Abstract
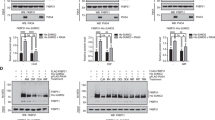
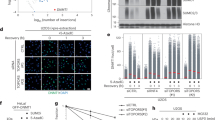
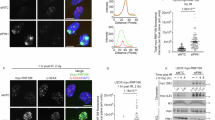
The RGSZ1 and RGSZ2 proteins, members of the RGS-Rz subfamily of GTPase-activating proteins (GAP), are involved in Mu-opioid receptor desensitization. The expression of these proteins, as well as of their main target the Gz protein, is virtually restricted to the nervous tissue. In synaptosomal membranes, these Rz proteins undergo post-translational modifications such as glycosylation and phosphorylation, and they may covalently attach to small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) proteins. While RGSZ1 exists in conjugated and non-conjugated forms, RGSZ2 is mostly conjugated to SUMO-1, SUMO-2 and SUMO-3 proteins. These sumoylated forms of the GAPs readily associated with Mu-opioid receptors but they associated only poorly with Delta receptors. Furthermore, Gαi2 and Gαz subunits co-precipitated with the sumoylated forms of RGSZ1/Z2 proteins, but to a lesser extent with the Ser phosphorylated SUMO-free form of RGSZ1. Upon Mu-opioid receptor activation, there is a strong increase in the association of Gα proteins with RGSZ2 proteins that persists for intervals longer than 24 h. This effect probably accounts for their role in Mu-opioid receptor desensitization. Only a moderate increase was observed with RGSZ1, the non-sumoylated form of which probably acts as an efficient GAP for these Gα subunits. Therefore, sumoylation regulates the biological activity of RGS-Rz proteins and it is likely that it serves to switch their behavior, from that of a GAP for activated Gα subunits to that of a scaffold protein for specific signaling proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Barker SA, Wang J, Sierra DA, Ross EM (2001). RGSZ1 and Ret RGS: two of several splice variants from the gene RGS20. Genomics 78: 223–229.
Berman DM, Gilman AG (1998). Mammalian RGS proteins: barbarians at the gate. J Biol Chem 273: 1269–1271.
Berman DM, Wilkie TM, Gilman AG (1996). GAIP and RGS4 are GTPase-activating proteins for the Gi subfamily of G protein alpha subunits. Cell 86: 445–452.
Carrasco GA, Barker SA, Zhang Y, Damjanoska KJ, Sullivan NR, Garcia F et al (2004). Estrogen treatment increases the levels of regulator of G protein signaling-Z1 in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: possible role in desensitization of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptors. Neuroscience 127: 261–267.
De Vries L, Elenko E, Hubler L, Jones TL, Farquhar MG (1996). GAIP is membrane-anchored by palmitoylation and interacts with the activated (GTP-bound) form of Gαi subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 15203–15208.
De Vries L, Mousli M, Wurmser A, Farquhar MG (1995). GAIP, a protein that specifically interacts with the trimeric G protein Gαi3, is a member of a protein family with a highly conserved core domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 11916–11920.
Fong HK, Yoshimoto KK, Eversole-Cire P, Simon MI (1988). Identification of a GTP-binding protein α subunit that lacks an apparent ADP-ribosylation site for pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 3066–3070.
Gagnon AW, Manning DR, Catani L, Gewirtz A, Poncz M, Brass LF (1991). Identification of Gzα as a pertussis toxin-insensitive G protein in human platelets and megakaryocytes. Blood 78: 1247–1253.
Garzón J, Martínez-Peña Y, Sánchez-Blázquez P (1997). Gx/z is regulated by μ but not δ opioid receptors in the stimulation of the low Km GTPase activity in mouse periaqueductal grey matter. Eur J Neurosci 9: 1194–1200.
Garzón J, Rodríguez-Muñoz M, López-Fando A, García-España A, Sánchez-Blázquez P (2004). RGSZ1 and GAIP regulate μ- but not δ-opioid receptors in mouse CNS: role in tachyphylaxis and acute tolerance. Neuropsychopharmacology 29: 1091–1104.
Garzón J, Rodríguez-Muñoz M, López-Fando A, Sánchez-Blázquez P (2005a). The RGSZ2 protein exists in a complex with mu opioid receptors and regulates the desensitizing capacity of Gz proteins. Neuropsychopharmacology 30: 1632–1648.
Garzón J, Rodríguez-Muñoz M, López-Fando A, Sánchez-Blázquez P (2005b). Activation of Mu-opioid receptors transfers control of Gα subunits to the regulator of G-protein signaling RGS9-2. Role in receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem 280: 8951–8960.
Garzón J, Rodríguez-Muñoz M, De la Torre-Madrid E, Sánchez-Blázquez P (2005c). Effector antagonism by the regulators of G protein signalling (RGS) proteins causes desensitization of mu-opioid receptors in CNS. Psychopharmacology 180: 1–11.
Garzón J, Rodríguez-Muñoz M, Sánchez-Blázquez P (2005d). In mouse periaqueductal grey matter, morphine alters the selective association between Mu-opioid receptors and specific RGS proteins. Neuropharmacology 48: 853–868.
Giorgino F, de Robertis O, Laviola L, Montrone C, Perrini S, McCowen KC et al (2000). The sentrin-conjugating enzyme mUbc9 interacts with GLUT4 and GLU1 glucose transporters and regulates transporter levels in skeletal muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 1125–1130.
Glick JL, Meigs TE, Miron A, Casey PJ (1998). RGSZ1, a Gz-selective regulator of G protein signaling whose action is sensitive to the phosphorylation state of Gzα. J Biol Chem 273: 26008–26013.
Gocke GB, Yu H, Kang J (2005). Systematic identification and analysis of mammalian small ubiquitin-like modifier substrates. J Biol Chem 280: 5004–5012.
Grafstein-Dunn E, Young KH, Cockett MI, Khawaja XZ (2001). Regional distribution of regulators of G-protein signaling (RGS) 1, 2, 13, 14, 16, and GAIP messenger ribonucleic acids by in situ hybridization in rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 88: 113–123.
Hepler JR, Berman DM, Gilman AG, Kozasa T (1997). RGS4 and GAIP are GTPase-activating proteins for Gqα and block activation of phospholipase Cβ by γ-thio-GTP-Gqα. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 428–432.
Hietakangas V, Ahlskog JK, Jakobsson AM, Hellesuo M, Sahlberg NM, Holmberg CI et al (2003). Phosphorylation of serine 303 is a prerequisite for the stress-inducible SUMO modification of heat shock factor 1. Mol Cell Biol 23: 2953–2968.
Hunt TW, Fields TA, Casey PJ, Peralta EG (1996). RGS10 is a selective activator of Gαi GTPase activity. Nature 383: 175–177.
Kadaré G, Toutant M, Formstecher E, Corvol J-C, Carnaud M, Boutterin M-C et al (2003). PIAS1-mediated sumoylation of focal adhesion kinase activates its autophosphorylation. J Biol Chem 278: 47434–47440.
Klenk C, Humrich J, Quitterer U, Lohse MJ (2006). SUMO-1 controls the protein stability and the biological function of phosducin. J Biol Chem 281: 8357–8364.
Mao H, Zhao Q, Daigle M, Ghahremani MH, Chidiac P, Albert PR (2004). RGS17/RGSZ2, a novel regulator of Gi/o, Gz and Gq signaling. J Biol Chem 279: 26314–26322.
Matsuoka M, Itoh H, Kozasa T, Kaziro Y (1988). Sequence analysis of cDNA and genomic DNA for a putative pertussis toxin-insensitive guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein α subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 5382–5388.
Matunis MJ, Wu J, Blobel G (1998). SUMO-1 modification and its role in targeting the Ran GTPase-activating protein, RanGAP1, to the pore nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol 140: 499–509.
Melchior F, Schergaut M, Pichler A (2003). SUMO: ligases, isopeptidases and nuclear pores. Trends Biochem Sci 28: 612–618.
Müller S, Berger M, Lahembre F, Seeler J-S, Haupt Y, Dejean A (2000). c-Jun and p53 activity is modulated by SUMO-1 modification. J Biol Chem 275: 13321–13329.
Ross EM, Wilkie TM (2000). GTPase-activating proteins for heterotrimeric G proteins: regulators of G protein signalling (RGS) and RGS-like proteins. Ann Rev Biochem 69: 795–827.
Saitoh H, Hinchey J (2000). Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3. J Biol Chem 275: 6252–6258.
Sánchez-Blázquez P, García-España A, Garzón J (1995). In vivo injection of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to Gα subunits and supraspinal analgesia evoked by mu and delta opioid agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275: 1590–1596.
Sobko A, Ma H, Firtel RA (2002). Regulated SUMOylation and ubiquitination of DdMEK1 is required for proper chemotaxis. Dev Cell 2: 745–756.
Sowa ME, He W, Wensel TG, Lichtarge O (2000). A regulator of G protein signaling interaction surface linked to effector specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 1483–1488.
Tatham MH, Jaffray E, Vaughan OA, Desterro JMP, Botting CH, Naismith JH et al (2001). Polymeric chains of SUMO-2 and SUMO-3 are conjugated to protein substrates by SAE1/SAE2 and Ubc9. J Biol Chem 276: 35368–35374.
Tesmer JJ, Berman DM, Gilman AG, Sprang SR (1997). Structure of RGS4 bound to AlF4-activated Giα1: stabilization of the transition state for GTP hydrolysis. Cell 89: 251–261.
Tu Y, Wang J, Ross EM (1997). Inhibition of brain Gz GAP and other RGS proteins by palmitoylation of G protein α subunits. Science 278: 1132–1135.
Wang J, Ducret A, Tu Y, Kozasa T, Aebersold R, Ross EM (1998). RGSZ1, a Gz-selective RGS protein in brain. Structure, membrane association, regulation by Gαz phosphorylation and relationship to Gz GTPase-activating protein subfamily. J Biol Chem 273: 26014–26025.
Wang J, Tu Y, Woodson J, Song X, Ross EM (1997). A GTPase-activating protein for the G protein Gαz. Identification, purification, and mechsnism of action. J Biol Chem 272: 5732–5740.
Yaksh TL, Yeung JC, Rudy TA (1976). Systematic examination in the rat of brain sites sensitive to the direct application of morphine: observation of differential effects within the periaqueductal grey. Brain Res 114: 83–103.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grants SAF2003-01121 and SAF2005-01772. We are indebted to Dr Brigitte L Kieffer (University Louis Pasteur, Illkirch, France) for providing us with the C57BL/6 Mu-opioid receptor null (−/−) mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-Muñoz, M., Bermúdez, D., Sánchez-Blázquez, P. et al. Sumoylated RGS-Rz Proteins Act as Scaffolds for Mu-Opioid Receptors and G-Protein Complexes in Mouse Brain. Neuropsychopharmacol 32, 842–850 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301184
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301184
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Human HINT1 Mutant Proteins that Cause Axonal Motor Neuropathy Exhibit Anomalous Interactions with Partner Proteins
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Nitric Oxide and Zinc-Mediated Protein Assemblies Involved in Mu Opioid Receptor Signaling
Molecular Neurobiology (2013)
-
The function of alpha-2-adrenoceptors in the rat locus coeruleus is preserved in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain
Psychopharmacology (2012)
-
Gz Mediates the Long-Lasting Desensitization of Brain CB1 Receptors and is Essential for Cross-Tolerance with Morphine
Molecular Pain (2009)
-
G protein alpha z
AfCS-Nature Molecule Pages (2009)