Abstract
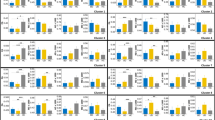
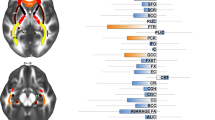
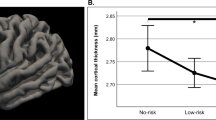
This article reports on preliminary findings describing microstructural abnormalities in the white matter of cortical areas thought to be associated with bipolar disorder. In all, 14 patients with bipolar disorder and 21 nonpsychiatrically ill control subjects underwent MR imaging including a diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) pulse sequence (six directions, b=1000 mm2/s). DTI data were analyzed on a workstation using a program that allowed calculation of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and fractional anisotropy (FA) within the following three white matter fiber tracts bilaterally: the orbital frontal cortex, and the superior and middle frontal gyri. These values were compared across patient groups. The left and right orbital frontal white matter exhibited significantly higher ADC values in bipolar subjects than control subjects on both the left (p=0.028) and right (p=0.011). Microstructural changes in the white matter of the orbital frontal areas as reflected by increased ADC values appear to be associated with bipolar disorder. Further research is needed to better understand the interaction of microstructural changes and bipolar symptoms and whether these changes are specific to bipolar disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adler CM, Holland SK, Schmithorst V, Wilke M, Weiss KL, Pan H et al (2004). Abnormal frontal white matter tracts in bipolar disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Bipolar Disorders 6: 197–203.
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996). Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111: 209–219.
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1998). A simplified method to measure the diffusion tensor from seven MR images. Magn Reson Med 39: 928–934.
Blumberg HP, Stern E, Ricketts S, Martinez D, de Asis J, White T et al (1999). Rostral and orbital prefrontal cortex dysfunction in the manic state of bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry 156: 1986–1988.
Bremner JD, Vythilingam M, Vermetten E, Nazeer A, Adil J, Khan S et al (2002). Reduced volume of orbitofrontal cortex in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 51: 273–379.
Buchsbaum MS, Tang CY, Peled S, Gudbjartsson H, Lu D, Hazlett EA et al (1998). MRI white matter diffusion anisotropy and PET metabolic rate in schizophrenia. Neuroreport 9: 425–430.
Conturo TE, McKinstry RC, Akbudak E, Robinson BH (1996). Encoding of anisotropic diffusion with tetrahedral gradients: a general mathematical diffusion formalism and experimental results. Magn Reson Med 35: 399–412.
Drevets WC (2000). Neuroimaging studies of mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 48: 813–829.
Drevets WC, Price JD, Simpson JR, Todd RD, Reich T, Vannier M et al (1997). Subgenual prefrontal cortex abnormalities in mood disorders. Nature 386: 824–827.
Gray L, MacFall J (1998). Overview of diffusion imaging. MRI Clin N Am 6: 125–138.
Guo AC, MacFall JR, Provenzale JM (2002). Diffusion tensor imaging of multiple sclerosis: evaluation of normal-appearing white matter. Radiology 222: 729–736.
Hanyu H, Sakurai H, Iwamoto T, Takasaki M, Shindo H, Abe K (1998). Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the hippocampus and temporal white matter in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurological Sci 156: 195–200.
Lai TJ, Payne ME, Byrum CE, Steffens DC, Krishnan KRR (2000). Reduction in orbital frontal cortex in geriatric depression. Biol Psychiatry 48: 971–975.
Lee SH, Payne ME, Steffens DC, McQuoid DR, Lai TJ, Provenzale JM et al (2003). Subcortical lesion severity and orbitofrontal cortex volume in geriatric depression. Biol Psychiatry 54: 529–533.
Mayberg HS (1997). Limbic-cortical dysregulation: a proposed model of depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9: 471–481.
Taylor WD, Hsu E, Krishnan KR, MacFall JR (2004a). Diffusion tensor imaging: background, potential, and utility in psychiatric research. Biol Psychiatry 55: 201–207.
Taylor WD, MacFall JR, Payne ME, McQuoid DR, Provenzale JM, Steffens DC et al (2004b). Late-life depression and abnormalities in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex white matter microstructure. Am J Psychiatry 161: 1293–1296.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a NARSAD Young Investigator Award and NIMH Grant #5ROI-MH57027. We would like to acknowledge the image processing assistance of Mr Brian Boyd and Ms Cynthia Key of the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Duke University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beyer, J., Taylor, W., MacFall, J. et al. Cortical White Matter Microstructural Abnormalities in Bipolar Disorder. Neuropsychopharmacol 30, 2225–2229 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300802
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300802
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of Bipolar Disorder Using fMRI
Wireless Personal Communications (2023)
-
Differences in attentional control and white matter microstructure in adolescents with attentional, affective, and behavioral disorders
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2020)
-
A Critical Review on Structural Neuroimaging Studies in BD: a Transdiagnostic Perspective from Psychosis to Fronto-Temporal Dementia
Current Behavioral Neuroscience Reports (2020)
-
Structural dysconnectivity of key cognitive and emotional hubs in young people at high genetic risk for bipolar disorder
Molecular Psychiatry (2018)
-
Myelin vs Axon Abnormalities in White Matter in Bipolar Disorder
Neuropsychopharmacology (2015)