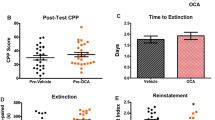
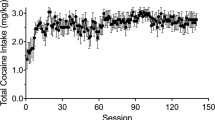
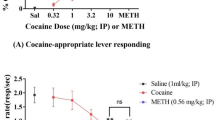
Abstract
Chronic cocaine use has been shown to produce neurochemical alterations which persist after acute withdrawal. This study assessed the effects of cocaine use on the acoustic startle response and sensorimotor gating using prepulse inhibition (PPI) of startle. Nine male control subjects (mean age = 41.6) and 15 male cocaine users (mean age = 43.2) were tested, the latter after heavy cocaine use ranging from 4 to 27 years (mean age = 16.7). Cocaine users had been cocaine free for four days to six months (mean = 17 days) at testing. Cocaine users exhibited a 68% reduction in startle amplitudes (F = 7.4; df = 1,22; p < .01) compared to controls. There were trends towards increased PPI in cocaine users under certain conditions; however, there were no significant main effects. These results indicate that chronic cocaine use produces impairment of the startle response which persists after cessation of cocaine use. These findings may reflect changes in the dopaminergic system resulting from chronic cocaine use.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abduljawad KA, Langley RW, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E . (1997): Effects of clonidine and diazepam on the acoustic startle response and its inhibition by ‘prepulses’ in man. J Psychopharmacol 11: 29–34
Adams LM, Geyer MA . (1981): Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of locus coeruleus on startle in rats. Psychopharmacology 73: 394–398
Alper KR, Prichep LS, Kowalik SC, Rosenthal MS, John ER . (1998): Persistent QEEG abnormality in crack cocaine users at 6 months of drug abstinence. Neuropsycho-pharmacology 19: 1–9
Astrachan DI, Davis M . (1981): Spinal modulation of the acoustic startle response: The role of norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine. Brain Res 206: 223–228
Bartlett E, Hallin A, Chapman B, Angrist B . (1997): Selective sensitization to the psychosis inducing effects of cocaine: A possible marker for addiction relapse vulnerability? Neuropsychopharmacology 16: 77–82
Belej J, Manji D, Sioutis S, Barros HMT, Nobrega JN . (1996): Changes in serotonin and norepinephrine uptake sites after chronic cocaine: Pre- vs. post withdrawal effects. Brain Res 736: 187–196
Braff DL, Grillon C, Geyer MA . (1992): Gating and habituation of the startle reflex in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49: 206–215
Commissaris RL, Davis M . (1982): Opposite effects of N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) and 5-Methoxy-N,N-Dimethyltriptamine (5-MeOMDT) on acoustic startle: Spinal vs. brain sites of action. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 6: 515–520
Cunningham KA, Bradberry CW, Chang AS, Reith MA . (1996): The role of serotonin in the actions of psychostimulants: Molecular and pharmacological analyses. Behav Brain Res 73: 93–102
Davis M . (1980): Neurochemical modulation of sensory-motor reactivity: Acoustic and tactile startle reflexes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 4: 241–263
Davis M, Astrachan I, Gendelman PM, Gendelman DS . (1980): 5-Methoxy-N,N-Dimethyltriptamine: Spinal cord and brainstem mediation of excitatory effects on acoustic startle. Psychopharmacology 70: 123–130
Davis M, Cassella JV, Wrean WH, Kehne JH . (1986): Serotonin receptor subtype agonists: Differential effects on sensorimotor reactivity measured with acoustic startle. Psychopharm Bull 22: 837–843
Davis M, Gendelman DS, Tischler MD, Gendelman PM . (1982): A primary acoustic startle circuit: Lesion and stimulation studies. J Neurosci 2 (6): 791–805
Davis M, Mansbach RS, Swerdlow NR, Campeau S, Braff DL, Geyer MA . (1990): Apomorphine disrupts the inhibition of acoustic startle induced by weak prepulse in rats. Psychopharmology 102: 1–4
Essman WD, Singh A, Lucki I . (1994): Serotonergic properties of cocaine: effects on a 5-HT2 receptor mediated behavior and on extracellular concentrations of serotonin and dopamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 49: 107–113
Fendt M, Koch M, Schnitzler H-U . (1994): Amygdaloid noradrenaline is involved in the sensitization of the acoustic startle response in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 48: 307–314
Fechter LD . (1974): The effects of L-dopa, clonidine, and apomorphine on the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacologia 39: 331–344
Geyer MA, Warbritton JD, Menkes DB, Zook JA, Mandell AJ . (1975): Opposite effects of intraventricular serotonin and bufotenin on rat startle responses. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 3: 687–691
Graham FK . (1975): The more or less startling effects of weak prestimuli. Psychophysiology 12: 238–248
Hoffman HS, Searle JL . (1968): Acoustic and temporal factors in the evocation of startle. J Acoust Soc Am 43: 269–282
Izenwasser S, Cox BM . (1990): Daily cocaine treatment produces a persistent reduction of [3H] dopamine uptake in vitro in rat nucleus accumbens but not in striatum. Brain Res 531: 338–341
Johansson C, Jackson DM, Zhang J, Svensson L . (1995): Prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle, a measure of sensorimotor gating: Effects of antipsychotics and other agents in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 52 (4): 649–654
Kehne JH, Padich RA, McCloskey TC, Taylor VL, Schmidt CJ . (1996): 5-HT modulation of auditory and visual sensorimotor gating. 1. Effects of 5-HT releasers on sound and light prepulse inhibition in Wistar rats. Psychopharmacology 124: 95–106
Kehne JH, Sorenson CA . (1978): The effects of pimozide and phenoxybenzamine pretreatments on amphetamine and apomorphine potentiation of the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacology 58: 137–144
Kleven MS, Perry BD, Woolverton WL, Seiden LS . (1990): Effects of repeated injections of cocaine on D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 532: 265–270
Koch M, Kungel M, Herbert H . (1993): Cholinergic neurons in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus are involved in the mediation of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response in the rat. Exp Brain Res 97: 71–82
Kuhar MJ, Pilotte NS . (1996): Neurochemical changes in cocaine withdrawal. Trends Pharm Sci 17: 260–264
Laurier LG, Corrigall WA, George SR . (1994): Dopamine receptor density, sensitivity and mRNA levels are altered following self-administration of cocaine in the rat. Brain Res 634: 31–40
Malison RT, Best SE, van Dyck CH, McCance EF, Wallace EA, Laruelle M, Baldwin RM, Seibyl JP, Price LH, Kosten TR, Innis RB . (1998): Elevated striatal dopamine transporters during acute cocaine abstinence as measured by [123I]Beta CIT-SPECT. Am J Psychiatry 155: 832–834
Mansbach RS, Braff DL, Geyer MA . (1989): Prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response is disrupted byN-ethyl-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDEA): in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 167: 49–55
Mansbach R, Geyer MA, Braff DL . (1988): Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 94: 507–514
Martinez ZA, Ellison GD, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR . (1999): Effects of sustained cocaine exposure on sensorimotor gating of startle in rats. Psychopharmacology 142: 253–260
Martinez DL, Geyer MA . (1997): Characterization of the disruptions of prepulse inhibition and habituation of startle induced by alpha-ethyltryptamine. Neuropsychopharmacology 16: 246–255
Padich RA, McCloskey TC, Kehne JH . (1996): 5-HT modulation of auditory and visual sensorimotor gating. II. Effects of the 5-HT2A antagonist MDL 100,907 on disruption of sound and light prepulse inhibition produced by 5-HT agonists in Wistar rats. Psychopharmacology 124: 107–116
Parsons LH, Smith AD, Justice JB . (1991): Basal extracellular dopamine is decreased in the rat nucleus accumbens during abstinence from chronic cocaine. Synapse 9: 60–65
Peng RY, Mansbach RS, Braff DL, Geyer MA . (1990): A D2 dopamine receptor agonist disrupts sensorimotor gating in rats. Implications for dopaminergic abnormalities in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 3: 211–218
Pilotte NS, Sharpe LG, Kuhar MJ . (1994): Withdrawal of repeated intravenous infusions of cocaine persistently reduces binding to dopamine transporters in the nucleus accumbens of Lewis rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 269: 963–969
Ritz MC, Cone EJ, Kuhar MJ . (1990): Cocaine inhibition of ligand binding at dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin receptors: a structure-activity study. Life Sci 46: 635–645
Saitoh K, Shaw S, Tilson HA . (1986): Noradrenergic influence on the prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle. Toxicol Lett 34: 209–216
Strickland TL, ViLanueva-Meyer J, Miller BL, Cummings J, Mehringer CM, Satz P, Myers H . (1993): Cerebral perfusion and neuropsychological consequences of chronic cocaine use. J Neuropsychiat Clin Neurosci 5: 419–427
Swerdlow NR, Braff DL, Geyer MA, Koob GF . (1986): Central dopamine hyperactivity in rats mimics abnormal acoustic startle response in schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 21: 23–33
Swerdlow NR, Caine BC, Geyer MA . (1992): Regionally selective effects of intracerebral dopamine infusion on sensorimotor gating of the startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology 108: 189–195
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA . (1993): Clozapine and haloperidol in an animal model of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44: 741–744
Swerdlow NR, Keith VA, Braff DL, Geyer MA . (1991): The effects of spiperone, raclopride, SCH 23390 and clozapine on apomorphine-inhibition of sensorimotor gating of the startle response in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256: 530–536
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wolf AP, Hitzemann R, Dewey S, Bendreim B, Alpert R, Hoff A . (1991): Changes in brain glucose metabolism in cocaine dependence and withdrawal. Am J Psychiatry 148: 621–626
Volkow ND, Hitzemann R, Wang C, Fowler JS, Wolf AP, Dewey SL, Handleman L . (1992): Long-term frontal brain metabolic changes in cocaine abusers. Synapse 11: 184–190
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang G, Hitzemann R, Logan J, Schyler DJ, Dewey SL, Wolf AP . (1993): Decreased dopamine D2 receptor availability is associated with reduced frontal metabolism in cocaine abusers. Synapse 14: 169–177
Vollenweider FX, Remensberger S, Hell D, Geyer MA . (1999): Opposite effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on sensorimotor gating in rats vs. healthy humans. Psychopharmacology 143: 365–372
Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Logan J, Fowler JS, Schyler D, MacGregor R, Hitzmann RJ, Gjedde A, Wolf AP . (1995): Serotonin 5-HT2 receptor availability in chronic cocaine abusers. Life Sci 56: PL299–301
Wamsley JR, Alburges ME . (1993): Cocaine causes a time dependant and dose dependant increase in D1 receptors and dopamine transporters. Proc West Pharmacol Soc 36: 277–282
Weiss F, Paulus MP, Lorang MT, Koob GF . (1992): Increases in extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens by cocaine are inversely related to basal levels: Effects of acute repeated administration. J Neurosci 12: 4372–4380
Wilson JM, Nobrega JN, Carroll ME, Niznik HB, Shannak K, Lac ST, Pristupa ZB, Dixon LM, Kish SJ . (1994): Heterogeneous subregional binding patterns of [3H]-WIN 35, 428 and [3H]GBR 12,935 are differently regulated by chronic cocaine self-administration. J Neurosci 14: 2966–2979
Wolfsohn R, Sanfilipo M, Angrist B . (1993): A placebo-controlled trial of L-DOPA/ Carbidopa in early cocaine abstinence. Neuropsychopharmcology 9: 49–53
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Michael Sanfilipo for his assistance with statistical analyses of the data. This work was supported by NIDA/VA MDRU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Efferen, T., Duncan, E., Szilagyi, S. et al. Diminished Acoustic Startle in Chronic Cocaine Users. Neuropsychopharmacol 22, 89–96 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00089-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00089-5
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prepulse inhibition deficit as a transdiagnostic process in neuropsychiatric disorders: a systematic review
BMC Psychology (2023)
-
Baseline prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex predicts the sensitivity to the conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine in male and female mice
Psychopharmacology (2018)
-
Selective developmental alterations in The HIV-1 transgenic rat: Opportunities for diagnosis of pediatric HIV-1
Journal of NeuroVirology (2017)
-
Acoustic startle reduction in cocaine dependence persists for 1 year of abstinence
Psychopharmacology (2011)
-
Effects of cocaine self-administration history under limited and extended access conditions on in vivo striatal dopamine neurochemistry and acoustic startle in rhesus monkeys
Psychopharmacology (2009)