Abstract
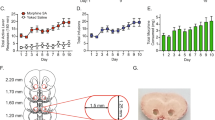
The following experiments were performed to ascertain the role of the nucleus accumbens in opiate-dopamine interactions using measures of locomotor activity. Three separate experiments were carried out. In Experiment 1, rats received systemic morphine (10 mg/kg IP) or saline (1 ml/kg IP) every other day for 5 days, followed by systemic amphetamine (1.5 mg/kg) 48 hours following the fifth injection. Animals in the morphine pretreatment group exhibited a sensitized locomotor response to amphetamine. In Experiment 2, animals received the same systemic pretreatment and were subsequently given intraaccumbens saline, amphetamine (2.5 μg/0.5 μl) or cocaine (7 μg/0.5 μl), each separated by 48 hours. Morphine-pretreated animals showed enhanced motor activity in response to intraaccumbens microinfusion of the psychostimulant drugs. Finally, in Experiment 3, multiple microinjections of morphine (0.5 μg/0.5 μl) directly into the nucleus accumbens resulted in a potentiated locomotor response to intraaccumbens amphetamine (2.5 μg/0.5 μl). These data indicate that the nucleus accumbens may contribute to both the development and expression of opiate-stimulant cross-sensitization. The neural basis of this sensitization is hypothesized to be a common intracellular pathway affected by both classes of drugs, such as the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP) system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cunningham, S., Finn, M. & Kelley, A. Sensitization of the Locomotor Response to Psychostimulants after Repeated Opiate Exposure: Role of the Nucleus Accumbens. Neuropsychopharmacol 16, 147–155 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(96)00166-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(96)00166-2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mechanisms of Locomotor Sensitization to Drugs of Abuse in a Two-Injection Protocol
Neuropsychopharmacology (2010)
-
The Ventral Pallidum is Critically Involved in the Development and Expression of Morphine-Induced Sensitization
Neuropsychopharmacology (2009)
-
Stimulant-induced psychosis and schizophrenia: The role of sensitization
Current Psychiatry Reports (2002)
-
Effects of α-adrenoceptor agonists in chronic morphine administered DSP4-treated rats: Evidence for functional cross-sensitization
Neurotoxicity Research (2001)