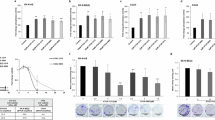
Abstract
Amplification of the MYCN oncogene contributes to the malignant progression of human neuroblastomas, but the mechanisms have remained unclear. We have previously demonstrated that N-Myc facilitates angiogenesis by downregulating an angiogenesis inhibitor identified as the inhibin βA homodimer activin A. Here, we have sought to define the molecular, biological and clinical consequences of activin A expression in human neuroblastoma. We report that enhanced activin A expression suppresses proliferation and colony formation of human neuroblastoma cells with amplified MYCN in vitro; that it inhibits neuroblastoma growth and angiogenesis in vivo; that it is highly expressed in differentiated, but not undifferentiated human neuroblastomas; and that it correlates with favourable outcome of neuroblastoma patients. Our results indicate that high activin A expression plays an important beneficial role in human neuroblastoma.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- du:
-
density units
- EFS:
-
cumulative event-free survival rate after 5 years
- GAPDH:
-
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IGF:
-
insulin-like growth factor
- INHBA:
-
inhibin βA
- NB:
-
neuroblastoma
- TGF:
-
transforming growth factor
- TrkA/B:
-
tyrosine receptor kinase A or B, respectively
- VIP:
-
vasoactive intestinal peptide
References
Altaba ARI and Melton DA . (1989). Nature, 341, 33–38.
Andreasson K and Worley PF . (1995). Neuroscience, 69, 781–796.
Breit S, Ashman K, Wilting J, Rössler J, Hatzi E, Fotsis T and Schweigerer L . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 4596–4601.
Brodeur GM . (2003). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 3, 203–216.
Brodeur GM, Pritchard J, Berthold F, Carlsen NLT, Castel V, Castleberry RP, De Bernardi B, Evans AE, Favrot M, Hedborg F, Kaneko M, Kemshead J, Lampert F, Lee REJ, Look AT, Pearson ADJ, Philip T, Roald B, Sawada T, Seeger RC, Tsuchida Y and Voute PA . (1993). J. Clin. Oncol., 11, 1466–1477.
Cantero R, Torres AJ, Maestro M, Fernandez C, Hernando F, del Barco V, Sanz T and Balibrea JL . (1999). World J. Surg., 23, 1294–1299; discussion 1299–1300.
Chen YG, Lui HM, Lin SL, Lee JM and Ying SY . (2002). Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood), 227, 75–87.
Chomczynski P . (1993). Biotechniques, 15, 532–534, 536–537.
Cinatl Jr J, Kotchetkov R, Blaheta R, Driever PH, Vogel JU and Cinatl J . (2002). Int. J. Oncol., 20, 97–106.
Fotsis T, Breit S, Lutz W, Rössler J, Hatzi E, Schwab M and Schweigerer L . (1999). Eur. J. Biochem., 263, 757–764.
Fotsis T, Pepper MS, Aktas E, Breit S, Rasku S, Adlercreutz H, Wähälä K, Montesano R and Schweigerer L . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 2916–2921.
Giusti AF, Hinman VF, Degnan SM, Degnan BM and Morse DE . (2000). Evol. Dev., 2, 294–302.
Hermanson O, Sugihara TM and Andersen B . (1999). Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand), 45, 677–686.
Hübner G and Werner S . (1996). Exp. Cell. Res., 228, 106–113.
Iwahori Y, Saito H, Torii K and Nishiyama N . (1997). Brain Res., 760, 52–58.
Mather JP, Moore A and Li R-H . (1997). Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 215, 209–222.
Rössler J, Breit S, Havers W and Schweigerer L . (1999). Int. J. Cancer, 81, 113–117.
Schweigerer L, Breit S, Wenzel A, Tsunamoto K, Ludwig R and Schwab M . (1990). Cancer Res., 50, 4411–4416.
Schweigerer L, Neufeld G, Friedman J, Abraham JA, Fiddes JC and Gospodarowicz D . (1987). Nature, 325, 257–259.
Tuuri T, Erämaa M, Van Schaik RHN and Ritvos O . (1996). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 121, 1–10.
Visvader JE, Venter D, Hahm K, Santamaria M, Sum EY, O'Reilly L, White D, Williams R, Armes J and Lindeman GJ . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 14452–14457.
Wai DH, Schaefer KL, Schramm A, Korsching E, Van Valen F, Ozaki T, Boecker W, Schweigerer L, Dockhorn-Dworniczak B and Poremba C . (2002). Int. J. Oncol., 20, 441–451.
Westermann F and Schwab M . (2002). Cancer Lett., 184, 127–147.
Woodruff TK, Sluss P, Wang E, Janssen I and Mersol-Barg MS . (1997). J. Endocrinol., 152, 167–174.
Wu DD, Lai M, Hughes PE, Sirimanne E, Gluckman PD and Williams CE . (1999). Brain Res., 835, 369–378.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Wilhelm-Sander-Stiftung to LS. We thank Professor Theodore Fotsis for sharing unpublished data, Ruth Frenk and Stefanie Paschen for excellent technical assistance and Drs Stephen Breit, Ludger Klein-Hitpaß, and Daniel Wai for help with transfection studies or sharing their knowledge on microarray analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schramm, A., Schuetz, V., Christiansen, H. et al. High activin A-expression in human neuroblastoma: suppression of malignant potential and correlation with favourable clinical outcome. Oncogene 24, 680–687 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208087
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208087
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Activin A Is Anti-Lymphangiogenic in a Melanoma Mouse Model
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2015)
-
Exon-level expression analyses identify MYCN and NTRK1 as major determinants of alternative exon usage and robustly predict primary neuroblastoma outcome
British Journal of Cancer (2012)
-
Activin A inhibits vascular endothelial cell growth and suppresses tumour angiogenesis in gastric cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2011)
-
Chemoresistance acquisition induces a global shift of expression of aniogenesis-associated genes and increased pro-angogenic activity in neuroblastoma cells
Molecular Cancer (2009)
-
Distinct morphological and immunohistochemical features and different growth rates among four human neuroblastomas heterotransplanted into nude mice
Medical Molecular Morphology (2008)