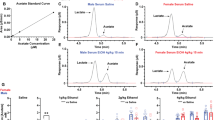
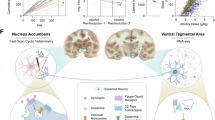
Abstract
Components of the mesolimbic dopamine system, in particular dopaminergic cells in the ventral tegmental area (VTA), have been implicated in the acute reinforcing actions of ethanol. The ventral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (vBNST) potently regulates dopaminergic cell firing in the VTA, and has been implicated in the behavioral actions of ethanol. The N-methyl-D-asparate receptor (NMDAR) is a major molecular target of ethanol, however, current evidence suggests that ethanol regulation of NMDAR function is widely variable and likely depends on a number of factors. Thus, it is critical to investigate ethanol regulation of NMDAR function at synapses relevant to ethanol-regulated behaviors, such as in the vBNST. Here we show, using multiple techniques, that ethanol inhibits NMDAR function in vBNST neurons in a postsynaptic fashion. Further, we demonstrate the functional presence of both NR2A and NR2B-containing NMDARs in the vBNST. While genetic removal of NR2A did not alter the magnitude of ethanol inhibition, pharmacological blockade of NR2B rendered synaptically activated NMDARs insensitive to ethanol inhibition. Finally, we demonstrate that ethanol inhibits NMDARs in cells in the vBNST that project to the VTA, providing a direct means by which ethanol in the vBNST can modulate the dopaminergic system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bartlett TE, Bannister NJ, Collett VJ, Dargan SL, Massey PV, Bortolotto ZA et al (2006). Differential roles of NR2A and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in LTP and LTD in the CA1 region of two-week old rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 52: 60–70.
Berberich S, Punnakkal P, Jensen V, Pawlak V, Seeburg PH, Hvalby O et al (2005). Lack of NMDA receptor subtype selectivity for hippocampal long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 25: 6907–6910.
Boyce-Rustay JM, Holmes A (2005). Functional roles of NMDA receptor NR2A and NR2B subunits in the acute intoxicating effects of ethanol in mice. Synapse 56: 222–225.
Brodie MS, Pesold C, Appel SB (1999). Ethanol directly excites dopaminergic ventral tegmental area reward neurons. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23: 1848–1852.
Burow A, Day HE, Campeau S (2005). A detailed characterization of loud noise stress: intensity analysis of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis and brain activation. Brain Res 1062: 63–73.
Choi DC, Furay AR, Evanson NK, Ostrander MM, Ulrich-Lai YM, Herman JP (2007). Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis subregions differentially regulate hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity: implications for the integration of limbic inputs. J Neurosci 27: 2025–2034.
Chu B, Anantharam V, Treistman SN (1995). Ethanol inhibition of recombinant heteromeric NMDA channels in the presence and absence of modulators. J Neurochem 65: 140–148.
Crane JW, Buller KM, Day TA (2003). Evidence that the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis contributes to the modulation of hypophysiotropic corticotropin-releasing factor cell responses to systemic interleukin-1beta. J Comp Neurol 467: 232–242.
Cull-Candy SG, Leszkiewicz DN (2004). Role of distinct NMDA receptor subtypes at central synapses. Sci STKE 2004: re16.
Dumont EC, Mark GP, Mader S, Williams JT (2005). Self-administration enhances excitatory synaptic transmission in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Nat Neurosci 8: 413–414.
Dumont EC, Williams JT (2004). Noradrenaline triggers GABAA inhibition of bed nucleus of the stria terminalis neurons projecting to the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 24: 8198–8204.
Egli RE, Winder DG (2003). Dorsal and ventral distribution of excitable and synaptic properties of neurons of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J Neurophysiol 90: 405–414.
Eiler II WJ, June HL (2007). Blockade of GABA(A) receptors within the extended amygdala attenuates D(2) regulation of alcohol-motivated behaviors in the ventral tegmental area of alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Neuropharmacology 52: 1570–1579.
Eiler II WJ, Seyoum R, Foster KL, Mailey C, June HL (2003). D1 dopamine receptor regulates alcohol-motivated behaviors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Synapse 48: 45–56.
Engblom AC, Courtney MJ, Kukkonen JP, Akerman KE (1997). Ethanol specifically inhibits NMDA receptors with affinity for ifenprodil in the low micromolar range in cultured cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem 69: 2162–2168.
Erreger K, Dravid SM, Banke TG, Wyllie DJ, Traynelis SF (2005). Subunit-specific gating controls rat NR1/NR2A and NR1/NR2B NMDA channel kinetics and synaptic signalling profiles. J Physiol 563: 345–358.
Fink K, Gothert M (1996). Both ethanol and ifenprodil inhibit NMDA-evoked release of various neurotransmitters at different, yet proportional potency: potential relation to NMDA receptor subunit composition. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 354: 312–319.
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (1997). The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press: New York.
Frizelle PA, Chen PE, Wyllie DJ (2006). Equilibrium constants for (R)-[(S)-1-(4-bromo-phenyl)-ethylamino]-(2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquino xalin-5-yl)-methyl]-phosphonic acid (NVP-AAM077) acting at recombinant NR1/NR2A and NR1/NR2B N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors: Implications for studies of synaptic transmission. Mol Pharmacol 70: 1022–1032.
Fu Z, Logan SM, Vicini S (2005). Deletion of the NR2A subunit prevents developmental changes of NMDA-mEPSCs in cultured mouse cerebellar granule neurones. J Physiol 563: 867–881.
Georges F, Aston-Jones G (2001). Potent regulation of midbrain dopamine neurons by the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J Neurosci 21: RC160.
Georges F, Aston-Jones G (2002). Activation of ventral tegmental area cells by the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: a novel excitatory amino acid input to midbrain dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 22: 5173–5187.
Grillner P, Mercuri NB (2002). Intrinsic membrane properties and synaptic inputs regulating the firing activity of the dopamine neurons. Behav Brain Res 130: 149–169.
Harris GC, Aston-Jones G (2007). Activation in extended amygdala corresponds to altered hedonic processing during protracted morphine withdrawal. Behav Brain Res 176: 251–258.
Hatton CJ, Paoletti P (2005). Modulation of triheteromeric NMDA receptors by N-terminal domain ligands. Neuron 46: 261–274.
Hendricson AW, Sibbald JR, Morrisett RA (2004). Ethanol alters the frequency, amplitude, and decay kinetics of Sr2+-supported, asynchronous NMDAR mEPSCs in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol 91: 2568–2577.
Hyytia P, Koob GF (1995). GABAA receptor antagonism in the extended amygdala decreases ethanol self-administration in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 283: 151–159.
Izumi Y, Nagashima K, Murayama K, Zorumski CF (2005). Acute effects of ethanol on hippocampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression are mediated by different mechanisms. Neuroscience 136: 509–517.
Jin C, Woodward JJ (2006). Effects of 8 different NR1 splice variants on the ethanol inhibition of recombinant NMDA receptors. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30: 673–679.
Kash T, Winder DG (2007). NMDAR LTP and LTD induction: 2B or Not 2B is that the question? Debates Neurosci [E-pub ahead of print].
Kiyama Y, Manabe T, Sakimura K, Kawakami F, Mori H, Mishina M (1998). Increased thresholds for long-term potentiation and contextual learning in mice lacking the NMDA-type glutamate receptor epsilon1 subunit. J Neurosci 18: 6704–6712.
Lopez de Armentia M, Sah P (2003). Development and subunit composition of synaptic NMDA receptors in the amygdala: NR2B synapses in the adult central amygdala. J Neurosci 23: 6876–6883.
Lovinger DM (1995). Developmental decrease in ethanol inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat neocortical neurons: relation to the actions of ifenprodil. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274: 164–172.
Lovinger DM, White G, Weight FF (1989). Ethanol inhibits NMDA-activated ion current in hippocampal neurons. Science 243: 1721–1724.
Lu C, Fu Z, Karavanov I, Yasuda RP, Wolfe BB, Buonanno A et al (2006). NMDA receptor subtypes at autaptic synapses of cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurophysiol 96: 2282–2294.
Luo J, Wang Y, Yasuda RP, Dunah AW, Wolfe BB (1997). The majority of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complexes in adult rat cerebral cortex contain at least three different subunits (NR1/NR2A/NR2B). Mol Pharmacol 51: 79–86.
Maldve RE, Zhang TA, Ferrani-Kile K, Schreiber SS, Lippmann MJ, Snyder GL et al (2002). DARPP-32 and regulation of the ethanol sensitivity of NMDA receptors in the nucleus accumbens. Nat Neurosci 5: 641–648.
Mallon AP, Auberson YP, Stone TW (2005). Selective subunit antagonists suggest an inhibitory relationship between NR2B and NR2A-subunit containing N-methyl-D: -aspartate receptors in hippocampal slices. Exp Brain Res 162: 374–383.
Matys T, Pawlak R, Strickland S (2005). Tissue plasminogen activator in the bed nucleus of stria terminalis regulates acoustic startle. Neuroscience 135: 715–722.
Melendez RI, Rodd-Henricks ZA, Engleman EA, Li TK, McBride WJ, Murphy JM (2002). Microdialysis of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens of alcohol-preferring (P) rats during anticipation and operant self-administration of ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26: 318–325.
Mirshahi T, Woodward JJ (1995). Ethanol sensitivity of heteromeric NMDA receptors: effects of subunit assembly, glycine and NMDAR1 Mg(2+)-insensitive mutants. Neuropharmacology 34: 347–355.
Neyton J, Paoletti P (2006). Relating NMDA receptor function to receptor subunit composition: limitations of the pharmacological approach. J Neurosci 26: 1331–1333.
Pawlak R, Melchor JP, Matys T, Skrzypiec AE, Strickland S (2005). Ethanol-withdrawal seizures are controlled by tissue plasminogen activator via modulation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 443–448.
Philpot BD, Cho KK, Bear MF (2007). Obligatory role of NR2A for metaplasticity in visual cortex. Neuron 53: 495–502.
Popp RL, Lickteig R, Browning MD, Lovinger DM (1998). Ethanol sensitivity and subunit composition of NMDA receptors in cultured striatal neurons. Neuropharmacology 37: 45–56.
Popp RL, Lickteig RL, Lovinger DM (1999). Factors that enhance ethanol inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in cerebellar granule cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289: 1564–1574.
Rainnie DG (1999). Neurons of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST). Electrophysiological properties and their response to serotonin. Ann NY Acad Sci 877: 695–699.
Roberto M, Schweitzer P, Madamba SG, Stouffer DG, Parsons LH, Siggins GR (2004). Acute and chronic ethanol alter glutamatergic transmission in rat central amygdala: an in vitro and in vivo analysis. J Neurosci 24: 1594–1603.
Smothers CT, Clayton R, Blevins T, Woodward JJ (2001). Ethanol sensitivity of recombinant human N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Neurochem Int 38: 333–340.
Spencer SJ, Buller KM, Day TA (2005). Medial prefrontal cortex control of the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus response to psychological stress: possible role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J Comp Neurol 481: 363–376.
Suvarna N, Borgland SL, Wang J, Phamluong K, Auberson YP, Bonci A et al (2005). Ethanol alters trafficking and functional N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR2 subunit ratio via H-Ras. J Biol Chem 280: 31450–31459.
Thomas CG, Miller AJ, Westbrook GL (2006). Synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptor NR2 subunits in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 95: 1727–1734.
Tovar KR, Westbrook GL (1999). The incorporation of NMDA receptors with a distinct subunit composition at nascent hippocampal synapses in vitro. J Neurosci 19: 4180–4188.
Vicini S, Wang JF, Li JH, Zhu WJ, Wang YH, Luo JH et al (1998). Functional and pharmacological differences between recombinant N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Neurophysiol 79: 555–566.
Walker DL, Toufexis DJ, Davis M (2003). Role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis versus the amygdala in fear, stress, and anxiety. Eur J Pharmacol 463: 199–216.
Weitlauf C, Egli RE, Grueter BA, Winder DG (2004). High-frequency stimulation induces ethanol-sensitive long-term potentiation at glutamatergic synapses in the dorsolateral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J Neurosci 24: 5741–5747.
Weitlauf C, Honse Y, Auberson YP, Mishina M, Lovinger DM, Winder DG (2005). Activation of NR2A-containing NMDA receptors is not obligatory for NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 25: 8386–8390.
Xu M, Woodward JJ (2006). Ethanol inhibition of NMDA receptors under conditions of altered protein kinase A activity. J Neurochem 96: 1760–1767.
Zhang TA, Hendricson AW, Morrisett RA (2005). Dual synaptic sites of D(1)-dopaminergic regulation of ethanol sensitivity of NMDA receptors in nucleus accumbens. Synapse 58: 30–44.
Zhu W, Bie B, Pan ZZ (2007). Involvement of non-NMDA glutamate receptors in central amygdala in synaptic actions of ethanol and ethanol-induced reward behavior. J Neurosci 27: 289–298.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by INIA-STRESS (NIAAA) and an NRSA F32 award (NIAAA). We thank Dr Roger Colbran for critical comments on a previous version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Disclosure/Conflict of Interest
Dr Kash declares that, except for income received from primary employer, no financial support or compensation has been received from any individual or corporate entity over the past 3 years for research or professional service. Dr Matthews received compensation from Meharry Medical College. Dr Winder received a distribution from Columbia University for the licensing of transgenic mouse technology to Memory Pharmaceuticals and received a consultancy fee from MEDAcorp. All of the authors declare that there are no personal financial holdings that could be perceived as constituting a potential conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kash, T., Matthews, R. & Winder, D. Alcohol Inhibits NR2B-Containing NMDA Receptors in the Ventral Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis. Neuropsychopharmacol 33, 1379–1390 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301504
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301504
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Influence of combined treatment with naltrexone and memantine on alcohol drinking behaviors: a phase II randomized crossover trial
Neuropsychopharmacology (2020)
-
Ethanol-induced conditioned place preference and aversion differentially alter plasticity in the bed nucleus of stria terminalis
Neuropsychopharmacology (2019)
-
GluN2B Subunit of the NMDA Receptor: The Keystone of the Effects of Alcohol During Neurodevelopment
Neurochemical Research (2019)
-
The Regulation of GluN2A by Endogenous and Exogenous Regulators in the Central Nervous System
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2017)
-
Translational Research on Habit and Alcohol
Current Addiction Reports (2016)