Abstract
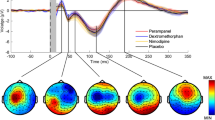
Ampakines act as positive allosteric modulators of AMPA-type glutamate receptors and facilitate hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP), a mechanism associated with memory storage and consolidation. The present study investigated the acute effects of farampator, 1-(benzofurazan-5-ylcarbonyl) piperidine, on memory and information processes in healthy elderly volunteers. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, cross-over study was performed in 16 healthy, elderly volunteers (eight male, eight female; mean age 66.1, SD 4.5 years). All subjects received farampator (500 mg) and placebo. Testing took place 1 h after drug intake, which was around Tmax for farampator. Subjects performed tasks assessing episodic memory (wordlist learning and picture memory), working and short-term memory (N-back, symbol recall) and motor learning (maze task, pursuit rotor). Information processing was assessed with a tangled lines task, the symbol digit substitution test (SDST) and the continuous trail making test (CTMT). Farampator (500 mg) unequivocally improved short-term memory but appeared to impair episodic memory. Furthermore, it tended to decrease the number of switching errors in the CTMT. Drug-induced side effects (SEs) included headache, somnolence and nausea. Subjects with SEs had significantly higher plasma levels of farampator than subjects without SEs. Additional analyses revealed that in the farampator condition the group without SEs showed a significantly superior memory performance relative to the group with SEs. The positive results on short-term memory and the favorable trends in the trail making test (CTMT) are interesting in view of the development of ampakines in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Ammons RB (1951). Effect of distribution of practice on rotary pursuit hits. J Exp Psychol 41: 17–22.
Arai A, Kessler M, Xiao P, AmbrosIngerson J, Rogers G, Lynch G (1994). A centrally active-drug that modulates Ampa receptor gated currents. Brain Res 638: 343–346.
Bittner AC, Carter RC, Kennedy RS, Harbeson MM, Krause M (1986). Performance evaluation tests for environmental-research (Peter)—evaluation of 114 measures. Percept Mot Skills 63: 683–708.
Bittner AC, Carter RC, Krause M, Kennedy RS, Harbeson MM (1983). Performance evaluation tests for environmental-research (Peter)—moran and computer batteries. Aviat Space Environ Med 54: 923–928.
Bond A, Lader M (1974). Use of analog scales in rating subjective feelings. Br J Med Psychol 47: 211–218.
Bouma A, Mulder J, Lindeboom J (1998). Neuropsychologische diagnostiek, handboek. Zwets & Zeitlinger: Lisse.
Carver CS (1994). Cognitive-processes and self-regulation—determinants of concentration and distraction. Appl Psychol Int Rev 43: 387–391.
Chen EYH, Hui CLM, Dunn ELW, Miao MYK, Yeung WS, Wong CK et al (2005). A prospective 3-year longitudinal study of cognitive predictors of relapse in first-episode schizophrenic patients. Schizophr Res 77: 99–104.
de Jong WP, Hulstijn W, Jogems-Kosterman BJM, Smits-Engelsman BCM (1996). OASIS software and its application in experimental handwriting research. In: Simmers ML, Leedham CG, Thomassen AJWM (eds). Handwriting and Drawing Research: Basic and Applied Issues. IOS: Amsterdam.
Donohoe G, Robertson IH (2003). Can specific deficits in executive functionina explain the negative symptoms of schizophrenia? A review. Neurocase 9: 97–108.
Ekstrom RB, French JW, Harmon H, Dermen D (1976). Manual for the Kit of Factor Referenced Cognitive Tests. Educational Testing Service: Princeton, New York.
French JW (1954). Manual for Kit of Selected Tests for Reference Aptitude and Achievement Factors. Educational Testing Service: Princeton, New York.
Foster JK, Lidder PG, Sunram SI (1998). Glucose and memory: fractionation of enhancement effects? Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 137: 227–259.
Goff DC, Leahy L, Berman I, Posever T, Herz L, Leon AC et al (2001). A placebo-controlled pilot study of the ampakine CX516 added to clozapine in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 21: 484–487.
Grady CL, Craik FI (2000). Changes in memory processing with age. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10: 224–231.
Granger R, Deadwyler S, Davis M, Moskovitz B, Kessler M, Rogers G et al (1996). Facilitation of glutamate receptors reverses an age-associated memory impairment in rats. Synapse 22: 332–337.
Granger R, Staubli U, Davis M, Perez Y, Nilsson L, Rogers GA et al (1993). A drug that facilitates glutamatergic transmission reduces exploratory activity and improves performance in a learning-dependent task. Synapse 15: 326–329.
Green MF, Nuechterlein KH, Gold JM, Barch DM, Cohen J, Essock S et al (2004). Approaching a consensus cognitive battery for clinical trials in schizophrenia: the NIMH-MATRICS conference to select cognitive domains and test criteria. Biol Psychiatry 56: 301–307.
Hampson RE, Rogers G, Lynch G, Deadwyler SA (1998). Facilitative effects of the ampakine CX516 on short-term memory in rats: Enhancement of delayed-nonmatch-to-sample performance. J Neurosci 18: 2740–2747.
Hege SG, Ellinwood Jr EH, Wilson WH, Helligers CA, Graham SM (1997). Psychomotor effects of the anxiolytic abecarnil: a comparison with lorazepam. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 131: 101–107.
Heinrichs RW, Zakzanis KK (1998). Neurocognitive deficit in schizophrenia: a quantitative review of the evidence. Neuropsychology 12: 426–445.
Hollmann M, Muller-Peltzer H, Greger G, Brode E, Perucca E, Grimaldi R (1987). Pharmacokinetic-dynamic study on different oral biperiden formulations in volunteers. Pharmacopsychiatry 20: 72–77.
Ingvar M, AmbrosIngerson J, Davis M, Granger R, Kessler M, Rogers GA et al (1997). Enhancement by an ampakine of memory encoding in humans. Exp Neurol 146: 553–559.
Jogems-Kosterman BJM, Zitman FG, van Hoof JJM, Hulstijn W (2001). Psychomotor slowing and planning deficits in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 48: 317–333.
Johnson SA, Luu NT, Herbst TA, Knapp R, Lutz D, Arai A et al (1999). Synergistic interactions between ampakines and antipsychotic drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289: 392–397.
Kaplan E, Fein D, Morris R, Delis D (1991). Wais-R as a neuropsychological instrument. The Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX.
Larson J, Lieu T, Petchpradub V, Leduc B, Ngo H, Rogers GA et al (1995). Facilitation of olfactory learning by a modulator of AMPA receptors. J Neurosci 15: 8023–8030.
Larson J, Quach CN, Leduc BQ, Nguyen A, Rogers GA, Lynch G (1996). Effects of an AMPA receptor modulator on methamphetamine-induced hyperactivity in rats. Brain Res 738: 353–356.
Lebrun C, Pilliere E, Lestage P (2000). Effects of S 18986-1, a novel cognitive enhancer, on memory performances in an object recognition task in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 401: 205–212.
Lezak MD (1995). Neuropsychological Assessment, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press: New York.
Li SC, Dinse HR (2002). Aging of the brain, sensorimotor, and cognitive processes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26: 729–732.
Lynch G (2004). AMPA receptor modulators as cognitive enhancers. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4: 4–11.
Lynch G (1998). Memory and the brain: unexpected chemistries and a new pharmacology. Neurobiol Learn Memory 70: 82–100.
Lynch G, Granger R, Ambros-Ingerson J, Davis CM, Kessler M, Schehr R (2003). Evidence that a positive modulator of AMPA-type glutamate receptors improves delayed recall in aged humans. Exp Neurol 145: 89–92.
Lynch G, Granger R, AmbrosIngerson J, Davis CM, Kessler M, Schehr R (1997). Evidence that a positive modulator of AMPA-type glutamate receptors improves delayed recall in aged humans. Exp Neurol 145: 89–92.
Lynch G, Kessler M, Rogers G, AmbrosIngerson J, Granger R, Schehr RS (1996). Psychological effects of a drug that facilitates brain AMPA receptors. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 11: 13–19.
Marenco S, Egan MF, Goldberg TE, Knable MB, McClure RK, Winterer G et al (2002). Preliminary experience with an ampakine (CX516) as a single agent for the treatment of schizophrenia: a case series. Schizophr Res 57: 221–226.
Meyer JS, Thornby J, Crawford K, Rauch GM (2000). Reversible cognitive decline accompanies migraine and cluster headaches. Headache 40: 638–646.
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Poline JB, Kohn PD, Holt JL, Egan MF, Weinberger DR et al (2001). Evidence for abnormal cortical functional connectivity during working memory in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 158: 1809–1817.
Nuechterlein KH, Barch DM, Gold JM, Goldberg TE, Green MF, Heaton RK (2004). Identification of seperable cognitive factors in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 72: 29–39.
Pantelis C, Barber FZ, Barnes TRE, Nelson HE, Owen AM, Robbins TW (1999). Comparison of set-shifting ability in patients with chronic schizophrenia and frontal lobe damage. Schizophr Res 37: 251–270.
Peretti CS, Danion JM, Kauffmannmuller F, Grange D, Patat A, Rosenzweig P (1997). Effects of haloperidol and amisulpride on motor and cognitive skill learning in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 131: 329–338.
Petrides M, Milner B (1982). Deficits on subject-ordered tasks after frontal-lobe and temporal-lobe lesions in man. Neuropsychologia 20: 249.
Rammsayer TH, Rodewald S, Groh D (2000). Dopamine-antagonistic, anticholinergic, and GABAergic effects on declarative and procedural memory functions. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 9: 61–71.
Reitan RM (1958). Qualitative versus quantitative mental changes following brain-damage. J Psychol 46: 339–346.
Reitan RM, Wolfson D (1995). Category test and trail making test as measures of frontal-lobe functions. Clin Neuropsychol 9: 50–56.
Robbins TW, Semple J, Kumar R, Truman MI, Shorter J, Ferraro A et al (1997). Effects of scopolamine on delayed-matching-to-sample and paired associates tests of visual memory and learning in human subjects: comparison with diazepam and implications for dementia. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 134: 95–106.
Sabbe B, Hulstijn W, van Hoof J, Tuynman-Qua HG, Zitman F (1999). Retardation in depression: assessment by means of simple motor tasks. J Affect Disord 55: 39–44.
Schmidt RA, Lee TD (1999). Motor Control and Learning: A Behavioral Emphasis, 3rd edn. Human Kinetics Publishers: USA.
Schmitt WB, Sprengel R, Mack V, Draft RW, Seeburg PH, Deacon RMJ et al (2005). Restoration of spatial working memory by genetic rescue of GluR-A-deficient mice. Nat Neurosci 8: 270–272.
Shors TJ, Servatius RJ, Thompson RF, Rogers G, Lynch G (1995). Enhanced glutamatergic neurotransmission facilitates classical-conditioning in the freely moving rat. Neurosci Lett 186: 153–156.
Siegel BV, Trestman RL, O’Flaithbheartaigh S, Mitropoulou V, Amin F, Kirrane R et al (1996). D-amphetamine challenge effects on wisconsin card sort test. Performance in schizotypal personality disorder. Schizophr Res 20: 29–32.
Staubli U, Perez Y, Xu FB, Rogers G, Ingvar M, Stoneelander S et al (1994a). Centrally active modulators of glutamate receptors facilitate the induction of long-term potentiation in-vivo. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 91: 11158–11162.
Staubli U, Rogers G, Lynch G (1994b). Facilitation of glutamate receptors enhances memory. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 91: 777–781.
Stefani MR, Groth K, Moghaddam B (2003). Glutamate receptors in the rat medial prefrontal cortex regulate set-shifting ability. Behav Neurosci 117: 728–737.
Vakil E, Blachstein H (1993). Rey auditory-verbal learning test—structure-analysis. J Clin Psychol 49: 883–890.
van Hoof JJM, Jogems-Kosterman BJM, Sabbe BGC, Zitman FG, Hulstijn W (1998). Differentiation of cognitive and motor slowing in the Digit Symbol Test (DST): differences between depression and schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 32: 99–103.
Van Mier H, Hulstijn W, Petersen SE (1993). Changes in motor planning during the acquisition of movement patterns in a continuous task. Acta Psychol 82: 291–312.
Van Mier H, Tempel LW, Perlmutter JS, Raichle ME, Petersen SE (1998). Changes in brain activity during motor learning measured with PET: effects of hand of performance and practice. J Neurophysiol 80: 2177–2199.
Wechsler D (1981). The psychometric tradition—developing the wechsler adult intelligence scale. Contemp Educ Psychol 6: 82–85.
Weinberger DR, Mattay V, Callicott J, Kotrla K, Santha A, vanGelderen P et al (1996). fMRI applications in schizophrenia research. Neuroimage 4: S118–S126.
Wezenberg E, Hulstijn W, Sabbe BGC, Ruigt GSF, Verkes RJ (2004). Psychomotor and cognitive effects of lorazepam and d-amphetamine in healthy subjects. Development of sensitive screening tests of psychomotor- and cognitive functions. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 14: S362.
Wezenberg E, Verkes RJ, Sabbe BGC, Ruigt GSF, Hulstijn W (2005). Modulation of memory and visuospatial processes by biperiden and rivastigmine in elderly healthy subjects. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 181: 582–594.
Yamada KA (1998). Modulating excitatory synaptic neurotransmission: Potential treatment for neurological disease? Neurobiol Dis 5: 67–80.
Acknowledgements
We thank them for their financial and technical support. We also thank Jan Leijtens and Sevla Cinar (MD) for their valuable assistance in the collection and analysis of the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest
Funding for the study was provided by NV Organon.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wezenberg, E., Jan Verkes, R., Ruigt, G. et al. Acute Effects of the Ampakine Farampator on Memory and Information Processing in Healthy Elderly Volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacol 32, 1272–1283 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301257
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301257
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Distinct contributions of GluA1-containing AMPA receptors of different hippocampal subfields to salience processing, memory and impulse control
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Augmenting cognitive work: a review of cognitive enhancement methods and applications for operational domains
Cognition, Technology & Work (2022)
-
Cellular and Molecular Changes in Hippocampal Glutamate Signaling and Alterations in Learning, Attention, and Impulsivity Following Prenatal Nicotine Exposure
Molecular Neurobiology (2020)
-
Postmortem Brain: An Underutilized Substrate for Studying Severe Mental Illness
Neuropsychopharmacology (2014)
-
Newer antipsychotics and upcoming molecules for schizophrenia
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2013)