Abstract
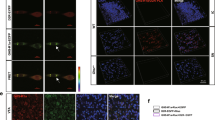
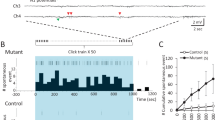
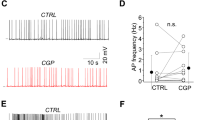
S(-)3-amino-1-hydroxypyrrolidone-2 (S(-)HA-966), a potent γ-hydroxybutyrate-like drug, inhibits spontaneous firing and induces a pacemaker-like discharge pattern in nigral dopamine (DA)-containing neurons. Recent evidence has suggested that these effects could be mediated by GABAB receptors and, thus, is likely to involve G protein intermediaries. To test this hypothesis, extracellular single-unit recording techniques were used to assess the effects of S(-)HA-966 in animals that had received an intranigral injection of pertussis toxin (PT). Failure to respond to the inhibitory effects of apomorphine was taken as presumptive evidence that PT-sensitive G protein-coupled receptors had been inactivated. No significant differences were observed in the basal firing properties of DA cells recorded in control and PT-lesioned animals. However, in marked contrast to the inhibitory effects observed in uninjected and sham-lesioned animals, S(-)HA-966 significantly increased the firing rate of apomorphine-insensitive DA neurons in PT-lesioned rats. The excitatory effects of S(-)HA-966 were accompanied by a significant reduction in bursting activity and an increase in the regularity of firing. These data indicate that the inhibitory effects of S(-)HA-966 are mediated locally within the substantia nigra by a PT-sensitive substrate, presumably a G protein-coupled receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Akaoka H, Charlety P, Saunier CF, Buda M, Chouvet G . (1992): Inhibition of nigral dopamine neurons by systemic and local apomorphine: Possible contribution of dendritic autoreceptors. Neuroscience 49: 879–891
Andrade R, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA . (1986): A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science 234: 1261–1265
Baring MD, Walters JR, Eng N . (1980): Action of systemic apomorphine on dopamine cell firing after neostriatal kainic acid lesion. Brain Res 181: 214–218
Bernasconi R, Lauber J, Marescaux C, Vergnes M, Martin P, Rubio V, Leonhardt T, Reymann N, Bittiger H . (1992): Experimental absence seizures: Potential role of gammahydroxybutyric acid and GABAB receptors. J Neural Transm Suppl 35: 155–177
Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Bowery N . (1998): GABAB receptors: Drugs meet clones. Curr Opinion Neurobiol 8: 345–350
Bonta IL, De Vos CJ, Grijsen H, Hillen FC, Noach EL, Sim AW . (1971): 1-Hydroxy-3-amino-pyrrolidone-2(HA966): A new GABA-like compound, with potential use in extrapyramidal diseases. Br J Pharmacol 43: 514–535
Bunney BS, Walters JR, Roth RH, Aghajanian GK . (1973): Dopaminergic neurons: Effect of antipsychotic drugs and amphetamine on single cell activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 185: 560–571
Diana M, Mereu G, Mura A, Fadda F, Passino N, Gessa G . (1991): Low doses of gammahydroxybutyric acid stimulate the firing rate of dopaminergic neurons in unanesthetized rats. Brain Res 566: 208–211
Engberg G, Nissbrandt H . (1993): Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHBA) induces pacemaker activity and inhibition of substantia nigra dopamine neurons by activating GABAB-receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 348: 491–497
Erhardt S, Andersson B, Nissbrandt H, Engberg G . (1998): Inhibition of firing rate and changes in the firing pattern of nigral dopamine neurons by gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHBA) are specifically induced by activation of GABA(B) receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 357: 611–619
Gähwiler BH, Brown DA . (1985): GABAB-receptor-activated K+ current in voltage-clamped CA3 pyramidal cells in hippocampal cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 1558–1562
Gallimberti L, Ferri M, Ferrara SD, Fadda F, Gessa GL . (1992): Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in the treatment of alcohol dependence: A double-blind study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 16: 673–676
Gallimberti L, Cibin M, Pagnin P, Sabbion R, Pani PP, Pirastu R, Ferrara SD, Gessa GL . (1993): Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid for treatment of opiate withdrawal syndrome. Neuropsychopharmacology 9: 77–81
Gessa GL, Vargiu I, Crabai F, Boero GC, Caboni F, Camba R . (1966): Selective increase of brain dopamine induced by gamma-hydroxybutyrate. Life Sci 5: 1921–1930
Grace AA, Bunney BS . (1984): The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: Burst firing. J Neurosci 4: 2877–2890
Grobaski KC, Ping H, da Silva HM, Bowery NG, Connelly ST, Shepard PD . (1997): Responses of rat substantia nigra dopamine-containing neurones to (-)HA-966 in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 120: 575–580
Hechler V, Ratomponirina C, Maittre M . (1997): γ-Hydroxybutyrate conversion into GABA induces displacement of GABAB binding that is blocked by valproate and ethosuximide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281: 753–760
Hillen FC, Noach EL . (1971): The influence of 1-hydroxy-3-amino-pyrrolidone-2 (HA-966) on dopamine metabolism in the rat corpus striatum. Eur J Pharmacol 16: 222–224
Innis RB, Aghajanian GK . (1987): Pertussis toxin blocks autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of dopaminergic neurons in rat substantia nigra. Brain Res 411: 139–143
Jentsch JD, Elsworth JD, Redmond DE Jr, Roth RH . (1997): Phencyclidine increases forebrain monoamine metabolism in rats and monkeys: Modulation by the isomers of HA-966. J Neurosci 17: 1769–1775
Kim KM, Nakajima Y, Nakajima S . (1995): G protein-coupled inward rectifier modulated by dopamine agonists in cultured substantia nigra neurons. Neuroscience 69: 1145–1158
Koenig JFR, Klippel RA . (1963): The Rat Brain: A Stereotaxic Atlas. Baltimore, Williams & Wilkins
Kreiss DS, Bergstrom DA, Gonzalez AM, Huang KX, Sibley DR, Walters JR . (1995): Dopamine receptor agonist potencies for inhibition of cell firing correlate with dopamine D3 receptor binding affinities. Eur J Pharmacol 277: 209–214
Lüscher C, Jan LY, Stoffel M, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA . (1997): G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ channels (GIRKs) mediate postsynaptic but not presynaptic transmitter actions in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 19: 687–695
Madden TE, Johnson SW . (1998): Gamma-hydroxybutyrate is a GABAB receptor agonist that increases a potassium conductance in rat ventral tegmental dopamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287: 261–265
Maitre M . (1997): The gamma-hydroxybutyrate signaling system in brain: Organization and functional implications. Prog Neurobiol 51: 337–361
Martin LP, Cox RF, Waszczak BL . (1990): Efficacy and potency comparisons among apomorphine enantiomers: Effects on dopamine neurons in substantia nigra of rat. Neuropharmacology 29: 135–143
Misgeld U, Bijak M, Jarolimek W . (1995): A physiological role for GABAB receptors and the effects of baclofen in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 46: 423–462
Möhler H, Fritschy J-M . (1999): GABAB receptors make it to the top–as dimers. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20: 87–89
Morrow BA, Lee EJK, Taylor JR, Elsworth JD, Nye HE, Roth RH . (1997): S)-(-)HA-966, a gamma-hydroxybutyrate-like agent, prevents enhanced mesocorticolimbic dopamine metabolism and behavioral correlates of restraint stress, conditioned fear, and cocaine sensitization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283: 712–721
Newberry NR, Nicoll RA . (1984): Direct hyperpolarizing action of baclofen on hippocampal pyramidal cells. Nature 308: 450–452
Nissbrandt H, Engberg G . (1996): The GABAB-receptor antagonist, CGP 35348, antagonizes gamma-hydroxybutyrate and baclofen-induced alterations in locomotor activity and forebrain dopamine levels in mice. J Neural Transm 103: 1255–1263
Overton PG, Clark D . (1997): Burst firing in midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 25: 312–334
Ratomponirina C, Hode Y, Hechler V, Maitre M . (1995): Gamma-hydroxybutyrate receptor binding in rat brain is inhibited by guanyl nucleotides and pertussis toxin. Neurosci Lett 189: 51–53
Reisine T . (1990): Pertussis toxin in the analysis of receptor mechanisms. Biochem Pharmacol 39: 1499–1504
Roth RH, Walters JR, Aghajanian GK . (1973): Effects of impulse flow on the release and synthesis of dopamine in the rat striatum. In Usdin E. Synder SH (eds), Frontiers in Catecholamine Research. New York, Pergamon Press, pp 567–574
Shepard PD, Connelly ST, Lehmann H, Grobaski KC . (1995): Effects of the enantiomers of (+/−)HA-966 on dopamine neurons: An electrophysiological study of a chiral molecule. Eur J Pharmacol 285: 79–88
Shepard PD, Lehmann H . (1992): ±)-1-Hydroxy-3-aminopyrrolidone-2 (HA-966) inhibits the activity of substantia nigra dopamine neurons through a non-N-methyl-D-aspartate-mediated mechanism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261: 387–394
Singh L, Donald AE, Foster AC, Hutson PH, Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Kemp JA, Leeson PD, Marshall GR, Oles RJ et-al . (1990): Enantiomers of HA-966 (3-amino-1-hydroxypyrrolid-2-one) exhibit distinct central nervous system effects: (+)HA-966 is a selective glycine/N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, but (-)-HA-966 is a potent gamma-butyrolactone-like sedative. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 347–351
Snead OC . (1992): Evidence for G protein modulation of experimental-generalized absence seizures in rat. Neurosci Lett 148: 15–18
Snead OC . (1988): Gamma-hydroxybutyrate model of generalized absence seizures: Further characterization and comparison with other absence models. Epilepsia 29: 361–368
Snead OC . (1996): Relation of the [3H]γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) binding site to the γ-aminobutyric acidB (GABAB) receptor in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 52: 1235–1243
Thompson SM, Gähwiler BH . (1992): Comparison of the actions of baclofen at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol Lond 451: 329–345
Waldmeier PC . (1991): The GABAB antagonist, CGP 35348, antagonizes the effects of baclofen, gammabutyrolactone, and HA-966 on rat striatal dopamine synthesis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 343: 173–178
Werner G, Mountcastle VB . (1963): The variability of central neural activity in a sensory system and its implications for the central reflection of sensory events. J Neurophysiol 26: 958–977
Wess J . (1998): Molecular basis of receptor/G-protein-coupling selectivity. Pharmacol Ther 80: 231–264
Williams SR, Turner JP, Crunelli V . (1995): Gamma-hydroxybutyrate promotes oscillatory activity of rat and cat thalamocortical neurons by a tonic GABAB, receptor-mediated hyperpolarization. Neuroscience 66: 133–141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shepard, P., Connelly, S. Pertussis Toxin Lesions of the Rat Substantia Nigra Block the Inhibitory Effects of the γ-Hydroxybutyrate Agent, S(-)HA-966 without Affecting the Basal Firing Properties of Dopamine Neurons. Neuropsychopharmacol 21, 650–661 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00063-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00063-9