Abstract
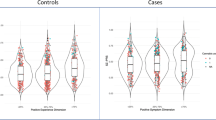
Observational studies have suggested that psychometric psychosis liability and a functional polymorphism in the catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT Val158Met) gene moderate the psychosis-inducing effect of cannabis. To replicate and extend this finding, a double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over design was used in which patients with a psychotic disorder (n=30), relatives of patients with a psychotic disorder (n=12), and healthy controls (n=32) were exposed to Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ-9-THC, the principal component of cannabis) or placebo, followed by cognitive assessment and assessment of current psychotic experiences. Previous expression of psychometric psychosis liability was also assessed. Models of current psychotic experiences and cognition were examined with multilevel random regression analyses to assess (i) main effects of genotype and condition, (ii) interactions between condition and genotype, and (iii) three-way interactions between condition, genotype, and psychometric psychosis liability. Carriers of the Val allele were most sensitive to Δ-9-THC-induced psychotic experiences, but this was conditional on prior evidence of psychometric psychosis liability. Δ-9-THC impacted negatively on cognitive measures. Carriers of the Val allele were also more sensitive to Δ-9-THC-induced memory and attention impairments compared to carriers of the Met allele. Experimental effects of Δ-9-THC on cognition and psychosis are moderated by COMT Val158Met genotype, but the effects may in part be conditional on the additional presence of pre-existing psychosis liability. The association between cannabis and psychosis may represent higher order gene–environment and gene–gene interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Akil M, Kolachana BS, Rothmond DA, Hyde TM, Weinberger DR, Kleinman JE (2003). Catechol-O-methyltransferase genotype and dopamine regulation in the human brain. J Neurosci 23: 2008–2013.
Bates JA, Goldman D, Malhotra AK (2003). COMT and neurocognition: new evidence for a role in visual memory. Schizophr Res 60 (Suppl 1): 123.
Bilder RM, Volavka J, Lachman HM, Grace AA (2004). The catechol-O-methyltransferase polymorphism: relations to the tonic-phasic dopamine hypothesis and neuropsychiatric phenotypes. Neuropsychopharmacology 29: 1943–1961.
Bloom AS (1982). Effect of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on the synthesis of dopamine and norepinephrine in mouse brain synaptosomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 221: 97–103.
Caspi A, Moffitt TE, Cannon M, McClay J, Murray R, Harrington H et al (2005). Moderation of the effect of adolescent-onset cannabis use on adult psychosis by a functional polymorphism in the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene: longitudinal evidence of a gene × environment interaction. Biol Psychiatry 57: 1117–1127.
Chapman LJ, Chapman JP, Kwapil TR, Eckblad M (1994). Putatively psychosis-prone subjects 10 years later. J Abnorm Psychol 103: 171–183.
Chen WJ, Faraone SV (2000). Sustained attention deficits as markers of genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 97: 52–57.
Daniels JK, Williams NM, Williams J, Jones LA, Cardno AG, Murphy KC et al (1996). No evidence for allelic association between schizophrenia and a polymorphism determining high or low catechol O-methyltransferase activity. Am J Psychiatry 153: 268–270.
de Frias CM, Annerbrink K, Westberg L, Eriksson E, Adolfsson R, Nilsson LG (2004). COMT gene polymorphism is associated with declarative memory in adulthood and old age. Behav Genet 34: 533–539.
D'Souza DC, Abi-Saab WM, Madonick S, Forselius-Bielen K, Doersch A, Braley G et al (2005). Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol effects in schizophrenia: implications for cognition, psychosis, and addiction. Biol Psychiatry 57: 594–608.
Egan MF, Goldberg TE, Kolachana BS, Callicott JH, Mazzanti CM, Straub RE et al (2001). Effect of COMT Val108/158 Met genotype on frontal lobe function and risk for schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 6917–6922.
Eisenberg J, Mei-Tal G, Steinberg A, Tartakovsky E, Zohar A, Gritsenko I et al (1999). Haplotype relative risk study of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): association of the high-enzyme activity Val allele with ADHD impulsive-hyperactive phenotype. Am J Med Genet 88: 497–502.
Fan JB, Zhang CS, Gu NF, Li XW, Sun WW, Wang HY et al (2005). Catechol-O-methyltransferase gene Val/Met functional polymorphism and risk of schizophrenia: a large-scale association study plus meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry 57: 139–144.
Giuffrida A, Leweke FM, Gerth CW, Schreiber D, Koethe D, Faulhaber J et al (2004). Cerebrospinal anandamide levels are elevated in acute schizophrenia and are inversely correlated with psychotic symptoms. Neuropsychopharmacology 29: 2108–2114.
Giuffrida A, Parsons LH, Kerr TM, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Navarro M, Piomelli D (1999). Dopamine activation of endogenous cannabinoid signaling in dorsal striatum. Nat Neurosci 2: 358–363.
Grace AA (1991). Phasic versus tonic dopamine release and the modulation of dopamine system responsivity: a hypothesis for the etiology of schizophrenia. Neuroscience 41: 1–24.
Hanssen M, Bak M, Bijl R, Vollebergh W, van Os J (2005). The incidence and outcome of subclinical psychotic experiences in the general population. Br J Clin Psychol 44 (Part 2): 181–191.
Hanssen M, Krabbendam L, Vollema M, Delespaul P, Van Os J (2006). Evidence for instrument and family-specific variation of subclinical psychosis dimensions in the general population. J Abnorm Psychol 115: 5–14.
Henquet C, Krabbendam L, Spauwen J, Kaplan C, Lieb R, Wittchen HU et al (2005a). Prospective cohort study of cannabis use, predisposition for psychosis, and psychotic symptoms in young people. BMJ 330: 11–15.
Henquet C, Murray R, Linszen D, van Os J (2005b). The environment and schizophrenia: the role of cannabis use. Schizophr Bull 31: 608–612.
Houx PJ, Vreeling FW, Jolles J (1991). Age-associated cognitive decline is related to biological life events. In: Iqbal K, McLachlan DRC, Winbald B, Wisniewski HM (eds). Alzheimer's Disease: Basic Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Stratigies. John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK. pp 353–358.
Howes OD, McDonald C, Cannon M, Arseneault L, Boydell J, Murray RM (2004). Pathways to schizophrenia: the impact of environmental factors. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 7 (Suppl 1): S7–S13.
Jacobs N, Myin-Germeys I, Derom C, Vlietinck R, van Os J (2005). Deconstructing the familiarity of the emotive component of psychotic experiences in the general population. Acta Psychiatr Scand 112: 394–401.
Jentsch JD, Verrico CD, Le D, Roth RH (1998). Repeated exposure to delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol reduces prefrontal cortical dopamine metabolism in the rat. Neurosci Lett 246: 169–172.
Johns LC, van Os J (2001). The continuity of psychotic experiences in the general population. Clin Psychol Rev 21: 1125–1141.
Kapur S (2003). Psychosis as a state of aberrant salience: a framework linking biology, phenomenology, and pharmacology in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 160: 13–23.
Kendler KS, Diehl SR (1993). The genetics of schizophrenia: a current, genetic-epidemiologic perspective. Schizophr Bull 19: 261–285.
Konings M, Bak M, Hanssen M, van Os J, Krabbendam L (2006). Validity and reliability of the CAPE: a self-report instrument for the measurement of psychotic experiences in the general population. Acta Psychiatr Scand 114: 55–61.
Krabbendam L, Marcelis M, Delespaul P, Jolles J, van Os J (2001). Single or multiple familial cognitive risk factors in schizophrenia? Am J Med Genet 105: 183–188.
Krabbendam L, Myin-Germeys I, Hanssen M, van Os J (2005). Familial covariation of the subclinical psychosis phenotype and verbal fluency in the general population. Schizophr Res 74: 37–41.
Laloup M, Ramirez Fernandez Mdel M, Wood M, De Boeck G, Henquet C, Maes V et al (2005). Quantitative analysis of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in preserved oral fluid by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1082: 15–24.
Leweke FM, Giuffrida A, Wurster U, Emrich HM, Piomelli D (1999). Elevated endogenous cannabinoids in schizophrenia. Neuroreport 10: 1665–1669.
Lieberman JA, Sheitman BB, Kinon BJ (1997). Neurochemical sensitization in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia: deficits and dysfunction in neuronal regulation and plasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology 17: 205–229.
Linszen DH, Dingemans PM, Lenior ME (1994). Cannabis abuse and the course of recent-onset schizophrenic disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51: 273–279.
Luteijn F, van der Ploeg FAE (1983). Handleiding Groninger Intelligentie Test (GIT) [Manual Groningen Intelligence Test]. Lisse: Swets and Zeitlinger.
Maitre L, Staehelin M, Bein HJ (1970). Effect of an extract of cannabis and of some cannabinols on catecholamine metabolism in rat brain and heart. Agents Actions 1: 136–143.
Mattay VS, Goldberg TE, Fera F, Hariri AR, Tessitore A, Egan MF et al (2003). Catechol O-methyltransferase val158-met genotype and individual variation in the brain response to amphetamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 6186–6191.
McGuffin P, Farmer A, Harvey I (1991). A polydiagnostic application of operational criteria in studies of psychotic illness. Development and reliability of the OPCRIT system. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48: 764–770.
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Kohn PD, Kolachana B, Kippenhan S, McInerney-Leo A, Nussbaum R et al (2005). Midbrain dopamine and prefrontal function in humans: interaction and modulation by COMT genotype. Nat Neurosci 8: 594–596.
Munafo MR, Bowes L, Clark TG, Flint J (2005). Lack of association of the COMT (Val(158/108) Met) gene and schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. Mol Psychiatry 10: 765–770.
Nestor PG, Faux SF, McCarley RW, Sands SF, Horvath TB, Peterson A (1991). Neuroleptics improve sustained attention in schizophrenia. A study using signal detection theory. Neuropsychopharmacology 4: 145–149.
Nuechterlein KH, Asarnow RF, Subotnik KL, Fogelson DL, Payne DL, Kendler KS et al (2002). The structure of schizotypy: relationships between neurocognitive and personality disorder features in relatives of schizophrenic patients in the UCLA family study. Schizophr Res 1: 121–130.
Ramaekers JG, Berghaus G, van Laar M, Drummer OH (2004). Dose related risk of motor vehicle crashes after cannabis use. Drug Alcohol Depend 73: 109–119.
Ramaekers JG, Moeller MR, van Ruitenbeek P, Theunissen EL, Schneider E, Kauert G (2006). Cognition and motor control as a function of Delta(9)-THC concentration in serum and oral fluid: Limits of impairment. Drug Alcohol Depend, 24 May 2006 [E-pub ahead of print].
Rey A (1964). L'examen psychologique dans les cas d'encephalopathie traumatique. Presses de Universitaires de France: Paris.
Rosa A, Peralta V, Cuesta MJ, Zarzuela A, Serrano F, Martinez-Larrea A et al (2004). New evidence of association between COMT gene and prefrontal neurocognitive function in healthy individuals from sibling pairs discordant for psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 161: 1110–1112.
Sahakian BJ, Morris RG, Evenden JL, Heald A, Levy R, Philpot M et al (1988). A comparative study of visuospatial memory and learning in Alzheimer-type dementia and Parkinson's disease. Brain 111 (Part 3): 695–718.
Sevy S, Robinson DG, Holloway S, Alvir JM, Woerner MG, Bilder R et al (2001). Correlates of substance misuse in patients with first-episode schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Acta Psychiatr Scand 104: 367–374.
Simes RJ (1986). An improved Bonferroni procedure for multiple tests of significance. Biometrika 73: 751–754.
Sim-Selley LJ (2003). Regulation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the central nervous system by chronic cannabinoids. Crit Rev Neurobiol 15: 91–119.
Stroop (1935). Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J Exp Psychol 18: 643–662.
van Os J, Bak M, Hanssen M, Bijl RV, de Graaf R, Verdoux H (2002). Cannabis use and psychosis: a longitudinal population-based study. Am J Epidemiol 156: 319–327.
van Os J, Hanssen M, Bijl RV, Ravelli A (2000). Strauss (1969) revisited: a psychosis continuum in the general population? Schizophr Res 45: 11–20.
van Os J, Hanssen M, Bijl RV, Vollebergh W (2001). Prevalence of psychotic disorder and community level of psychotic symptoms: an urban–rural comparison. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58: 663–668.
Verdoux H, Gindre C, Sorbara F, Tournier M, Swendsen JD (2003). Effects of cannabis and psychosis vulnerability in daily life: an experience sampling test study. Psychol Med 33: 23–32.
Voruganti LN, Slomka P, Zabel P, Mattar A, Awad AG (2001). Cannabis induced dopamine release: an in-vivo SPECT study. Psychiatry Res 107: 173–177.
Wechsler D (1981). Manual for the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised. Psychological Corporation: New York.
WHO (1990). Composite International Diagnostic Interview (CIDI). World Health Organization: Geneva.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded in part through an unrestricted educational grant from Glaxo-Smith Kline and Fundació La Marató de TV3 (014430/31). No conflicts of interest have been declared by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henquet, C., Rosa, A., Krabbendam, L. et al. An Experimental Study of Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Val158Met Moderation of Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol-Induced Effects on Psychosis and Cognition. Neuropsychopharmacol 31, 2748–2757 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301197
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301197
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Rates and correlates of cannabis-associated psychotic symptoms in over 230,000 people who use cannabis
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Biological activity of Cannabis compounds: a modern approach to the therapy of multiple diseases
Phytochemistry Reviews (2022)
-
THC-induced behavioral stereotypy in zebrafish as a model of psychosis-like behavior
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The why behind the high: determinants of neurocognition during acute cannabis exposure
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2021)
-
Pharmacogenetic-guided cannabis usage in the community pharmacy: evaluation of a pilot program
Journal of Cannabis Research (2020)