Abstract
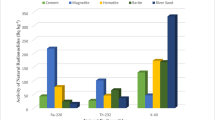
THE radioactivity of bottom sediments has been but little investigated. Data published by Joly, Pettersson, Piggot and Iimori refer to determinations of radium, contained mainly in oceanic deep-water sediments in red clays, radiolarian, globigerina oozes, blue muds and manganese concretions. The determinations have shown the manganese concretions to be richest as regards content of radium (up to 108 per cent); red clays and radiolarian ooze also possess a rather high content of radium. Other types of sediments are less rich in radium.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KURBATOV, L. Radioactivity of Ferro-Manganese Formations in Seas and Lakes of the U.S.S.R.. Nature 136, 871 (1935). https://doi.org/10.1038/136871a0
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/136871a0
This article is cited by
-
Photographische Bestimmung der Aktivitätsverteilung in einer Manganknolle der Tiefsee
Naturwissenschaften (1950)
-
Age of Ferro-Manganese Concretions
Nature (1936)