Abstract
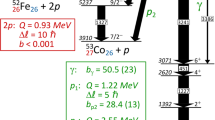
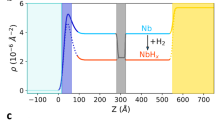
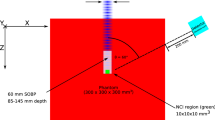
IT has been shown by Fermi and his collaborators1 that the efficiency of radioactivation of certain elements by neutron bombardment is greatly increased by surrounding them with water, paraffin or similar hydrogen-containing substances. This effect is attributed to multiple collisions between neutrons and protons, similar to those due to the thermal agitation of gas molecules, producing reduction in speed of the neutrons, which facilitates capture by other nuclei.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
La Ricerca Scientifica, V, 2, 7–8; 1934. V, 2, 380; 1934. VI, 1, 2; 1935.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOPWOOD, F., CHALMERS, T. Directed Diffusion or Canalisation of Slow Neutrons. Nature 135, 341–342 (1935). https://doi.org/10.1038/135341b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/135341b0
This article is cited by
-
Canalization of Gamma Rays
Nature (1938)
-
Absorption of Slow Neutrons
Nature (1936)