Abstract
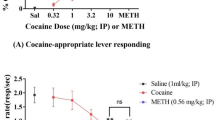
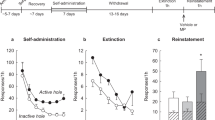
The 5-HT indirect agonist, d-fenfluramine, attenuates cue reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-seeking behavior. To investigate the role of 5-HT receptor subtypes in this effect, we examined whether the attenuation is reversed by either a 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A/C, or 5-HT2C receptor antagonist. We also examined the effects of the antagonists alone on both cue and cocaine-primed reinstatement. Rats that had been trained to press a lever for cocaine (0.75 mg/kg/0.1 ml, i.v.) paired with light and tone cues underwent daily extinction sessions during which responding had no consequences. We then examined the effects of WAY 100635 (0–1.0 mg/kg, s.c.), ketanserin (0–10.0 mg/kg, i.p.), or SB 242,084 (0–1.0 mg/kg, i.p.) with and without d-fenfluramine (1.0 mg/kg, i.p.) pretreatment on cue reinstatement. Subsequently, we examined the effects of the antagonists on cocaine-primed (7.5 or 15.0 mg/kg, i.p.) reinstatement. The 5-HT1A antagonist, WAY 100635, failed to alter cue reinstatement, but attenuated cocaine reinstatement. Conversely, the 5-HT2A/C antagonist, ketanserin, attenuated cue reinstatement, but failed to alter cocaine reinstatement. The 5-HT2C-selective antagonist, SB 242,084, did not alter cue or cocaine reinstatement, but was the only drug that reversed the d-fenfluramine-induced attenuation of cue reinstatement. The findings suggest that stimulation of 5-HT1A receptors plays a critical role in cocaine-primed, but not cue, reinstatement. Furthermore, 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors may play oppositional roles in cue reinstatement. The SB 242,084 reversal of the d-fenfluramine attenuation suggests that stimulation of 5-HT2C receptors inhibits cue reinstatement, whereas the ketanserin-induced attenuation of cue reinstatement suggests that decreased stimulation of 5-HT2A receptors inhibits this behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Alleweireldt AT, Weber SM, Kirschner KF, Bullock BL, Neisewander JL (2002). Blockade or stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors attenuates cue reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 159: 285–293.
Baker DA, Tran-Nguyen LTL, Fuchs RA, Neisewander JL (2001). Influence of individual differences and chronic fluoxetine treatment on cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 155: 18–26.
Baxter G, Kennett G, Blaney F, Blackburn T (1995). 5-HT2 receptor subtypes: a family re-united? Trend Pharmacol Sci 16: 105–110.
Burmeister JJ, Lungren EM, Neisewander JL (2003). Effects of fluoxetine and d-fenfluramine on cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 168: 146–154.
Cao BJ, Rodgers RJ (1997). Influence of 5-HT1A receptor antagonism on plus-maze behaviour in mice. II. WAY 100635, SDZ 216-525 and NAN-190. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 58: 593–603.
Carey RJ, DePalma G, Damianopoulos E (2001). Cocaine and serotonin: a role for the 5-HT1A receptor site in the mediation of cocaine stimulant effects. Behav Brain Res 126: 127–133.
Carroll ME, France CP, Meisch RA (1981). Intravenous self-administration of etonitazene, cocaine and phencyclidine in rats during food deprivation and satiation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 217: 241–247.
Cervo L, Carnovali F, Stark JA, Mennini T (2003). Cocaine-seeking behavior in response to drug-associated stimuli in rats: involvement of D3 and D2 dopamine receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 28: 1150–1159.
Curzon G, Gibson EL, Oluyomi AO (1997). Appetite suppression by commonly used drugs depends on 5-HT receptors but not on 5-HT availability. Trend Pharmacol Sci 18: 21–25.
De La Garza II R, Callahan Pm, Cunningham KA (1998). The discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine, a 5-HT1A agonist or antagonist, into the ventral tegmental area. Psychopharma-cology 137: 1–6.
de Wit H, Stewart J (1981). Reinstatement of cocaine-reinforced responding in the rat. Psychopharmacology 75: 134–143.
Di Giovanni G, De Deurwaerdere P, Di Mascio M, Di Matteo V, Esposito E, Spampinato U (1999). Selective blockade of serotonin-2C/2B receptors enhances mesolimbic and mesostriatal dopaminergic function: a combined in vivo electrophysiology and microdialysis study. Neuroscience 91: 587–597.
Di Matteo V, Di Mascio M, Di Giovanni G, Esposito E (1999). SB 242 084, a selective serotonin2C receptor antagonist, increases dopaminergic transmission in the mesolimbic system. Neuropharmacology 38: 1195–1205.
Di Matteo V, Di Mascio M, Di Giovanni G, Esposito E (2000a). Acute administration of amitriptyline and mianserin increases dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens: possible involvement of serotonin2C receptors. Psychopharmacology 150: 45–51.
Di Matteo V, Di Mascio M, Di Giovanni G, Esposito E (2000b). Biochemical and electrophysiological evidence that RO 60-0175 inhibits mesolimbic dopaminergic function through serotonin2C receptors. Brain Res 865: 85–90.
Ehrman RN, Robbins SJ, Childress AR, O'Brien CP (1992). Conditioned responses to cocaine-related stimuli in cocaine abuse patients. Psychopharmacology 107: 523–529.
Fletcher PJ (1995). Effects of d-fenfluramine and metergoline on responding for conditioned reward and the response potentiating effect of nucleus accumbens d-amphetamine. Psychopharmacology 118: 155–163.
Fletcher PJ, Grottick AJ, Higgins GA (2002a). Differential effects of the 5-HT2A receptor antagonist M100,907 and the 5-HT2C receptor antagonist SB242,084 on cocaine-induced locomotor activity, cocaine self-administration and cocaine-induced reinstatement of responding. Neuropsychopharmacology 27: 576–586.
Fletcher PJ, Korth KM, Robinson SR, Baker GB (2002b). Multiple 5-HT receptors are involved in the effects of acute MDMA treatment: studies on locomotor activity and responding for conditioned reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 162: 282–291.
Fuchs RA, Tran-Nguyen LTL, Specio SE, Groff RS, Neisewander JL (1998). Predictive validity of the extinction/reinstatement model of drug craving. Psychopharmacology 135: 151–160.
Griebel G, Rodgers RJ, Perrault G, Sanger DJ (2000). The effects of compounds varying in selectivity as 5-HT1A receptor antagonists in three rat models of anxiety. Neuropharmacology 39: 1848–1857.
Grottick AJ, Fletcher PJ, Higgins GA (2000). Studies to investigate the role of 5-HT2C receptors on cocaine- and food-maintained behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295: 1183–1191.
Higgins GA, Ouagazzal AM, Grottick AJ (2001). Influence of the 5-HT2C receptor antagonist SB 242,084 on behaviour produced by the 5-HT2 agonist Ro 60-0175 and the indirect 5-HT agonist dexfenfluramine. Br J Pharmacol 133: 459–466.
Israilova M, Suzuki F, Tanaka T, Nagatomo T, Taniguchi T, Muramatsu I (2002). Binding and functional affinity of sarpogrelate, its metabolite m-1 and ketanserin for human recombinant alpha-1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Pharmacology 65: 69–73.
Jaffe JH, Cascella NG, Kumor KM, Sherer MA (1989). Cocaine-induced cocaine craving. Psychopharmacology 97: 59–64.
Khroyan TV, Barrett-Larimore RL, Rowlett JK, Apealman RD (2000). Dopamine D1- and D1-like receptor mechanisms in relapse to cocaine-seeking behavior: effects of selective antagonists and agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294: 680–687.
Leferrere B, Wurtman RJ (1989). Effect of D-fenfluramine on serotonin release in brains of anaesthetized rats. Brain Res 504: 258–263.
Markou A, Weiss F, Gold LH, Caine SB, Schulteis G, Koob GF (1993). Animal models of drug craving. Psychopharmacology 112: 163–182.
McMahon LR, Cunningham KA (2001a). Role of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B/2C receptors in the behavioral interactions between serotonin and catecholamine reuptake inhibitors. Neuropsychopharmacology 24: 319–329.
McMahon LR, Cunningham KA (2001b). Antagonism of 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptors attenuates the behavioral effects of cocaine in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297: 357–363.
McMahon LR, Filip M, Cunningham KA (2001). Differential regulation of the mesoaccumbens circuit by serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. J Neurosci 21: 7781–7787.
Muller CP, Carey RJ, De Souza Silva MA, Jocham G, Huston JP (2002a). Cocaine increases serotonergic activity in hippocampus and nucleus accumbens in vivo: 5-HT1A-receptor antagonism blocks behavioral but potentiates sertonergic activation. Synapse 45: 67–77.
Muller CP, De Souza Silva MA, DePalma G, Tomaz C, Carey RJ, Huston JP (2002b). The selective serotonin(1A)-receptor antagonist WAY 100635 blocks behavioral stimulating effects of cocaine but not ventral striatal dopamine increase. Behav Brain Res 134: 337–346.
Munzar P, Justinova Z, Kutkat SW, Goldberg SR (2002). Differential involvement of 5-HT2A receptors in the discriminative-stimulus effects of cocaine and methamphetamine. Eur J Pharmacol 436: 75–82.
Neisewander JL, Baker DA, Fuchs RA, Tran-Nguyen LTL, Palmer A, Marshall JF (2000). Fos protein expression and cocaine-seeking behavior in rats after exposure to a cocaine self-administration environment. J Neurosci 20: 798–805.
Przegalinski E, Filip M (1997). Stimulation of serotonin (5-HT)1A receptors attenuates the locomotor, but not the discriminative, effects of amphetamine and cocaine in rats. Behav Pharmacol 8: 699–706.
Robbins TW, Watson BA, Gaskin M, Ennis C (1983). Contrasting interactions of pipradrol, d-amphetamine, cocaine, cocaine analogues, apomorphine and other drugs with conditioned reinforcement. Psychopharmacology 80: 113–119.
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993). The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Rev 18: 247–291.
Rohsenow DJ, Childress AR, Monti PM, Niaura RS, Abrams DB (1991). Cue reactivity in addictive behaviors: theoretical and treatment implication. Int J Addict 25: 957–993.
Rothman RB, Baumann MH (2002). Serotonin releasing agents: neurochemical, therapeutic and adverse effects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71: 825–836.
Rothman RB, Bauman MH, Dersch CM, Romero DV, Rice KC, Carroll FI et al (2001). Amphetamine-type central nervous system stimulants release norepinephrine more potently than they release dopamine and serotonin. Synapse 39: 32–41.
Rowland NE, Carlton J (1986). Neurobiology of an anorectic drug: fenfluramine. Prog Neurobiol 27: 13–62.
Schenk S (2000). Effects of the serotonin 5-HT2 antagonist, ritanserin, and the serotonin 5-HT1A antagonist, WAY 100635, on cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67: 363–369.
Stewart J (1983). Conditioned and unconditioned drug effects in relapse to opiate and stimulant drug self-administration. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 7: 591–597.
Tran-Nguyen LTL, Baker DA, Grote KA, Solano J, Neisewander JL (1999). Serotonin depletion attenuates cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 146: 60–66.
Tran-Nguyen LTL, Bellew JG, Grote KA, Neisewander JL (2001). Serotonin depletion attenuates cocaine seeking but enhances sucrose seeking and the effects of cocaine priming on reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 157: 340–348.
Wallace BC (1989). Psychological and environmental determinants of relapse in crack cocaine smokers. J Subst Abuse Treat 6: 95–106.
Weissenborn R, Deroche V, Koob GF, Weiss F (1996). Effects of dopamine agonists and antagonists on cocaine-induced operant responding for a cocaine-associated stimulus. Psychopharma-cology 126: 311–322.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Arturo Zavala, Adam Taylor, and Dr Brock Schroeder for their expert technical assistance, and Arturo Zavala and Andrea Alleweireldt for their comments on a previous version of this manuscript. This research was supported by a grant from NIDA, DA11064, and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute through the Undergraduate Biology Enrichment Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burmeister, J., Lungren, E., Kirschner, K. et al. Differential Roles of 5-HT Receptor Subtypes in Cue and Cocaine Reinstatement of Cocaine-Seeking Behavior in Rats. Neuropsychopharmacol 29, 660–668 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300346
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300346
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Corticosterone Potentiation of Cocaine-Induced Reinstatement of Conditioned Place Preference in Mice is Mediated by Blockade of the Organic Cation Transporter 3
Neuropsychopharmacology (2017)
-
Effects of 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor agonists and antagonists on responding for a conditioned reinforcer and its enhancement by methylphenidate
Psychopharmacology (2017)
-
Attenuation of cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug seeking in squirrel monkeys by direct and indirect activation of 5-HT2C receptors
Psychopharmacology (2015)
-
The role of serotonin in memory: interactions with neurotransmitters and downstream signaling
Experimental Brain Research (2014)
-
Multiple controls exerted by 5-HT2C receptors upon basal ganglia function: from physiology to pathophysiology
Experimental Brain Research (2013)