Abstract
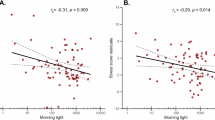
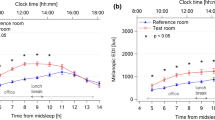
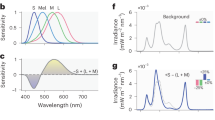
Both dim and bright light has been shown to suppress the nocturnal secretion of the pineal hormone melatonin. Early reports suggests that an abnormal response to light occurs in patients with bipolar affective disorder, where as patients with major depressive disorder respond similarly to controls. It has been suggested that this abnormal sensitivity of the melatonin response to light could be a trait marker of bipolar affective disorder. However reports lack consistency. Hence, we investigated the melatonin suppression by dim light (200 lux) in patients with bipolar affective disorder, seasonal affective disorder and major depressive disorder. Results suggest that a supersensitive melatonin suppression to light in bipolar affective disorder (p < .005), and seasonal affective disorder (p < .05), whereas patients with major depressive disorder display similar suppression to controls. The supersensitivity may be a mechanism where by phase-delayed rhythms, are re-synchronised to a new circadian position. Conversely, an abnormality may exist in the pathway from the retina to the suprachiamatic nucleus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
American Psychiatric Association. (1994): Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed. Washington, D.C, APA
Amir S . (1992): Blocking NMDA receptors or nitric oxide production disrupts light transmission to the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res 586: 336–339
Bojkowski CJ, Aldhous ME, English J, Franey C, Poulton AL, Skene DJ, Arendt J . (1987): Suppression of nocturnal plasma melatonin and 6-sulphatoxymelatonin by bright light and dim light in man. Horm Metabol Res 19: 437–440
Boyce P, Kennaway DJ . (1987): Effects of light on melatonin production. Biol Psychiatry 22: 473–478
Cassone VM, Warren WS, Brooks DS, Lu J . (1993): Melatonin the pineal gland and circadian rhythms. J Biol Rhythms 8(suppl):S73–S81
Cowell CS, Ralph MR, Menaker M . (1990): Do NMDA receptors mediate the effects of light on circadian behaviour. Brain Res 523: 117–120
Cowell CS, Foster RG, Menaker M . (1991): NMDA receptor antagonists block the effects of light on circadian behaviour in the mouse. Brain Res 554: 105–110
Cummings MA, Berga SL, Cummings KL, Kripte DF, Haviland MG, Golshan S, Gillin JC . (1989): Light suppression of melatonin in unipolar depressed patients. Psychiatry Res 27: 351–355
DeVries MJ, Cardozo BN, Vander Want J, DeWolf A, Meijer JH . (1993): Glutamate immunoreactivity in terminals of the retinohypothalamic tract of the Norwegian rat. Brain Res 506: 231–234
Duncan WC . (1996): Circadian rhythms and the pharmacology of affective illness. Pharmacol Ther 71 (3): 253–312
Fraser S, Cowen P, Franklin M, Franey C, Arendt J . (1983): A direct radioimmunoassay for melatonin. Clin Chem 29: 396–399
Kripke DlF, Mullaney DJ, Atkinson M, Wolf S . (1978): Circadian rhythm disorders in manic depressives. Biol Psychiatry 13: 335–351
Laakso ML, Porkka-Heiskanen T, Stenberg D, Alila A . (1991): Interindividual differences in the reponses of serum and salivary melatonin to light. In Fraschini F, Reiter RJ (eds), Role of Melatonin and Pineal Peptides in Neuroimmunomodulation. New York, Plenum Press, pp 1–60
Lam RW, Berkowitz AL, Berga SL, Clark CM, Krepke DF, Gillin JC . (1990): Melatonin suppression in bipolar and unipolar mood disorders. Psychiatry Res 32: 129–134
Lewy AJ, Wehr TA, Goodwin FK, Newsome DA, Markey SP . (1980): Light suppress melatonin secretion in humans. Science 210: 1267–1269
Lewy AJ, Wehr TA, Goodwin FK, Newsome DA, Rosenthal NE . (1981): Manic-depressive patients may be supersensitive to light. Lancet 1: 383–384
Lewy AJ, Brainard G, Menaker M . (1983): Fluence-response relationship between light radiance suppression of melatonin reduction and treatment of winter depression (letter). Neuroendocrinol Lett 5: 409
Lewy AJ, Nurnberger JI, Wehr TA, Pack D, Becker LE, Powell RL, Newsome DA . (1985): Supersensitivity to light: possible trait marker for manic-depressive illness. Am J Psychiatry 142 (6): 725–727
Lewy AJ, Sack RL . (1986): Biological Rhythms and behaviour in humans: the effect of light. In Dennerstein L, Fraser I (eds), Hormones and behaviour. New York, Elsevier, B.V
McIntyre IM, Norman TR, Burrows GD, Armstrong SM . (1989a): Human melatonin suppression by light is intensity dependent. J Pineal Res 6: 149–156
McIntyre IM, Norman TR, Burrows GD, Armstrong SM . (1990): Melatonin supersensitivity to dim light in seasonal affective disorder. Lancet 335: 488
Minors DS, Waterhouse JM . (1981): Circadian rhythm in patients with SAD. In Wright J (ed), Circadian Rhythms and the Human. London, Elsevier, pp 3–20
Mikkelsen JD, Larsen PJ, Mick G, Vrang N, Ebling FJP, Maywood ES, Hastings MH, Moller M . (1995): Gating of retinal imputs through the suprachiasmatic nucleus: role of excitatory neurotransmission. Neurochem Int 27 (3)): 263–272
Moore RY, Lenn NJ . (1972): A retinohypothalamic projection in the rat. J Comp Neurol 146: 1–14
Murphy DGM, Abas M, Winton F . (1990): A neurophysiological approach. In Thompson C, Silverstone T (eds), Seasonal Affective Disorders. London, Farrand Press, pp 233–242
Nurnberger JI, Berrettini WH, Tamrkin L, Hamovit J . (1988): Supersensitivity to light in youg people at high risk for affective disorder: a priliminary report. Neuropsychopharmacology 1 (3): 217–223
Ohi K, Takashima M, Nishihawa T, Takahashi K . (1993): N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor participates in neural transmission of photic information through the hypothalamic tract. Neuroendocrinology 53: 344–348
Poeggeler BH, Barlow-Walden LR, Reiter RJ, Sarela S, Pelaez AM, Yaga K, Manchester LC, Chen LD . (1995): Red light induced suppression of melatonin synthesis is mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation in retinally normal and retinally degererate rats. J Neurobiol 28 (1): 1–8
Rosenthal NE, Sack DA, Gillin JC, Lewy AJ, Goodwin FK, Davenport Y, Mueller PS, Newsome DA, Wehr TA . (1984): Seasonal affective disorder. A description of the syndrome and preliminary findings with light therapy. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41: 72–80
Silverstone T, Romans S, Hunt N, McPherson H . (1994): Is there a seasonal pattern of relapse in bipolar affective disorder? A dual northern and southern heisphere study. Br J Psychiatry 167: 58–60
SPSS . (1986): SPSSX Users Manual. Mahwah, New Jersey, McGraw-Hill Book Company & SPSS Inc, pp 863
Thompson C, Stinson D, Smith A . (1990): Seasonal affective disorder and season-dependent abnormalities of melatonin suppression by light. Lancet 336: 703–706
Vaughan GM, Bell R, De La Pena . (1979): Nocturnal plama melatonin in humans: episodic pattern and influence of light. Neurosci Lett 14: 81–84
Whalley LJ, Perini T, Shering A, Bennie J . (1990): Melatonin response to bright light in recovered, drug free, bipolar patients. Pscyhiatry Res 38: 13–19
Wehr TA, Goodwin FK . (1981): Biological rhythms and psychiatry. In Arieti S (ed), American Handbook of Psychiatry, 2nd ed., vol 7. New York, Basic Books, pp 320–340
Wehr TA . (1992): Seasonal vulnerability to depression: Implications for etiology and treatment. L'Encephale XVIII: 479–483
Acknowledgements
Authors wish to thank the Theodore & Vada Stanley Foundation for their financial support, and Angela Komiti and Jacqueline McGrath for their assistance during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nathan, P., Burrows, G. & Norman, T. Melatonin Sensitivity to Dim White Light in Affective Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacol 21, 408–413 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00018-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00018-4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Seasonality of brain function: role in psychiatric disorders
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
-
Sleep disturbances in the context of neurohormonal dysregulation in patients with bipolar disorder
International Journal of Bipolar Disorders (2022)
-
Hypnotic and Melatonin/Melatonin-Receptor Agonist Treatment in Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
CNS Drugs (2022)
-
Melanopsin-mediated pupillary responses in bipolar disorder—a cross-sectional pupillometric investigation
International Journal of Bipolar Disorders (2021)
-
Use of “Lights” for Bipolar Depression
Current Psychiatry Reports (2019)