Abstract
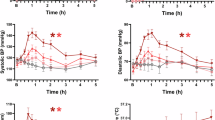
D-methamphetamine is abused for its euphoric effects and stimulatory action on cognitive function. Its abuse can, however, be associated with massive hypertension resulting in strokes, ruptured aneurysms, or myocardial infarction. We examined the utility of isradipine, a dihydropyridine-class calcium channel antagonist, in treating d-methamphetamine induced hypertension and evaluated its effects on cognitive function, both of which are mediated by dopaminergic mechanisms. D-methamphetamine dose-dependently increased all vital signs (systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressure, and pulse rate) parameters. Isradipine significantly reduced d-methamphetamine-induced increases in diastolic and mean arterial pressure; however, this potentially beneficial therapeutic effect was offset by a significant reflex rise in pulse rate. D-methamphetamine also improved attention, accuracy of reasoning ability, and performance on computerized cognitive function tasks. D-methamphetamine's cognitive improving effects were not altered significantly by isradipine. Isradipine increased the false responding rate but was without significant effect on any other attentional task, or on reasoning ability, or performance. Isradipine does not appear to enhance cognitive function in healthy humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Abekawa T, Ohmori T, Koyama T . (1997): Effect of NO synthesis inhibition on striatal dopamine release and stereotyped behavior induced by a single administration of methamphetamine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 21: 831–838
Angrist BC, Corwin J, Bartlik B, Cooper T . (1987): Early pharmacokinetics and clinical effects of oral d-amphetamine in normal subjects. Biol Psychiatry 22: 1357–1568
Apostolakos MJ, Varon ME . (1996): Antiarrhythmic and anti-ischemic properties of calcium-channel antagonists. New Horizons 4: 45–57
Baer PR, Gispen WH . (1996): Ageing and neuronal plasticity: The role of calcium. In Stefanis CN, Hippius H (eds), Neuropsychiatry in Old Age: An Update. Psychiatry in Progress Series. Goettingen, Germany, Hogrefe and Huber Publishers, pp 1–8
Baddeley AD . (1968): A three minute reasoning test based on grammatical transformation. Psychonomic Science 10: 341–342
Beebe D, Walley E . (1995): Smokable methamphetamine (’ice’): An old drug in a different form. Am Fam Physician 51: 449–453
Bennett BA, Hollingsworth CK, Martin RS, Harp JJ . (1998): Methamphetamine-induced alterations in dopamine transporter. Brain Res 782: 219–227
Besson JA, Palin AN, Ebmeier KP, Eagles JM . (1988): Calcium antagonists and multi-infarct dementia: A trial involving sequential NMR and psychometric assessment. Intl J Geriat Psychiatry 3: 99–105
Brogden RN, Sorkin EM . (1995): Isradipine: An update of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of mild to moderate hypertension. Drugs 49: 618–649
Carrara V, Porchet H, Dayer P . (1994): Influence of imput rates on isradipine haemodynamics and concentration effect. Eur J Pharmacol 46: 29–33
Cole BJ, Robbins TW . (1987): Amphetamine impairs discriminative performance of rats with dorsal noradrenergic bundle lesions on a 5 choice serial reaction time task: New evidence for central dopaminergic-naradrenergic interactions. Psychopharmacology 91: 458–466
Cole BJ, Robbins TW . (1992): Forebrain norepinephrine: Role in controlled information processing in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 7: 129–142
Davis GG, Swalwell CI . (1994): Acute aortic dissections and ruptured berry aneurysms associated with methamphetmine abuse. J Forensic Sci 39: 1481–1485
Davis GG, Swalwell CI . (1996): The incidence of acute cocaine or methamphetamine intoxication in deaths due to ruptured cerebral (berry) aneurysms. J Foren Sci 41: 626–628
Derlet M, Horowitz B . (1995): Cardiotoxic drugs. Emerg Med Clin North Am 13: 771–791
De Vries D, Beart PM . (1984): Competitive inhibition of [3H]spiperone binding to D-2 dopamine receptors in striatal homogenates by organic calcium channel antagonists and polyvalent cations. Eur J Pharmacol 106: 133–139
Drachman DA . (1977): Memory and cognitive function in man: Does the cholinergic system have a specific role? Neurology 8: 783–790
Fischman M . (1987): Cocaine and the amphetamines. Psychopharmacology: The third generation of progress. In Meltzer HY (ed). New York, NY, Raven Press, pp 1543–1553
Fleckenstein AE, Metzger RR ., Wilkins DG, Gibb JW . (1997): Rapid and reversible effects of methamphetamine on dopamine transporters. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282: 834–838
Ginsberg MD, Lin B, Morikawa E, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Globus MY . (1991): Calcium antagonists in the treatment of experimental cerebral ischemia. Arzneimittel-Forschung 41: 334–337
Hanson GR, Gibb JW, Metzger RR, Kokoshka JM . (1998): Methamphetamine-induced rapid and reversible reduction in the activities of tryptophan hydroxylase and dopamine transporters: Oxidative consequences? Ann NY Acad Sci 844: 103–107
Harvey JA . (1987): Behavioural pharmacology of central nervous system stimulants. Neuropsychopharmacology 26: 887–892
Heidrich A, Rosler M, Riederer P . (1997): Pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer dementia: therapy of cognitive symptoms—New results of clinical studies. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 65: 108–121
Jerzy V, Battaglia M, Sansone M . (1997): Nimodipine on shuttle-box avoidance learning in mice: No impairement but slight improvement. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 56: 577–581
Johnson B, Lamki L, Simms D, Chen R, Fang B, Barron B, Wells L, Abramson D, Dhother S, Meisch R, Oderinde V . (1997): Reversal of cocaine-induced changes in brain blood flow by isradipine. In the 59th Annual College on Problems of Drug Dependence Meeting. Nashville, TN
Johnson B, Wells L, Kenny P, Abramson D, Chen R, Dother S, Overton D, Bordnick P . (1999): Effects of isradipine on intravenous cocaine-induced cardiovascular response: A pilot study. Human Psychopharmacol: Clin Exp 14: 37–43
Johnson BA, Bordnick PS, Tiouririne N, Chen R . (1998a): L-type calcium channel blockers on cocaine-induced subjective effects. In the Collegium Internationale Neuro-Psychopharmacologicum. Glasgow, Scotland
Johnson BA, Fang B, Barron B, Lamki L, Wagner L, Wells L, Kenny P, Overton D, Dhother S, Abramson D, Chen YR, Kramer L . (1998b): Isradipine prevents global and regional cocaine-induced changes in brain blood flow. Psychopharmacology 136: 335–341
Johnson BA, Oldman D, Goodall EM, Chen YR, Cowen PJ . (1996): Effects of GR68755 on d-amphetamine-induced changes in mood, cognitive performance, appetite, food preference, and caloric and macronutrient intake in humans. Behav Pharmacol 6: 216–227
Kirsten R, Nelson K, Kirsten D, Heintz B . (1998): Clinical pharmacokinetics of vasodilators. Part I. Clin Pharmacokinet 34: 457–482
Leslie JB . (1993): Hemodynamics and tissue specificity with isradipine. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 37: 33–37
LeVere SD, LeVere TE . (1994): Old age and cognition: Evaluation of a human short-term memory test with non-human primates and the memory enhancing effects of nimodipine. Psychobiology 22: 106–111
Levy A, Kong R, Stillman MJ, Shukitt-Hale B . (1991): Nimodipine improves spatial working memory and elevates hippocampal acetylcholine in young rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39: 781–786
Martin WR, Sloan JW, Sapira JD, Jasinski DR . (1971): Physiologic, subjective, and behavioral effects of amphetamine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 12: 245–258
Mayfield D . (1973): The effect of intravenous methamphetamine on mood. Intl J Addict 8: 565–568
Mendelson J, Jones RT, Upton R, Jacob P 3rd . (1995): Methamphetamine and ethanol interactions in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 57: 559–568
Mosby CV . (1997): Mosby's Complete Drug Reference. In Be Dell S, Hulbert MK (eds), St Louis, Missouri, Mosby-Year Book Inc
Pearigen PD, Benowitz NL . (1991): Poisoning due to calcium antagonists. Experience with verapamil, diltiazem and nifedipine. Drug Saf 6 (6): 408–430
Perez-Reyes M, White W, McDonald S, Hill J, Jeffcoat A, Cook C . (1991): Clinical effects of methamphetamine vapor inhalation. Life Sci 49: 953–959
Quevedo J, Vianna M, Datroit D, Born AG, Kuyven CR, Roesler R, Quillfeldt JA . (1998): L-Type voltage-dependent calcium channel blocker nifedipine enhances memory retention when infused into hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem 69: 320–325
Ramoska EA, Spiller HA, Winter M, Borys D . (1993): A one year evaluation of calcium channel blocker overdoses: toxicity and treatment. Ann Emerg Med 22 (2): 196–200
Riedel W, Hogervorst E, Leboux R, Verhey F, van Praag H, Jolles J . (1995): Caffeine attenuates scopolamine-induced memory impairment in humans. Psychopharmacology 122: 158–168
Salmone S, Silva C, Morel N, Godfraind T . (1996): Facilitation of the vasorelaxant action of calcium antagonists by basal nitric oxide in depolarized artery. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 354: 505–512
Schwartz BL, Fay-McCarthy M, Kendrick K, Rosse RB, Deutsch SI . (1997): Effects of nifedipine, a calcium channel antagonist, on cognitive function in schizophrenic patients with tardive dyskinesia. Clin Neuropharmacol 20: 364–370
Selmi F, Davies KG, Sharma RR, Neal JW . (1995): Intracerebral haemorrhage due to amphetamine abuse: Report of two cases with underlying arteriovenous malformations. Br J Neurosurg 9: 93–96
Shibata S, Mori K, Sekine I, Suyama H . (1988): An autopsy case of subarachnoid and intracerebral hemorrhage and necrotizing angitis associated with methamphetamine abuse. No to Shinkei. 40: 1089–1094
Snyder S . (1992): Nitric oxide: first in a new class of neurotransmitter. Science 257: 494–496
Spiegel R . (1979): Effects of amphetamines on performance and on polygraphic sleep parameters in man. In Passouant P, Oswald I (eds), Pharmacology of the States of Alertness. Oxford, Pergamon Press, pp 189–201
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (1997): Year-End Preliminary Estimates from the 1996 Drug Abuse Warning Network Series: D-3, Washington, DC, U.S. Dept of Health and Human Services
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (1998): Methamphetamine Abuse and Addiction. In NIDA Research Report Series, Booklet-NCADI PHD 756, Washington, DC, U.S. Dept of Health and Human Services
van Zweiten PA, Pfaffendorf M . (1993): Similarities and differences between calcium antagonists: Pharmacological aspects. J Hypertens Suppl 11 (1): S3–S11
Yamada S, Uchida S, Ohkura T, Kimura R, Yamagushi M, Suzuki M, Yamamoto M . (1996): Alterations in calcium antagonist receptors and calcium content in senescent brain and attenuation by nimodipine and nicardipine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277: 721–727
Yen DJ, Wang SJ, Ju TH, Chen CC, Liao KK, Fuh JL, Hu HH . (1994): Stroke associated with methamphetamine inhalation. Eur Neurol 34: 16–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, B., Ait-Daoud, N. & Wells, L. Effects of Isradipine, a Dihydropyridine-Class Calcium Channel Antagonist, on D-Methamphetamine-Induced Cognitive and Physiological Changes in Humans. Neuropsychopharmacol 22, 504–512 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00116-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(99)00116-5
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Isradipine augmentation of virtual reality cue exposure therapy for tobacco craving: a triple-blind randomized controlled trial
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
Gender differences in the behavioral and subjective effects of methamphetamine in healthy humans
Psychopharmacology (2019)
-
Effects of concurrent caffeine and mobile phone exposure on local target probability processing in the human brain
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Driving on ice: impaired driving skills in current methamphetamine users
Psychopharmacology (2013)
-
Is Cognitive Functioning Impaired in Methamphetamine Users? A Critical Review
Neuropsychopharmacology (2012)