Abstract
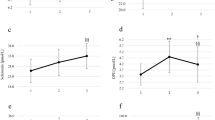
Several clinical studies suggest antidepressive and anxiolytic effects of regular aerobic exercise. To study the effects of exercise on central serotonergic receptor sensitivity, we performed neuroendocrine challenges using oral doses of meta-chlorophenylpiperazine (m-CPP, 0.4 mg/kg), ipsapirone (0.3 mg/kg) and placebo in 12 marathon runners and 12 healthy controls not practicing regular exercise. After administration of the nonselective serotonergic agonist m-CPP, which exerts a number of well-reproducible effects mainly by means of its action on 5-HT2C receptors, marathon runners showed a significantly reduced cortisol response in comparison to the control group. There was also a statistical trend toward a blunted prolactin response after m-CPP in the athlete group. In contrast, the increase of cortisol and the hypothermia observed after administration of the 5-HT1A agonist ipsapirone were of the same magnitude in both groups. The behavioral response to m-CPP or ipsapirone and the mean maximal increases of plasma adrenaline and noradrenaline did not differ between the marathon and the control group. In conclusion, exercise-induced downregulation of 5-HT2C receptors could play an important role in mediating the anxiolytic and antidepressive effects of exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aulakh CS, Hill JL, Murphy DL . (1992): Effects of various serotonin receptor subtype-selective antagonists alone and on m-chlorophenylpiperazine-induced neuroendocrine changes in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263: 588–595
Bailey SP, Davis JM, Ahlborn EN . (1992): Effect of increased brain serotonergic activity on endurance performance in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand 145: 75–76
Bailey SP, Davis JM, Ahlborn EN . (1993a): Neuroendocrine and substrate responses to altered brain 5-HT activity during prolonged exercise to fatigue. J Appl Physiol 74: 3006–3012
Bailey SP, Davis JM, Ahlborn EN . (1993b): Serotonergic agonists and antagonists affect endurance performance in the rat. Int J Sports Med 14: 330–333
Beckmann H, Ebert MH, Post R, Goodwin FK . (1979): Effect of moderate exercise on urinary MHPG in depressed patients. Pharmacopsychiatry 12
Blomstrand E, Celsing F, Newsholme EA . (1988): Changes in plasma concentrations of aromatic and branched-chain amino acids during sustained exercise in man and their possible role in fatigue. Acta Physiol Scand 133: 115–121
Borg G, Noble B . (1974): Perceived exertion. Exer Sports Sci Rev 2: 131–153
Brewerton TD, Murphy DL, Lesem MD, Brandt HA, Jimerson DC . (1992): Headache responses following m-chlorophenylpiperazine in bulimics and controls. Headache 32: 217–222
Broocks A, Bandelow B, Pekrun G, George A, Meyer TF, Bartmann U, Hillmer-Vogel U, Rüther E . (1998a): A comparison of aerobic exercise, clomipramine, and placebo in the treatment of panic disorder. Am J Psychiat 155: 603–609
Broocks A, George A, Jestrabek C, Optiz M, Bartmann U, Gleiter CH, Meineke I, Roed IS, Bandelow B, Hajak G, Rüther E . (1998b): Increased psychobehavioral sensitivity for both m-CPP and ipsapirone in patients with panic disorder. Psychiat Res (submitted).
Broocks A, Liu J, Pirke KM . (1990): Semistarvation-induced hyperactivity compensates for decreased norepinephrine and dopamine turnover in the mediobasal hypothalamus of the rat. J Neural Transm 79: 113–124
Broocks A, Meyer TF, Bandelow B, George A, Bartmann U, Rüther E, Hillmer-Vogel U . (1997): Exercise avoidance and impaiared endurance capacity in patients with panic disorder. Neuropsychobiology 36: 182–187
Broocks A, Schweiger U, Pirke KM . (1989): The influence of hyperactivity on the metabolism of central monoaminergic neurotransmitters and reproductive function in the semistarved rat. In Pirke KM, Wuttke W, Schweiger U, (eds), The Menstrual Cycle and its Disorders—Influences of Nutrition, Exercise, and Neurotransmitters. Berlin, Heidelberg, Springer Verlag pp 89–96
Broocks A, Schweiger U, Pirke KM . (1991): The influence of semistarvation-induced hyperactivity on hypothalamic serotonin metabolism. Physiol Behav 50: 385–388
Calogero AE, Bagdy G, Moncada ML, D'Agata R . (1993): Effect of selective serotonin agonists on basal, corticotrophin-releasing hormone- and vasopressin-induced ACTH release in vitro from rat pituitary cells. J Endocrinol 136: 381–387
Calogero AE, Bagdy G, Szemeredi K, Tartaglia ME, Gold PW, Chrousos GP . (1990): Mechanisms of serotonin receptor agonist-induced activation of the hypothalamic–pituitary-adrenal axis in the rat. Endocrinology 126: 1888–1894
Carr DB, Bullen BA, Skrinar GS, Arnold MA, Rosenblatt M, Beitins IZ, Martin JB, McArthur JW . (1981): Physical conditioning facilitates the exercise-induced secretion of beta-endorphin and beta-lipitropin in women. New Engl J Med 3: 560–563
Chaouloff F . (1994): Influence of physical exercise on 5-HT1A receptor- and anxiety-related behaviors. Neurosci Lett 176: 226–230
Chaouloff F . (1997): Effects of acute physical exercise on central serotonergic systems. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29: 58–62
Chaouloff F, Laude D, Elghozi JL . (1989): Physical exercise: Evidence for differential consequences of tryptophan on 5-HT synthesis and metabolism in central serotonergic cell bodies and terminal. J Neural Transm 78: 121–130
Chaouloff F, Laude D, Guezennec Y, Elghozi JL . (1986): Motor activity increases tryptophan, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, and homovanillic acid in ventricular cerebrospinal fluid of the conscious rat. J Neurochem 46: 1313–1316
Davis C, Brewer H, Ratusny D . (1993): Behavioral frequency and psychological commitment: Necessary concepts in the study of excessive exercising. J Behavioral Med 16: 611–628
Davis JM, Bailey SP, Woods JA, Galiano FJ, Hamilton MT, Bartoli WP . (1992): Effects of carbohydrate feedings on plasma-free tryptophan and branched-chain amino acids during prolonged cycling. Eur J Appl Physiol 65: 513–579
de Coverley Veale DMW . (1987): Exercise and mental health. Acta Psychiat Scand 76: 113–120
de Meirleir KL, L'Hermite-Baleriaux M, L'Hermite M, Rost R, Hollmann W . (1985): Evidence for serotoninergic control of exercise-induced prolactin secretion. Horm Metabol Res 17: 380–381
De Vry J, Glaser T, Schuurmann T, Schreiber R, Traber J . (1991): 5-HT1A receptors in anxiety. In Briley M (ed), New Concepts in Anxiety. London, McMillan
Dillon DJ, Gorman JM, Liebowitz MR, Fyer AJ, Klein DF . (1987): Measurement of lactate-induced panic and anxiety. Psychiat Res 20: 97–105
Dishman RK . (1997): Brain monoamines, exercise, and behavioral stress: Animal models. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29: 63–74
Doyne EJ, Ossip-Klein DJ, Bowman ED, Osborn KM, McDougall-Wilson IB, Neimeyer RA . (1987): Running versus weightlifting in the treatment of depression. J Consult Clin Psychol 55: 748–754
Dunn AL, Reigle TG, Youngstedt SG, Armstrong RB, Dishman RK . (1996): Brain norepinephrine and metabolites after treadmill training and wheel running in rats. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28: 204–209
Farmer ME, Locke BZ, Moscicki EK, Dannenberg AL, Larson DB, Radloff LS . (1988): Physical activity and depressive symptoms: The NHANES I epidemiological followup study. Am J Epidemiol 128: 1340–1351
Farrel PA . (1982): Increases in plasma β-endorphin/β-lipotropin immunoreactivity after treadmill running in humans. J Appl Physiol 52: 1245–1252
Fernstrom JD, Wurtman RJ . (1971): Brain serotonin content: Physiological dependence on plasma tryptophan levels. Science 173: 149–152
Fischer HG, Hollmann W, De Meirleir K . (1991): Exercise changes in plasma tryptophan fractions and relationship with prolactin. Int J Sports Med 12: 487–489
Gilliam PE, Spirduso WW, Martin TP, Walters TJ, Wilcox RE, Farrar RP . (1984): The effects of exercise training on [3H]-spiperone binding in rat striatum. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20: 863–867
Greenhouse SW, Geisser S . (1959): On methods in the analysis of profile data. Psychometrika 32: 95–112
Greist JH, Klein MH, Eischens RR, Faris J, Gurman AS, Morgan WP . (1979): Running as treatment for depression. Compr Psychiat 20: 41–54
Heuser IJ, Wark HJ, Keul J, Holsboer F . (1991): Hypothalamic–pituitary-adrenal axis function in elderly endurance athletes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 73: 485–488
Hollander E, DeCaria C, Nitescu A . (1992): Effects of chronic fluoxetine treatment on behavioral and neuroendocrine responses to m-CPP in obsessive–compulsive disorder. Psychiat Res 36: 1–17
Hughes JR . (1984): Psychological effects of habitual aerobic exercise: A critical review. Preventive Med 13: 66–78
Janal MN, Colt EWD, Clark WC, Glusman M . (1984): Pain sensitivity, mood, and plasma endocrine levels in man following long-distance running: Effects of naloxone. Pain 19: 13–25
Kahn RS, Trestman R, Lawlor BA, Gabriel S, Davidson M, Siever L . (1994): Effects of ipsapirone in healthy subjects: A dose-response study. Psychopharmacol Berl 114: 155–160
Kahn RS, Wetzler S . (1991): m-Chlorophenylpiperazine as a probe of serotonergic function. Biol Psychiat 30: 1139–1166
Kalin NH, Carnes M, Barksdale CM, Shelton SE, Stewart RD, Risch SC . (1985): Effects of acute behavioral stress on plasma and cerebrospinal fluid ACTH and beta-endorphin in rhesus monkeys. Neuroendocrinology 40: 97–101
Kennett GA, Whitton P, Shah K, Curzon G . (1989): Anxiogenic-like effects of mCPP and TFMPP in animal models are opposed by 5-HT1C receptor antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 164: 445–454
Krüger A, Wildmann J . (1986): Anstieg des β-Endorphinspiegels bei Wiederholungsbelastungen. D Zeitschr Sportmed 37: 245–250
Lennox SS, Bedell JR, Stone AA . (1990): The effect of exercise on normal mood. J Psychosom Res 34: 629–636
Lesch KP, Poten B, Sohnie K, Schulte HM . (1990): Pharmacology of the hypothermic response to 5-HT1A receptor activation in humans. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39: 17–19
Lesch KP, Rupprecht R, Poten B, Muller U, Sohnle K, Fritze J, Schulte HM . (1989): Endocrine responses to 5-hydroxytryptamine-1A receptor activation by ipsapirone in humans. Biol Psychiat 26: 203–205
Luger A, Deuster PA, Kyle SB, Gallucci WT, Montgomery LC, Gold PW, Leriaux DL, Chrousos GP . (1987): Acute hypothalamic–pituitary-adrenal responses to the stress of treadmill exercise. N Engl J Med 316: 1309–1315
MacMahon JR . (1990): The psychological benefits of exercise and the treatment of delinquent adolescents. Sports Med 9: 344–351
MacRae PG, Spirduso WW, Cartee GD, Farrar RP, Wilcox RE . (1987): Endurance training effects on striatal D2 dopamine receptor binding and striatal dopamine metabolite levels. Neurosci Lett 79: 138–144
Markoff RA, Ryan P, Young T . (1982): Endorphins and mood changes in long-distance running. Med Sci Sports Exerc 14: 11–15
Martinsen EW, Medhus A, Sandvik L . (1985): Effects of aerobic exercise on depression: A controlled study. Brit Med J 291: 109
Martinsen EW, Strand J, Paulsson G, Kaggestad J . (1989): Physical fitness level in patients with anxiety and depressive disorder. Int J Sports Med 10: 58–61
Mazzola-Pomietto P, Aulakh CS, Wozniak KM, Hill JL, Murphy DL . (1995): Evidence that 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI)-induced hyperthermia in rats is mediated by stimulation of 5-HT2A receptors. Psychopharmacology Berl 117: 193–199
McCann IL, Holmes DS . (1984): Influence of aerobic exercise on depression. J Personal Soc Psych 46: 1142–1147
Miyakoda H, Kitamura H, Kinuguwa T, Saito M, Kotake H, Mashiba H . (1990): Cardiac neurosis: Exercise tolerance and the role of sympathetic activity. Japan J Med 29: 493–499
Morgan ME, Yamamoto BK, Freed CR . (1984): Unilateral activation of caudate tyrosine hydroxylase during voluntary circling behavior. J Neurochem 43: 737–741
Murphy DL, Aulakh CS, Mazzola-Pomietto P, Briggs NC . (1996): Neuroendocrine responses to serotonergic agonists as indices of the functional status fo central serotonin neurotransmission in humans. Behav Brain Res 73: 209–214
Murphy DL, Lesch KP, Aulakh CS, Pigott TA . (1991): Serotonin-selective arylpiperazines with neuroendocrine, behavioral, temperature, and cardiovascular effects in humans. Pharmacol Rev 43: 527–552
Murphy DL, Mueller EA, Hill JL, Tolliver TJ, Jacobsen FM . (1989): Comparative anxiogenic, neuroendocrine, and other physiologic effects of m-chlorophenylpiperazine given intravenously or orally to healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacol Berl 98: 275–282
Oleshansky MA, Zoltick JM, Herman RH, Mougey EH, Meyerhoff JL . (1990): The influence of fitness on neuroendocrine responses to exhaustive treadmill exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 59: 405–410
Pappas GP, Golin S, Meyer DL . (1990): Reducing symptoms of depression with exercise. Psychosom 31: 112–113
Peroutka SJ . (1985): Selective interaction of novel anxiolytics with 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptors. Biol Psychiat 20: 971–979
Pigott TA, Hill JL, Grady TA, L'Heureux F, Bernstein S, Rubenstein CS, Murphy DL . (1993): A comparison of the behavioral effects of oral versus intravenous mCPP administration in OCD patients and the effect of metergoline prior to i.v. mCPP. Biol Psychiat 33: 3–14
Pirke KM, Schweiger U, Lemmel W, Krieg JC, Berger M . (1985): The influence of dieting on the menstrual cycle of healthy young women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 60: 1174–1179
Post RM, Kotin J, Goodwin FK, Gordon EK . (1973): Psychomotor activity and cerebrospinal fluid metabolites in affective illness. Am J Psychiat 130: 67–72
Przegalinski E, Budziszewska B, Warchol Kania A, Blaszczynska E . (1989): Stimulation of corticosterone secretion by the selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33: 329–334
Quested DJ, Sargent PA, Cowen PJ . (1997): SSRI treatment decreases prolactin and hyperthermic responses to mCPP. Psychopharmacology 133: 305–308
Roth DL . (1989): Acute emotional and psychophysiological effects of aerobic exercise. Psychophysiology 26: 593–602
Roth WT, Telch MJ, Taylor CB, Sachitano JA, Gallen CC, Kopell ML, McClenahen KL, Agras WS, Pfefferbaum A . (1986): Autonomic characteristics of agoraphobia with panic attacks. Biol Psychiat 21: 1133–1154
SAS. (1989): SAS User's Guides. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, North Carolina
Seibyl JP, Krystal JH, Price LH . (1991): Effects of ritanserin on the behavioral, neuroendocrine, and cardiovascular responses to m-CPP in human healthy subjects. Psychiat Res 38: 227–236
Sexton H, Maere A, Dahl NH . (1989): Exercise intensity and reduction in neurotic symptoms—A controlled follow-up study. Acta Psychiat Scand 80: 231–235
Sothman MS, Hart BA, Horn TS . (1992): Sympathetic nervous system and behavioral responses to stress following exercise training. Physiol & Behav 51: 1097–1103
Taylor CB, King R, Ehlers A, Margraf J, Clark D, Hayward C, Roth WT, Agras S . (1987): Treadmill exercise test and ambulatory measures in panic attacks. Am J Cardiol 60: 48J–52J
Wilckens T, Schweiger U, Pirke KM . (1992): Activation of alpha 2-adrenoceptors suppresses excessive wheel running in the semistarvation-induced hyperactive rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43: 733–738
Wildmann J, Krüger A, Schmole M, Niemann J, Matthaei H . (1986): increase of beta–endorphin-like immunoreactivity correlates with the change in feeling of pleasantness after running. Life Sci 38: 997–1003
Wurtman RJ, Fernstrom JD . (1976): Control of brain neurotransmitter synthesis by precursor availability and nutritional state. Biochem Pharmacol 25: 1691–1696
Zohar J, Insel TR, Zohar Kadouch RC, Hill JL, Murphy DL . (1988): Serotonergic responsivity in obsessive–compulsive disorder. Effects of chronic clomipramine treatment. Arch Gen Psychiat 45: 167–172
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a public grant from the Volkswagen Foundation, Hannover, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broocks, A., Meyer, T., George, A. et al. Decreased Neuroendocrine Responses to Meta-Chlorophenylpiperazine (m-CPP) but Normal Responses to Ipsapirone in Marathon Runners. Neuropsychopharmacol 20, 150–161 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00056-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00056-6
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Exercise in the treatment of clinical anxiety in general practice – a systematic review and meta-analysis
BMC Health Services Research (2018)
-
Exercise-Associated Changes in the Corticosterone Response to Acute Restraint Stress: Evidence for Increased Adrenal Sensitivity and Reduced Corticosterone Response Duration
Neuropsychopharmacology (2014)
-
Anxiety-like behaviors produced by acute fluoxetine administration in male Fischer 344 rats are prevented by prior exercise
Psychopharmacology (2008)