Abstract
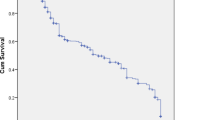
The purported advantages of second-generation or ‘atypical’ antipsychotics relative to first-generation antipsychotics have not been examined in patients with a first episode of schizophrenia. This flexible-dose study examined efficacy and safety in a randomized, double-blind, 52-week trial, comparing chlorpromazine (CPZ) and clozapine (CLZ) in treatment naive patients experiencing their first episode of schizophrenia. In all, 160 inpatients with first-episode schizophrenia or schizophreniform disorder were randomized to CPZ or CLZ and followed them for 52 weeks or until dropout. The primary efficacy measure was time to first remission and proportion of time remaining in remission. The analysis was supplemented by comparisons on a profile of clinical symptoms and side effects. Of these first-episode patients, 80% achieved remission within 1 year (79% CPZ, 81% CLZ). The Kaplan–Meier estimated median time to first remission was 8 weeks for CLZ vs 12 weeks for CPZ (χ2(1)=5.56, p=0.02). Both the rate of first achieving remission and the odds for being in remission during the trial were almost doubled for the CLZ group in comparison with the CPZ group. At 12 weeks, CLZ was superior on many rating scale measures of symptom severity while CPZ was not superior on any. These symptom differences remained significant when controlling for EPS differences. By 52 weeks many of the symptom differences between groups were no longer significantly different. Generally, CLZ produced fewer side effects than CPZ, particularly extrapyramidal side effects. There was no significant difference between treatments in weight change or glucose metabolism. For each prior year of untreated psychosis, there was a 15% decrease in the odds of achieving remission (OR=0.85; CI 0.75–0.95). A high proportion of first-episode patients remitted within 1 year. We detected no difference in the proportion of first-episode patients receiving CLZ or CPZ that achieved remission. However, first-episode patients receiving CLZ remitted significantly faster and remained in remission longer than subjects receiving CPZ. While the CLZ group showed significantly less symptomatology on some measures and fewer side effects at 12 weeks, the two treatment groups seemed to converge by 1 year. Longer duration of untreated psychosis was associated with lower odds of achieving remission.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Allison DB, Mentore JL, Heo M, Chandler LP, Cappelleri JC, Infante MC et al (1999). Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a comprehensive research synthesis. Am J Psychiatry 156: 1686–1696.
Barnes TR, Hutton SB, Chapman MJ, Mutsatsa S, Puri BK, Joyce EM (2000). West London first-episode study of schizophrenia: clinical correlates of duration of untreated psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 177: 207–211.
Beng-Choon H, Andreassen NC, Flaum M, Nopoulos P, Miller D (2000). Untreated initial psychosis: its relation to quality of life and symptom remission in first episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 157: 808–815.
Chakos MH, Alvir JMJ, Woerner MG, Koreen A, Geisler S, Mayerhoff D et al (1996). Incidence and correlates of tardive dyskinesia in first episode of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53: 313–319.
Chakos M, Lieberman JA, Hoffman E, Bradford D, Sheitman B (2001). Effectiveness of second-generation antipsychotics in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Am J Psychiatry 158: 518–526.
Chatterjee A, Chakos M, Koreen A, Geisler S, Sheitman B, Alvir J et al (1995). Prevalence and clinical correlates of extrapyramidal signs and spontaneous dyskinesias in never medicated schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 152: 1724–1729.
Craig TJ, Bromet EJ, Fennig S, Tanenberg-Karant M, Lavelle J, Galambos N (2000). Is there an association between duration of untreated psychosis and 24 month clinical outcome in a first admission series? Am J Psychiatry 157: 60–66.
Crow TJ, MacMillan JF, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC (1986). A randomized controlled trial of prophylactic neuroleptic treatment. Br J Psychiatry 148: 120–127.
Emsley RA (1999). Risperidone in the treatment of first-episode psychotic patients: a double-blind multicenter study. Schizophr Bull 25: 721–729.
Geddes J, Freemantle N, Bebbington P (2000). Atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia: systematic overview and meta-regression analysis. Br Med J 321: 1360–1361.
Hegarty JD, Baldessarini RJ, Tohen M, Waternaux C, Oepen G (1994). One hundred years of schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of the outcome literature. Am J Psychiatry 151: 1409–1416.
Henderson DC, Cagliero E, Gray C, Nasrallah RA, Hayden DL, Schoenfeld DA et al (2000). Clozapine, diabetes mellitus, weight gain and lipid abnormalities: a five year naturalistic study. Am J Psychiatry 157: 975–981.
Herz MI, Liberman RP, Lieberman JA, Marder SR, McGlashan TH, Wyatt RJ et al (1997). Practice guidelines for the treatment of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 154(Suppl): 4.
Johannesen JO, McGlashan TH, Larsen TK, Horneland M, Joa I, Mardal S et al (2001). Early detection strategies for untreated first-episode psychosis. Schizophr Res 51: 39–46.
Kinon BJ, Lieberman JA (1996). Mechanisms of action of atypical antipsychotic drugs: a critical analysis. Psychopharmacology 124: 2–34.
Kraeplin E (1919). Dementia Praecox and Paraphrenia. E&S Livingstone: Edinburgh, Scotland.
Leucht S, Pitschel-Walz G, Abraham D, Kissling W (1999). Efficacy and extrapyramidal side-effects of the new antipsychotics olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and sertindole compared to conventional antipsychotics and placebo. Schizophr Res 35: 51–68.
Lieberman J, Jody D, Geisler S, Alvir J, Loebel A, Szymanski S et al (1993). Time course and biologic correlates of treatment response in first-episode schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50: 369–376.
Lieberman JA (1996). Atypical antipsychotic drugs as a first-line treatment of schizophrenia: a rationale and hypothesis. J Clin Psychiatry 57(Suppl 11): 68–71.
Lieberman JA, Sheitman B, Chakos M, Robinson D, Schooler N, Keith S (1998). The development of treatment resistance in patients with schizophrenia: a clinical and pathophysiological perspective. J Clin Psychopharmacol 18: S20–S24.
Loebel AD, Lieberman JA, Alvir JMJ, Mayerhoff DI, Geisler SH, Szymanski SR (1992). Duration of psychosis and outcome in first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 149: 1183–1188.
McEvoy JP, Hogarty GE, Steingard S (1991). Optimal dose of neuroleptic in acute schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48: 739–745.
McGlashan TH (1988). A selective review of recent North American long-term follow-up studies of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 14: 515–542.
Norman RM, Malla AK (2001). Duration of untreated psychosis: a critical examination of the concept and its importance. Psychol Med 31: 381–400.
Phillips M (2001). Characteristics, experience and treatment of schizophrenia in China. Dialog Clin Neurosci 3: 109–119.
Phillips MR, Xiong W, Wang RW, Gao RH, Wang XQ, Zhang NP (1991). Reliability and validity of the Chinese versions of the scales for assessment of positive and negative symptoms. Acta Psychiatr Scand 84: 364–370.
Phillips MR, Xiong W, Zhao ZA (1990). Issues Involved in the Use of Scales for the Assessment of Negative and Positive Symptoms in Psychotic Patients. Hubei Science and Technology Publishing House: Wuhan, PRC (in Chinese).
Robinson D, Woerner M, Alvir J, Bilder R, Goldman R, Geisler S et al (1999). Predictors of treatment response from a first episode of schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Am J Psychiatry 156: 544–549.
Sanger TM, Lieberman JA, Tohen M, Grundy S, Beasley C, Tollefson GD (1999). Olanzapine versus haloperidol treatment in first-episode psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 156: 79–87.
Sheitman BB, Lee H, Strous R, Lieberman JA (1997). The evaluation and treatment of first episode psychoses. Schizophr Bull 23: 653–661.
Szymanski SR, Cannon TD, Gallacher F, Erwin RJ, Gur RE (1996). Course and treatment response in first-episode and chronic schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 153: 519–525.
Wu B, Wu JP (1995). Investigation of antipsychotic use in hospitalized patients. Appl Psychiatry 2: 19–22 (in Chinese).
Wyatt RJ (1999). Early intervention with neuroleptcis may decrease the long-term morbidity of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 5: 201–202.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the assistance of the following staff members at Beijing Hui Long Guan Hospital in carrying out this project: (alphabetically listed) Peiran Guo, Feifei Li, Guowang Li (Deceased), Huaqing Li, Lanying Li, Xianyun Li, Mei Meng, Yajuan Niu, Lan Shang, Jiancheng Song, Deliang Yan, Fude Yang, Xiuqin Zhao, and Fengyan Zhu. The investigators appreciate the support and encouragement of Drs Peter Jager, Rajinder Judge, Jeffrey Schwimmer, and Rene Speigel of Novartis in the development and implementation of the study. This work was supported by USPHS grants MH00537, MH33127 (Dr Lieberman), the UNC Mental Health and Neuroscience Clinical Research Center, and the Novartis Pharmaceutical Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lieberman, J., Phillips, M., Gu, H. et al. Atypical and Conventional Antipsychotic Drugs in Treatment-Naive First-Episode Schizophrenia: A 52-Week Randomized Trial of Clozapine Vs Chlorpromazine. Neuropsychopharmacol 28, 995–1003 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300157
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300157
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Heterogeneity in treatment outcomes and incomplete recovery in first episode psychosis: does one size fit all?
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
The association between BDNF levels and risperidone-induced weight gain is dependent on the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in antipsychotic-naive first episode schizophrenia patients: a 12-week prospective study
Translational Psychiatry (2021)
-
Genetic polymorphisms of BDNF on cognitive functions in drug-naive first episode patients with schizophrenia
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Diagnostik und Intervention bei ersten psychotischen Episoden
InFo Neurologie + Psychiatrie (2021)
-
Heterogeneity and efficacy of antipsychotic treatment for schizophrenia with or without treatment resistance: a meta-analysis
Neuropsychopharmacology (2020)