in a ß1-integrin-dependent manner.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht C, Borm PJ, Adolf B, Timblin CR and Mossman BT . (2002). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 184, 37–45.
Aplin AE, Howe A, Alahari SK and Juliano RL . (1998). Pharmacol. Rev., 50, 197–263.
Aronson JF and Cristofalo VJ . (1981). Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 15, 141–147.
Boylan AM, Sanan DA, Sheppard D and Broaddus VC . (1995). J. Clin. Invest., 96, 1987–2001.
Cobb MH and Goldsmith EJ . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 14843–14846.
Coffer PJ, Jin J and Woodgett JR . (1998). Biochem. J., 335, 1–13.
Danen EHJ and Yamada KM . (2001). J. Cell Physiol., 189, 1–13.
Jimenez LA, Zanella C, Fung H, Janssen YM, Vacek P, Charland C, Goldberg J and Mossman BT . (1997). Am. J. Physiol., 273, 1029–1035.
King WG, Mattaliano MD, Chan TO, Tsichlis PN and Brugge JS . (1997). Mol. Cell Biol., 17, 4406–4418.
Kuwahara M, Kuwahara M, Verma K, Ando T, Hemenway DR and Kagan E . (1994). Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 10, 167–176.
Lafreine RM and Yamada KM . (1996). J. Cell Biochem., 67, 543–553.
Levy Y, Ronen D, Bershadsky AD and Zick Y . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 14533–14542.
Lin TH, Aplin AE, Shen Y, Chen Q, Schaller M, Romer L, Aukhil I and Juliano RL . (1997). J. Cell Biol., 136, 1385–1395.
Liu W, Ernst JD and Broaddus VC . (2000). Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 23, 371–378.
Mossman BT, Bignon J, Corn M, Seaton A and Bowden DH . (1990). Science, 247, 294–301.
Mossman BT and Churg A . (1998). Am. J. Crit. Care Med., 157, 1666–1680.
Mossman BT, Faux S, Janssen Y, Jimenez LA, Timblin C, Zanella C, Goldberg J, Walsh E, Barchowsky A and Driscoll K . (1997). Environ. Health Perspect., 105 (Suppl 5), 1121–1125.
Persad S, Attwell S, Gray V, Delcomme M, Troussard A, Sanghera J and Dedhar S . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 27462–27469.
Pierschbacher MD and Ruoslahti E . (1984). Nature, 309, 30–33.
Roller M, Pott F, Kamino K, Althoff GH and Bellmann B . (1996). Exp. Toxicol. Pathol., 48, 3–12.
Ruoslahti E and Pierschbacher MD . (1987). Science, 238, 491–497.
Sandhu H, Dehnen W, Roller M, Abel J and Unfried K . (2000a). Carcinogenesis, 21, 1023–1029.
Sandhu H, Olbrück H, Abel J and Unfried K . (2000b). Inhal. Toxicol., 12 (Suppl 3), 337–343.
Schwartz MA and Baron V . (1999). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 11, 197–202.
Sieg DJ, Ilic D, Jones KC, Damsky CH, Hunter T and Schlaepfer DD . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 5933–5947.
Unfried K, Sandhu H, Schürkes C, Albrecht C and Abel J . (2000). Inhal. Toxicol., 12 (Suppl 3), 149–155.
Wary KK, Mainiero F, Isakoff SJ, Marcantoni EE and Giancotti FG . (1996). Cell, 87, 733–743.
Ye J, Zeidler P, Young SH, Martinez A, Robinson VA, Jones W, Baron P, Shi X and Castranova V . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 5360–5367.
Zanella CL, Posada J, Tritton TR and Mossman BT . (1996). Cancer Res., 56, 5334–5338.
Zanella CL, Timblin CR, Cummins A, Jung M, Goldberg J, Raabe R, Tritton TR and Mossman BT . (1999). Am. J. Physiol., 277, 684–693.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant UN 110/1–1 from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berken, A., Abel, J. & Unfried, K. ß1-Integrin mediates asbestos-induced phosphorylation of AKT and ERK1/2 in a rat pleural mesothelial cell line. Oncogene 22, 8524–8528 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207195
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207195