Abstract
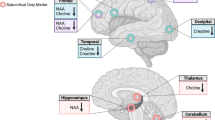
Alcoholism comorbidity is highly prevalent in individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Each condition is known to affect brain structure, function, and metabolism, but the combined effects on the brain have only recently been considered. Single-voxel, proton MR spectroscopy (MRS) has yielded sensitive measures of early brain deterioration in the progression of HIV, but has limited coverage of neocortex, whereas MRS imaging (MRSI) can simultaneously interrogate large regions of cortex. Included were 15 men with HIV+alcoholism, nine men with HIV alone, eight men with alcoholism alone (abstinent for 3–17 months), and 23 controls. The two HIV groups were matched in T-cell count and were not demented; the two alcoholism groups were relatively matched in lifetime alcohol consumption. We used MRSI with a variable-density spiral sequence to quantify major proton metabolites—N-acetylaspartate (NAA), creatine (Cr), and choline (Cho)—in the superior parietal–occipital cortex. Metabolites were expressed in absolute units and as the NAA/Cr ratio. Significant group effects were present for NAA and Cr. Only the HIV+alcoholism group was significantly affected, exhibiting a 0.8 SD deficit in NAA and a 1.0 SD deficit in Cr. The deficits were not related to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) status. Neither HIV infection nor alcoholism independently resulted in parietal–occipital cortical metabolite abnormalities, yet each disease carried a liability that put affected individuals at a heightened risk of neuronal compromise when the diseases were compounded. Further, the use of absolute measures revealed deficits in NAA and Cr that would have gone undetected if these metabolites were expressed as a ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adalsteinsson E, Langer-Gould A, Homer RJ, Rao A, Sullivan EV, Pfefferbaum A et al (2003). Gray matter NAA deficits in secondary progressive but not relapse remitting multiple sclerosis: quantification with volumetric MR spectroscopic imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 24: 1941–1945.
Adalsteinsson E, StarLack J, Meyer C, Spielman D (1999). Reduced spatial side lobes in chemical-shift imaging. Magn Reson Med 42: 314–323.
American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder (DSM-IV). American Psychiatric Association: Washington.
Bagby GJ, Stoltz DA, Zhang P, Kolls JK, Brown J, Bohm Jr RP et al (2003). The effect of chronic binge ethanol consumption on the primary stage of SIV infection in rhesus macaques. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27: 495–502.
Barker PB (2005). Fundamentals of MR spectroscopy. In: Gillard J, Waldman A, Barker P (eds). Clinical MR Neuroimaging: Diffusion, Perfusion and Spectroscopy. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge. pp 7–26.
Barker PB, Lee RR, McArthur JC (1995). AIDS dementia complex: evaluation with proton MR spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 195: 58–64.
Cerwonka ER, Isbell TR, Hansen CE (2000). Psychosocial factors as predictors of unsafe sexual practices among young adults. AIDS Educ Prev 12: 141–153.
Chang L, Ernst T, Leonido-Yee M, Witt M, Speck O, Walot I et al (1999). Highly active antiretroviral therapy reverses brain metabolite abnormalities in mild HIV dementia. Neurology 53: 782–789.
Chang L, Ernst T, Witt MD, Ames N, Gaiefsky M, Miller E (2002). Relationships among brain metabolites, cognitive function, and viral loads in antiretroviral-naive HIV patients. Neuroimage 17: 1638–1648.
Chang L, Lee PL, Yiannoutsos CT, Ernst T, Marra CM, Richards T et al (2004). A multicenter in vivo proton-MRS study of HIV-associated dementia and its relationship to age. Neuroimage 23: 1336–1347.
Ernst T (2005). Quantification and analysis in MR spectroscopy. In: Gillard J, Waldman A, Barker P (eds). Clinical MR Neuroimaging: Diffusion, Perfusion and Spectroscopy. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge. pp 27–37.
Ernst T, Chang L (2004). Effect of aging on brain metabolism in antiretroviral-naive HIV patients. AIDS 18 (Suppl 1): S61–S67.
Fein G, Bachman L, Fisher S, Davenport L (1990). Cognitive impairments in abstinent alcoholics. West J Med 152: 531–537.
Fein G, Biggins CA, MacKay S (1995). Alcohol abuse and HIV infection have additive effects on frontal cortex function as measured by auditory evoked potential P3a latency. Biol Psychiatry 37: 183–195.
Fein G, Fletcher DJ, Di Sclafani V (1998). Effect of chronic alcohol abuse on the CNS morbidity of HIV disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22: 196S–200S.
Fuller RA, Westmoreland SV, Ratai E, Greco JB, Kim JP, Lentz MR et al (2004). A prospective longitudinal in vivo 1H MR spectroscopy study of the SIV/macaque model of neuroAIDS. BMC Neurosci 5: 10.
Green JE, Saveanu RV, Bornstein RA (2004). The effect of previous alcohol abuse on cognitive function in HIV infection. Am J Psychiatry 161: 249–254.
Harrison MJ, Newman SP, Hall-Craggs MA, Fowler CJ, Miller R, Kendall BE et al (1998). Evidence of CNS impairment in HIV infection: clinical, neuropsychological, EEG, and MRI/MRS study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 65: 301–307.
Heaton RK, Grant I, Butters N, White DA, Kirson D, Atkinson JH et al (1995). The HNRC 500—neuropsychology of HIV infection at different disease stages. HIV Neurobehavioral Research Center. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 1: 231–251.
Hurd R, Sailasuta N, Srinivasan R, Vigneron DB, Pelletier D, Nelson SJ (2004). Measurement of brain glutamate using TE-averaged PRESS at 3T. Magn Reson Med 51: 435–440.
Karnofsky DA (1949). The clinical evaluation of chemotherapeutic agents in cancer. In: MacLeod CM (ed). Evaluation of Chemotherapeutic Agents. Columbia University Press: New York. pp 191–205.
Kim DH, Adalsteinsson E, Glover GH, Spielman DM (2002). Regularized higher-order in vivo shimming. Magn Reson Med 48: 715–722.
Lee PL, Yiannoutsos CT, Ernst T, Chang L, Marra CM, Jarvik JG et al (2003). A multi-center 1H MRS study of the AIDS dementia complex: validation and preliminary analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging 17: 625–633.
Lefevre F, O'Leary B, Moran M, Mossar M, Yarnold PR, Martin GJ et al (1995). Alcohol consumption among HIV-infected patients. J Gen Intern Med 10: 458–460.
Li BS, Wang H, Gonen O (2003). Metabolite ratios to assumed stable creatine level may confound the quantification of proton brain MR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging 21: 923–928.
Lim KO, Pfefferbaum A (1989). Segmentation of MR brain images into cerebrospinal fluid spaces, white and gray matter. J Comput Assist Tomogr 13: 588–593.
Mann K, Agartz I, Harper C, Shoaf S, Rawlings R, Momenan R et al (2001). Neuroimaging in alcoholism: ethanol and brain damage. Alcohol Clin Exp Res (Suppl) 25: 104–109S.
Martin PR, Gibbs SJ, Nimmerrichter AA, Riddle WR, Welch LW, Willcott MR (1995). Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies in recently abstinent alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 19: 1078–1082.
Mayer D, Kim D-H, Adalsteinsson E, Spielman DM (2004). Fast CT-PRESS based spiral CSI at 3T. Paper presented at: 12th Annual Meeting of the ISMRM (Kyoto, Japan)..
Meyerhoff DJ (2001). Effects of alcohol and HIV infection on the central nervous system. Alcohol Res Health 25: 288–298.
Meyerhoff DJ, Mackay S, Bachman L, Poole N, Dillon WP, Weiner MW et al (1993). Reduced brain N-acetylaspartate suggests neuronal loss in cognitively impaired human immunodeficiency virus seropositive individuals—in vivo H-1 magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Neurology 43: 509–515.
Meyerhoff DJ, Weiner MW, Fein G (1996). Deep gray matter structures in HIV infection: a proton MR spectroscopic study. Am J Neuroradiol 17: 973–978.
Miguez MJ, Shor-Posner G, Morales G, Rodriguez A, Burbano X (2003). HIV treatment in drug abusers: impact of alcohol use. Addict Biol 8: 33–37.
Moller HE, Vermathen P, Lentschig MG, Schuierer G, Schwarz S, Wiedermann D et al (1999a). Metabolic characterization of AIDS dementia complex by spectroscopic imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 9: 10–18.
Moller HE, Vermathen P, Lentschig MG, Schuierer G, Schwarz S, Wiedermann D et al (1999b). Metabolic characterization of AIDS dementia complex by spectroscopic imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 9: 10–18.
Nordahl TE, Salo R, Possin K, Gibson R, Flynn NM, Leamon M et al (2002). Low N-acetyl-aspartate and high choline in the anterior cingulum of recently abstinent methamphetamine dependent subjects: a proton MRS study. Psychiatry Res 116: 43–52.
O'Neill J, Cardenas VA, Meyerhoff DJ (2001a). Effects of abstinence on the brain: quantitative magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in chronic alcohol abuse. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25: 1673–1682.
O'Neill J, Cardenas VA, Meyerhoff DJ (2001b). Separate and interactive effects of cocaine and alcohol dependence on brain structures and metabolites: quantitative MRI and proton MR spectroscopic imaging. Addict Biol 6: 347–361.
Oscar-Berman M (2000). Neuropsychological vulnerabilities in chronic alcoholism. In: Noronha A, Eckardt M, Warren K (eds). Review of NIAAA's Neuroscience and Behavioral Research Portfolio, NIAAA Research Monograph No. 34, National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD. pp 437–472.
Otsu N (1979). A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet 9: 63–66.
Pfefferbaum A, Adalsteinsson E, Spielman D, Sullivan EV, Lim KO (1999a). In vivo brain concentrations of N-acetyl compounds, creatine and choline in Alzheimer's disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56: 185–192.
Pfefferbaum A, Adalsteinsson E, Spielman D, Sullivan EV, Lim KO (1999b). In vivo spectroscopic quantification of the N-acetyl moiety, creatine and choline from large volumes of gray and white matter: effects of normal aging. Magn Reson Med 41: 276–284.
Pfefferbaum A, Rosenbloom M, Sullivan E (2002). Alcoholism and AIDS: MR imaging approaches for detecting interaction neuropathology. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26: 1031–1046.
Ross B, Michaelis T (1994). Clinical applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Q 10: 191–247.
Samet JH, Horton NJ, Meli S, Freedberg KA, Palepu A (2004). Alcohol consumption and antiretroviral adherence among HIV-infected persons with alcohol problems. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28: 572–577.
Seitz D, Widmann U, Seeger U, Nagele T, Klose U, Mann K et al (1999). Localized proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the cerebellum in detoxifying alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23: 158–163.
Smith S (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17: 143–155.
Soher BJ, van Zijl PCM, Duyn JH, Barker PB (1996). Quantitative proton MR spectroscopic imaging of the human brain. Magn Reson Med 35: 356–363.
Spielman D, Pauly J, Macovski A, Enzmann D (1991). Spectroscopic imaging with multi-dimensional pulses for excitation: SIMPLE. Magn Reson Med 19: 67–84.
Stern RA, Silva SG, Chaisson N, Evans DL (1996). Influence of cognitive reserve on neuropsychological functioning in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection. Arch Neurol 53: 148–153.
Sullivan EV (2000). Human brain vulnerability to alcoholism: evidence from neuroimaging studies. In: Noronha A, Eckardt M, Warren K (eds). Review of NIAAA's Neuroscience and Behavioral Research Portfolio, NIAAA Research Monograph No. 34 National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD. pp 473–508.
Sullivan EV (2003). Compromised pontocerebellar and cerebellothalamocortical systems: speculations on their contributions to cognitive and motor impairment in nonamnesic alcoholism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27: 1409–1419.
Tracey I, Carr CA, Guimaraes AR, Worth JL, Navia BA, Gonzalez RG (1996). Brain choline-containing compounds are elevated in HIV-positive patients before the onset of AIDS dementia complex: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic study. Neurology 46: 783–788.
Viondury J, Meyerhoff DJ, Cozzone PJ, Weiner MW (1994). What might be the impact on neurology of the analysis of brain metabolism by in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy? J Neurol 241: 354–371.
von Giesen HJ, Wittsack HJ, Wenserski F, Koller H, Hefter H, Arendt G (2001). Basal ganglia metabolite abnormalities in minor motor disorders associated with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Arch Neurol 58: 1281–1286.
Wang Y, Watson RR (1995). Is alcohol consumption a cofactor in the development of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome? Alcohol 12: 105–109.
Yiannoutsos CT, Ernst T, Chang L, Lee PL, Richards T, Marra CM et al (2004). Regional patterns of brain metabolites in AIDS dementia complex. Neuroimage 23: 928–935.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the research assistants and clinicians in our laboratory for diligence and care in recruitment, scheduling, and data acquisition. Of special note are Andrea Spadoni, BA, for organizing this study as well as Jeffrey Eisen, MBA, Marya Schulte, BA, Carla Raassi, BA, Alex Jack, BA, Stephanie A Sassoon, PhD, Anne O'Reilly, PhD, Julia Buss, RN, Carol Kemper, MD, and Stanley Deresinski, MD. Support for this project came from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (AA12388, AA12999, AA05965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfefferbaum, A., Adalsteinsson, E. & Sullivan, E. Cortical NAA Deficits in HIV Infection without Dementia: Influence of Alcoholism Comorbidity. Neuropsychopharmacol 30, 1392–1399 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300723
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300723
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MR spectroscopy in HIV associated neurocognitive disorder in the era of cART: a review
AIDS Research and Therapy (2021)
-
In vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals region specific metabolic responses to SIV infection in the macaque brain
BMC Neuroscience (2009)
-
The Neuropsychology of HIV/AIDS in Older Adults
Neuropsychology Review (2009)
-
Development and Resolution of Brain Lesions Caused by Pyrithiamine- and Dietary-Induced Thiamine Deficiency and Alcohol Exposure in the Alcohol-Preferring Rat: A Longitudinal Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy Study
Neuropsychopharmacology (2007)