Abstract
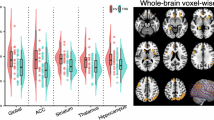
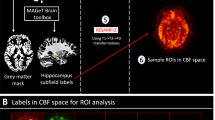
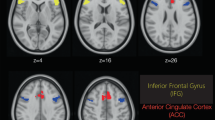
Recent functional neuroimaging strategies have evaluated cerebral blood flow (CBF) to determine specific sites of action of pharmacologic agents. Since many pharmacologic agents change global CBF, we investigated the effects of global CBF changes on regional perfusion with acetazolamide, which increases global CBF via non-neuronal mechanisms. We used the [15O]PET technique to measure CBF before and after we infused 8 schizophrenic patients and 10 healthy control subjects with acetazolamide. The rostral anterior cingulate cortex demonstrated a greater perfusion increase in the schizophrenic subjects after acetazolamide infusion, relative to other areas of the brain. During the baseline condition, this area showed relative hypoperfusion in our sample of schizophrenic subjects, consistent with previous functional neuroimaging studies. The results demonstrate the need for caution in interpreting CBF changes after pharmacologic challenge, because global CBF changes can confound the assessment of regionally-specific pharmacologic action.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
American Psychiatric Association. (1994): Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed (DSM-IV). Washington, DC, American Psychiatric Association
Andreasen NC, Rezai K, Alliger R, Swayze VW, Flaum M, Kirchner P, Cohen G, O'Leary DS . (1992): Hypofrontality in neuroleptic-naive patients and in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49: 943–958
Bonte FJ, Devous MD, Reisch JS . (1988): The effect of acetazolamide on regional cerebral blood flow in normal human subjects as measured by single-photon emission computed tomography. Invest Radiol 23: 564–568
Dolan RJ, Fletcher P, Frith CD, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS, Grasby PM . (1995): Dopaminergic modulation of impaired cognitive activation in the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia. Nature 378: 180–182
Edvinsson L, MacKenzie ET, McCulloch J . (1993): Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. New York, Raven Press
Haznedar MM, Buchsbaum MS, Luu C, Hazlett EA, Siegel BJ, Lohr J, Wu J, Haier RJ, Bunney WJ . (1997): Decreased anterior cingulate gyrus metabolic rate in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 154: 682–684
Holcomb HH, Cascella NG, Thaker GK, Medoff DR, Dannals RF, Tamminga CA . (1996): Functional sites of neuroleptic drug action in the human brain: PET/FDG studies with and without haloperidol. Am J Psychiatry 153: 41–49
Lahti AC, Holcomb HH, Medoff DR, Tamminga CA . (1995): Ketamine activates psychosis and alters limbic blood flow in schizophrenia. Neuroreport 6: 869–872
Lewis SW, Ford RA, Syed GM, Reveley AM, Toone BK . (1992): A controlled study of 99m-Tc-HMPAO single-photon emission imaging in chronic schizophrenia. Psychol Med 22: 27–35
Minoshima S, Berger KL, Lee KS, MM A . (1992): An automated method for rotational correction and centering of three-dimensional functional brain images. J Nuc Med 33: 1579–1585
Minoshima S, Koeppe RA, Frey KA, Kuhl DE . (1994): Anatomic standardization: Linear scaling and nonlinear warping of functional brain images. J Nucl Med 35: 1528–1537
Minoshima S, Koeppe RA, Mintun MA, Berger K, Taylor SF, Frey KA, Kuhl DE . (1993): Automated detection of the intercommissural (AC-PC) line for stereotactic localization of functional brain images. J Nuc Med 34: 322–329
Talairach J, Tournoux P . (1988): A Co-planar Stereotaxic Atlas of a Human Brain. Stuttgart, Thieme-Verlag
Tamminga CA, Thaker GK, Buchanan R, Kirkpatrick B, Alphs LD, Chase TN, Carpenter WT . (1992): Positron emission tomographic analysis of central D1 and D2 dopamine receptor occupancy in patients treated with classical neuroleptics and clozapine. Relation to extrapyramidal side effects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49: 538–544
Taylor SF, Tandon R, Koeppe RA . (1997): PET study of greater visual activation in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 154: 1296–1298
Vorstrup S, Henriksen L, Paulson OB . (1984): Effect of acetazolamide on cerebral blood flow and cerebral metabolic rate for oxygen. J Clin Invest 74: 1634–1639
Worsley KJ, Evans AC, Marrett S, Neelin P . (1992): A three-dimensional statistical analysis for CBF activation studies in human brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12: 900–918
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ann Arbor Veterans Administration Medical Center and a grant from the Scottish Rite Schizophrenia Research Program to the first author. Subject recruitment, screening and data collection were provided by Laura Decker, Lisa Becks, and JoAnn Goodson. Thanks are due to Kirk Frey for helpful suggestions on study design.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was previously presented at the Second International Conference on Functional Mapping of the Human Brain, Boston, MA, in June, 1996.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, S., Tandon, R. & Koeppe, R. Global Cerebral Blood Flow Increase Reveals Focal Hypoperfusion in Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol 21, 368–371 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00109-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00109-2