Abstract
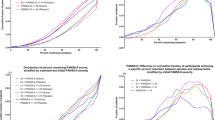
This double-blind, randomized, multicenter study investigated the use of divalproex with an antipsychotic agent in patients hospitalized for acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Patients (n=249) who met DSM-IV criteria for schizophrenia were randomly assigned to receive olanzapine monotherapy, risperidone monotherapy, divalproex plus olanzapine, or divalproex plus risperidone for 28 days. Divalproex was initiated at 15 mg/kg/day and titrated over 12 days to a maximum dosage of 30 mg/kg/day. Olanzapine and risperidone, were, respectively, initiated at 5 and 2 mg/day and were titrated over the first 6 days to respective target fixed daily dosages of 15 and 6 mg/day. Improvements from baseline were observed at all evaluation points throughout the 28-day treatment period in the two combination therapy and the two antipsychotic monotherapy groups, with statistically significant treatment differences favoring combination therapy as soon as day 3 for Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score, derived Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRSd) total score, as well as PANSS and BPRSd subscales. These findings were confirmed in post hoc repeated-measures analyses of variance in which treatment differences favoring combination therapy were observed for PANSS total (p=0.020) and PANSS positive scale scores (p=0.002). Both combination therapy and antipsychotic monotherapy were well tolerated. Treatment with divalproex in combination with an atypical antipsychotic agent resulted in earlier improvements in a range of psychotic symptoms among acutely hospitalized patients with schizophrenia. Further evaluation is warranted to confirm these findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Barnes TRE (1989). A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry 154: 672–676.
Benes FM, Berretta S (2001). GABAergic interneurons: Implications for understanding schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 25: 1–27.
Calandre EP, Rodriguez-Lopez C, Blazquez A, Cano D (1991). Serum lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins A and B in epileptic patients treated with valproic acid, carbamazepine, or Phenobarbital. Acta Neurol Scand 83: 250–253.
Chong S-A, Tan C-H, Lee -L, Liow P-H (1998). Augmentation of risperidone with valproic acid [letter]. J Clin Psychiatry 59: 430.
Citrome L, Levine J, Allingham B (2000). Changes in use of valproate and other mood stabilizers for patients with schizophrenia from 1994 to 1998. Psychiatr Serv 51: 634–638.
Conley RR, Mahmoud R (2001). A randomized double-blind study of risperidone and olanzapine in the treatment of schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Am J Psychiatry 158: 765–774.
Dose M, Hellweg R, Yassouridis A, Theison M, Emrich HM (1998). Combined treatment of schizophrenic psychoses with haloperidol and valproate. Pharmacopsychiatry 31: 122–125.
Edgell ET, Andersen SW, Johnstone BM, Dulisse B, Revicki D, Breier A (2000). Olanzapine versus risperidone. A prospective comparison of clinical and economic outcomes in schizophrenia. Pharmacoeconomics 18: 567–579.
Egan MF, Hyde TM (1999). Schizophrenia: neurobiology. Kaplan & Sadock's Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry. Lippincott Williams&Wilkins: Philadelphia.
Eiris JM, Lojo S, Del Rio MC, Novo I, Bravo M, Pavon P (1995). Effects of long-term treatment with antiepileptic drugs on serum lipid levels in children with epilepsy. Neurology 45: 1155–1157.
Ecli Lilly and Company (2000). Zyprexa®(Olanzapine) Prescribing Information. Eli Lilly: Indianapolis, IN.
Facciola G, Avenoso A, Scordo MG, Madia AG, Ventimiglia A, Perucca E (1999). Small effects of valproic acid on the plasma concentrations of clozapine and its major metabolites in patients with schizophrenia or affective disorders. Ther Drug Monit 21: 341–345.
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (1999). Research Version of the Structured Clinical Interview (SCID) for DSM-IV Axis 1 Disorders, Modified for Abbott Protocol M99-010. New York State Psychiatric Institute: New York.
Franzoni E, Govoni M, D'Addato S, Gualandi S, Sangiorgi Z, Descovich GC (1992). Total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides in children receiving antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia 33: 932–935.
Garbutt JC, van Kammen DP (1983). The interaction between GABA and dopamine: Implications for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 9: 336–353.
Gidal B, Spencer N, Maly M, Pitterle M, Williams E, Collins M (1994). Valproate-mediated disturbances of hemostasis: Relationship to dose and plasma concentration. Neurology 44: 1418–1422.
Goden Y, Heiner L, Mark J (1969). Effects of di-n-propylacetate, an anticonvulsant compound, on GABA metabolism. J Neurochem 16: 69–73.
Gundurewa VM, Beckman H, Zimmer R, Ruther E (1980). Effect of valproic acid on schizophrenic syndromes. Arzneimittelforschung 30: 1212–1213.
Guy W (1976). ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology, publication no. ADM 76-336. US Department of Health, Education and Welfare: Rockville, MD.
Heldenberg D, Harel S, Holtzman M, Levtow O, Tamir I (1983). The effect of chronic anticonvulsant therapy on serum lipids and lipoproteins in epileptic children. Neurology 33: 510–513.
Hessinger B, Normann C, Langosch JM, Klose P, Berger M, Walden J (1999). Effects of carbamazepine and valproate on haloperidol plasma levels and on psychopathologic outcome in schizophrenic patients. J Clin Psychopharmacol 19: 310–315.
Horie S, Suga T (1985). Enhancement of peroxisomal beta-oxidation in the liver of rats and mice treated with valproic acid. Biochem Pharmacol 34: 1357–1362.
Janssen Pharmaceuticals (1999). Risperdal®(Risperidone) Prescribing Information. Jansen Pharmaceutical: Titusville, NJ.
Kasper S, Jones M, Duchesne IRODOS Investigator Group (2001). Risperidone Olanzapine Drug Outcomes Studies in Schizophrenia (RODOS)* Health economic results of an international naturalistic study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 16: 189–196.
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987). The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13: 261–276.
Ko GN, Korpi ER, Freed WJ, Zalcman SJ, Bigelow LB (1985). Effect of valproic acid on behavior and plasma amino acid concentrations in chronic schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 20: 209–215.
Meltzer HY, Dai J, Ichikawa J (2001). Valproic acid, an anticonvulsant, mood stabilizer, potentiates antipsychotic drugs-induced dopamine release in rat medial prefrontal cortex but not nucleus accumbens [abstract]. Soc Neurosci Abstr vol 27, Program no. 572.14.
Moringo A, Martin J, Gonzalez S, Mateo I (1989). Treatment of resistant schizophrenia with valproate and neuroleptic drugs. Hillside J Clin Psychiatry 11: 199–207.
Preisendorfer U, Zeise ML, Klee MR (1987). Valproate enhances inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in hippocampal neurons in vitro. Brain Res 435: 213–219.
Reynolds GP, Zhang ZJ, Beasley CL (2001). Neurochemical correlates of cortical GABAergic deficits in schizophrenia: Selective losses of calcium binding protein immunoreactivity. Brain Res Bull 55: 579–584.
Seeman P (1987). Dopamine receptors and the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Synapse 1: 133–152.
Simpson GM, Angus JW (1970). A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatrica Scand Supp 212: 11–19.
Spina E, Avenoso A, Facciola G, Salemi M, Scordo MG, Giacobello T (2000). Plasma concentrations of risperidone and 9-hydroxyrisperidone: Effect of comedication with carbamazepine or valproate. Ther Drug Monit 22: 481–485.
Tran PV, Hamilton SH, Kuntz AJ, Potvin JH, Andersen SW, Beasley Jr C (1997). Double-blind comparison of olanzapine versus risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. J Clin Psychopharmacol 17: 407–418.
Volk D, Austin M, Pierri J, Sampson A, Lewis D (2001). GABA transporter-1 mRNA in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: Decreased expression in a subset of neurons. Am J Psychiatry 158: 256–265.
Wassef AA, Dott SG, Harris A, Brown A, O'Boyle M, Meyer III WJ (1999). Critical review of GABA-ergic drugs in the treatment of schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 19: 222–232.
Wassef AA, Dott SG, Harris A, Brown A, O'Boyle M, Meyer III WJ (2000). Randomized, placebo-controlled pilot study of divalproex sodium in the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 20: 357–361.
Wassef AA, Hafiz NG, Hampton D, Molloy M (2001). Divalproex sodium augmentation of haloperidol in hospitalized patients with schizophrenia: Clinical and economic implications. J Clin Psychopharmacol 21: 21–26.
Wassef A, Watson DJ, Morrison P, Bryant S, Flack J (1989). Neuroleptic-valproic acid combination in treatment of psychotic symptoms: A three-case report. J Clin Psychopharmacol 9: 45–48.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL. We wish to thank John Kane from Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Glen Oaks, NY,and Carol Tamminga, from the University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, for their contributions to the design of this study. We would also like to thank the other members of the Depakote Psychosis Group, as follows, for their enrollment of patients and participation in this study: George W Ainslie, Coatesville VA Medical Center, Coatesville, PA; Louise M Beckett, IPS Research Company, Oklahoma City, OK; Jeffrey A Borenstein, Holliswood Hospital, Holliswood, NY; Gary K Borrell, Department of Psychiatry, University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma City, OK; Anthony Braus, Wm S Middleton Memorial VA Hospital, Madison, WI; David W Brown, Community Clinical Research, Austin, TX; John S Carman, Carman Research, Smyrna, GA; Leslie L Citrome, Nathan Kline Institute, Orangeburg, NY; Ram Gopalan, Clinical Studies–Washington, Falls Church, VA; Mark B Hamner, Ralph H Johnson VA Medical Center, Charleston, SC; Richard R Jaffe, Belmont Center for Comprehensive Treatment, Philadelphia, PA; Mary Ann Knesevich, St. Paul Medical Center at Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; Michael D Lesem, Claghorn –Lesem Research Clinic, Bellaire, TX; Jean-Pierre Lindenmayer, Manhattan Psychiatric Center, New York, NY; Robert E Litman, Center for Behavioral Health, Rockville, MD; HE Logue, Birmingham Psychiatry Pharmaceutical Studies, Birmingham, AL; Charles H Merideth, Affiliated Research Institute, San Diego, CA; Alexander L Miller, San Antonio State Hospital, San Antonio, TX; Steven G Potkin, UC-Irvine Medical Center, Orange, CA; Robert A Riesenberg, Atlanta Center for Medical Research, Atlanta, GA; Murray H Rosenthal, Behavioral and Medicine Research, San Diego, CA; Alan L Schneider, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA; Rajiv P Sharma, Psychiatric Institute, Chicago, IL; Samuel D Shillcutt, Central State Hospital, Milledgeville, GA; Andre Tapp, VA Riget, Sound Health Care System, Tacoma, WA; Marshall R Thomas, Colorado Psychiatric Hospital, Denver, CO; Tram K Tran-Johnson, CNRI, San Diego, CA; Richard H Weisler, Raleigh, NC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casey, D., Daniel, D., Wassef, A. et al. Effect of Divalproex Combined with Olanzapine or Risperidone in Patients with an Acute Exacerbation of Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol 28, 182–192 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300023
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300023