Abstract
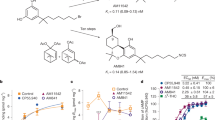
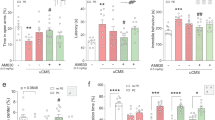
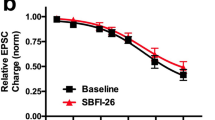
The mechanism of action responsible for the motor depressant effects of cannabinoids, which operate through centrally expressed cannabinoid CB1 receptors, is still a matter of debate. In the present study, we report that CB1 and adenosine A2A receptors form heteromeric complexes in co-transfected HEK-293T cells and rat striatum, where they colocalize in fibrilar structures. In a human neuroblastoma cell line, CB1 receptor signaling was found to be completely dependent on A2A receptor activation. Accordingly, blockade of A2A receptors counteracted the motor depressant effects produced by the intrastriatal administration of a cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonist. These biochemical and behavioral findings demonstrate that the profound motor effects of cannabinoids depend on physical and functional interactions between striatal A2A and CB1 receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Andersson M, Usiello A, Borgkvist A, Pozzi L, Dominguez C, Fienberg AA et al (2005). Cannabinoid action depends on phosphorylation of dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of 32 kDa at the protein kinase A site in striatal projection neurons. J Neurosci 25: 8432–8438.
Agnati LF, Ferré S, Lluis C, Franco R, Fuxe K (2003). Molecular mechanisms and therapeutical implications of intramembrane receptor/receptor interactions among heptahelical receptors with examples from the striatopallidal GABA neurons. Pharmacol Rev 55: 509–550.
Agnati LF, Fuxe K, Ferré S (2005). How receptor mosaics decode transmitter signals. Possible relevance of cooperativity. Trends Biochem Sci 30: 188–193.
Bidaut-Russell M, Devane WA, Howlett AC (1990). Cannabinoid receptors and modulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in the rat brain. J Neurochem 55: 21–26.
Chen JF, Huang Z, Ma J, Zhu J, Moratalla R, Standaert D et al (1999). A(2A) adenosine receptor deficiency attenuates brain injury induced by transient focal ischemia in mice. J Neurosci 19: 9192–9200.
Ciruela F, Casado V, Rodrigues RJ, Lujan R, Burgueno J, Canals M et al (2006). Presynaptic control of striatal glutamatergic neurotransmission by adenosine A1-A2A receptor heteromers. J Neurosci 26: 2080–2087.
Cunha RA, Constantino MD, Ribeiro JA (1997). ZM241385 is an antagonist of the facilitatory responses produced by the A2A adenosine receptor agonists CGS21680 and HENECA in the rat hippocampus. Br J Pharmacol 122: 1279–1284.
Darmani NA (2001). Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol and synthetic cannabinoids prevent emesis produced by the cannabinoid CB(1) receptor antagonist/inverse agonist SR 141716A. Neuropsychopharmacology 24: 198–203.
Demuth DG, Molleman A (2006). Cannabinoid signalling. Life Sci 78: 549–563.
Felder CC, Joyce KE, Briley EM, Mansouri J, Mackie K, Blond O et al (1995). Comparison of the pharmacology and signal transduction of the human cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Mol Pharmacol 48: 443–450.
Ferré S, Borycz J, Goldberg SR, Hope BT, Morales M, Lluis C et al (2005). Role of adenosine in the control of homosynaptic plasticity in striatal excitatory synapses. J Integr Neurosci 4: 445–464.
Ferré S, Fredholm BB, Morelli M, Popoli P, Fuxe K (1997). Adenosine-dopamine receptor–receptor interactions as an integrative mechanism in the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci 20: 482–487.
Franco R, Canals M, Marcellino D, Ferré S, Agnati L, Mallol J et al (2003). Regulation of heptaspanning-membrane-receptor function by dimerization and clustering. Trends Biochem Sci 28: 238–243.
Franco R, Casado V, Mallol J, Ferré S, Fuxe K, Cortes A et al (2005). Dimer-based model for heptaspanning membrane receptors. Trends Biochem Sci 30: 360–366.
Fusco FR, Martorana A, Giampa C, De March Z, Farini D, D'Angelo V et al (2004). Immunolocalization of CB1 receptor in rat striatal neurons: a confocal microscopy study. Synapse 53: 159–167.
George SR, O'Dowd BF, Lee SP (2002). G-protein-coupled receptor oligomerization and its potential for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1: 808–820.
Gerfen CR (2004). Basal Ganglia. In: Paxinos G (ed). The Rat Nervous System. Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam. pp 445–508.
Gifford AN, Bruneus M, Gatley SJ, Lan R, Makriyannis A, Volkow ND (1999). Large receptor reserve for cannabinoid actions in the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288: 478–483.
Gough AL, Olley JE (1978). Catalepsy induced by intrastriatal injections of delta9-THC and 11-OH-delta9-THC in the rat. Neuropharmacology 17: 137–144.
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, de Costa BR, Richfield EK (1991). Neuronal localization of cannabinoid receptors in the basal ganglia of the rat. Brain Res 547: 267–274.
Hettinger BD, Lee A, Linden J, Rosin DL (2001). Ultrastructural localization of adenosine A2A receptors suggests multiple cellular sites for modulation of GABAergic neurons in rat striatum. J Comp Neurol 431: 331–346.
Hillard CJ, Manna S, Greenberg MJ, DiCamelli R, Ross RA, Stevenson LA et al (1999). Synthesis and characterization of potent and selective agonists of the neuronal cannabinoid receptor (CB1). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289: 1427–1433.
Hillion J, Canals M, Torvinen M, Casado V, Scott R, Terasmaa A et al (2001). Coaggregation, cointernalization, and codesensitization of adenosine A2A receptors and dopamine D2 receptors. J Biol Chem 277: 18091–18097.
Hohmann AG, Herkenham M (2000). Localization of cannabinoid CB(1) receptor mRNA in neuronal subpopulations of rat striatum: a double-label in situ hybridization study. Synapse 37: 71–80.
Howlett AC, Song C, Berglund BA, Wilken GH, Pigg JJ (1998). Characterization of CB1 cannabinoid receptors using receptor peptide fragments and site-directed antibodies. Mol Pharmacol 53: 504–510.
Julian MD, Martin AB, Cuellar B, Rodriguez De Fonseca F, Navarro M, Moratalla R et al (2003). Neuroanatomical relationship between type 1 cannabinoid receptors and dopaminergic systems in the rat basal ganglia. Neuroscience 119: 309–318.
Karcz-Kubicha M, Antoniou K, Terasmaa A, Quarta D, Solinas M, Justinova Z et al (2003). Involvement of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors in the motor effects of caffeine after its acute and chronic administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 28: 1281–1291.
Klegeris A, Bissonnette CJ, McGeer PL (2003). Reduction of human monocytic cell neurotoxicity and cytokine secretion by ligands of the cannabinoid-type CB2 receptor. Br J Pharmacol 139: 775–786.
Kofalvi A, Rodrigues RJ, Ledent C, Mackie K, Vizi ES, Cunha RA et al (2005). Involvement of cannabinoid receptors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release in the rodent striatum: a combined immunochemical and pharmacological analysis. J Neurosci 25: 2874–2884.
Kull B, Ferré S, Arslan G, Svenningsson P, Fuxe K, Owman C et al (1999). Reciprocal interactions between adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptors in Chinese hamster ovary cells co-transfected with the two receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 58: 1035–1045.
Lan R, Liu Q, Fan P, Lin S, Fernando SR, McCallion D et al (1999). Structure–activity relationships of pyrazole derivatives as cannabinoid receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 42: 769–776.
Ledent C, Valverde O, Cossu G, Petitet F, Aubert JF, Beslot F et al (1999). Unresponsiveness to cannabinoids and reduced addictive effects of opiates in CB1 receptor knockout mice. Science 283: 401–404.
Maggio R, Novi F, Scarselli M, Corsini GU (2005). The impact of G-protein-coupled receptor hetero-oligomerization on function and pharmacology. FEBS J 272: 2939–2946.
Sanudo-Pena MC, Tsou K, Walker JM (1999). Motor actions of cannabinoids in the basal ganglia output nuclei. Life Sci 65: 703–713.
Rodriguez JJ, Mackie K, Pickel VM (2001). Ultrastructural localization of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor in mu-opioid receptor patches of the rat caudate putamen nucleus. J Neurosci 21: 823–833.
Salim H, Ferré S, Dalal A, Peterfreund RA, Fuxe K, Vincent JD et al (2000). Activation of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors modulates dopamine D2 receptor-induced responses in stably transfected human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 74: 432–439.
Sauer R, Maurinsh J, Reith U, Fulle F, Klotz KN, Muller CE (2000). Water-soluble phosphate prodrugs of 1-propargyl-8-styrylxanthine derivatives, A(2A)-selective adenosine receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 43: 440–448.
Soria G, Castane A, Berrendero F, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Maldonado R et al (2004). Adenosine A2A receptors are involved in physical dependence and place conditioning induced by THC. Eur J Neurosci 20: 2203–2213.
Twitchell W, Brown S, Mackie K (1997). Cannabinoids inhibit N- and P/Q-type calcium channels in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 78: 43–50.
van der Stelt M, Di Marzo V (2003). The endocannabinoid system in the basal ganglia and in the mesolimbic reward system: implications for neurological and psychiatric disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 480: 133–150.
Yao L, Fan P, Jiang Z, Mailliard WS, Gordon AS, Diamond I (2003). Addicting drugs utilize a synergistic molecular mechanism in common requiring adenosine and Gi-beta gamma dimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 14379–14384.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by grants from Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología (SAF2005-00903 to FC and SAF2005-00170 to EIC and SAF2003-04864 and PNSD to RM) and in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carriba, P., Ortiz, O., Patkar, K. et al. Striatal Adenosine A2A and Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Form Functional Heteromeric Complexes that Mediate the Motor Effects of Cannabinoids. Neuropsychopharmacol 32, 2249–2259 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301375
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301375
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Neuronal and astrocytic CB1R signaling differentially modulates goal-directed behavior and working memory by distinct temporal mechanisms
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Cannabidiol improves thyroid function via modulating vitamin D3 receptor in vitamin D3 deficiency diet-induced rat model
Journal of Food Science and Technology (2022)
-
Adenosine receptor signalling in Alzheimer’s disease
Purinergic Signalling (2022)
-
Epidemiological overview of multidimensional chromosomal and genome toxicity of cannabis exposure in congenital anomalies and cancer development
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Cannabinoids Exacerbate Alcohol Teratogenesis by a CB1-Hedgehog Interaction
Scientific Reports (2019)