Abstract
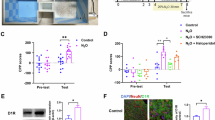
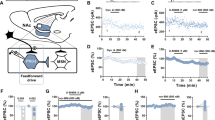
Previous studies from this laboratory indicated that D2 dopamine (DA) receptors within the nucleus accumbens (NAc) are important for regulating somatic signs of opiate withdrawal. The present study measured the expression of Fos-related antigens (FRAs) within the NAc during opiate withdrawal to determine whether decreases in somatic withdrawal signs produced by a D2 receptor agonist are accompanied by related changes in accumbens neuronal activity. In an initial experiment, quantitative analyses of FRA immunoreactivity revealed increases in the number of FRA-positive cells throughout the NAc of opiate dependent animals undergoing naltrexone-precipitated withdrawal relative to dependent or non-dependent animals that did not experience withdrawal. A second experiment showed that somatic signs and FRA expression within the NAc could each be attenuated when the D2 agonist propylnorapomorphine (NPA; 0.1 or 0.3 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered prior to naltrexone-precipitated withdrawal. These findings suggest that D2 regulation of neuronal activity within the NAc may be important for the expression of opiate withdrawal symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Acquas E, Carboni E, Di Chiara G . (1991): Profound depression of mesolimbic dopamine release after morphine withdrawal in dependent rats. Eur J Pharmacol 193: 133–134
Alheid GF, Heimer L . (1996): Theories of basal forebrain organization and the “emotional motor system.”. Prog Brain Res 107: 461–484
Baraban SC, Stornetta RL, Guyenet PG . (1995): Effects of morphine and morphine withdrawal on adrenergic neurons of the rat rostral ventrolateral medulla. Brain Res 676: 245–257
Berridge CW, Stratford TL, Foote SL, Kelley AE . (1997): Distribution of dopamine beta-hydroxylase-like immunoreactive fibers within the shell subregion of the nucleus accumbens. Synapse 27: 230–241
Bing G, Stone EA, Zhang Y, Filer D . (1992): Immunohistochemical studies of noradrenergic-induced expression of c-fos in the rat CNS. Brain Res 592: 57–62
Brown EE, Robertson GS, Fibiger HC . (1992): Evidence for conditional neuronal activation following exposure to a cocaine-paired environment: Role of forebrain limbic structures. J Neurosci 12: 4112–4121
Chieng B, Williams JT . (1998): Increased opioid inhibition of GABA release in nucleus accumbens during morphine withdrawal. J Neurosci 18: 7033–7039
Creese I, Padgett L, Fazzini E, Lopez F . (1979): 3H-N-n-propylnorapomorphine: A novel agonist ligand for central dopamine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 56: 411–412
Crippens D, Robinson TE . (1994): Withdrawal from morphine or amphetamine: Different effects on dopamine in the ventral-medial striatum studied with microdialysis. Brain Res 650: 56–62
Delfs JM, Zhu Y, Druhan JP, Aston-Jones G . (1998): Origin of noradrenergic afferents to the shell subregion of the nucleus accumbens: Anterograde and retrograde tract-tracing studies in the rat. Brain Res 806: 127–140
Delfs JM, Zhu Y, Druhan JP, Aston-Jones G . (2000): Noradrenaline in the ventral forebrain is critical for opiate withdrawal-induced aversion. Nature 403: 430–434
DiNardo LA, Travers JB . (1997): Distribution of fos-like immunoreactivity in the medullary reticular formation of the rat after gustatory elicited ingestion and rejection behaviors. J Neurosci 17: 3826–3839
Dragunow M, Faull R . (1989): The use of c-fos as a metabolic marker in neuronal pathway tracing. J Neurosci Meth 29: 261–265
Duman RS, Tallman JF, Nestler EJ . (1988): Acute and chronic opiate regulation of adenylate cyclase in brain: Specific effects in locus coeruleus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246: 1033–1039
Gomaa AA, Mohamed LH, Ahmed HN . (1989): Modification of morphine-induced analgesia, tolerance and dependence by bromocriptine. Eur J Pharmacol 170: 129–135
Hakan RL, Callaway C, Henriksen SJ . (1989): Electrophysiological analysis of the neural circuitry underlying opiate effects in the nucleus accumbens septi. Neurosci Lett 101: 163–168
Hakan RL, Henriksen SJ . (1989): Opiate influences on nucleus accumbens neuronal electrophysiology: Dopamine and non-dopamine mechanisms. J Neurosci 9: 3538–3546
Harris GC, Aston-Jones G . (1993): Beta-adrenergic antagonists attenuate somatic and aversive signs of withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology 9: 303–311
Harris GC, Aston-Jones G . (1994): Involvement of D2 dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbens in the opiate withdrawal syndrome. Nature 371: 155–157
Hays WL . (1981): Statistics, 3rd ed. New York, CBS College Publishing
Hayward MD, Duman RS, Nestler EJ . (1990): Induction of the c-fos proto-oncogene during opiate withdrawal in the locus coeruleus and other regions of rat brain. Brain Res 525: 256–266
Kohler C, Fuxe K, Ross SB . (1981): Regional in vivo binding of [3H]N-propylnorapomorphine in the mouse brain. Evidence for labelling of central dopamine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 72: 397–402
Koob GF, Wall TL, Bloom FE . (1989): Nucleus accumbens as a substrate for the aversive stimulus effects of opiate withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 98: 530–534
Martin JR, Takemori AE . (1987): Modification of the development of acute opiate tolerance by increased dopamine receptor sensitivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241: 48–55
McKittrick CR, Delfs JM, Aston-Jones G, Abercrombie ED . (1999): Differential spontaneous and withdrawal-induced efflux of catecholamines in nucleus accumbens shell of morphine-treated rats. Soc Neurosci Abstr 25: 948
Morgan JI, Curran T . (1991): Stimulus-transcription coupling in the nervous system: Involvement of the inducible proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Neurosci 14: 421–451
O'Donnell P, Grace AA . (1996): Dopaminergic reduction of excitability in nucleus accumbens neurons recorded in vitro. Neuropsychopharmacology 15: 87–97
Paxinos G, Watson C . (1998): The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th ed. San Diego, Academic Press
Pfaus JG, Marcangione C, Smith WJ, Manitt C, Abillamaa H . (1996): Differential induction of Fos in the female rat brain following different amounts of vaginocervical stimulation: Modulation by steroid hormones. Brain Res 741: 314–330
Rasmussen K, Brodsky M, Inturrisi CE . (1995): NMDA antagonists and clonidine block c-fos expression during morphine withdrawal. Synapse 20: 68–74
Rossetti ZL, Hmaidan Y, Gessa GL . (1992): Marked inhibition of mesolimbic dopamine release: A common feature of ethanol, morphine, cocaine and amphetamine abstinence in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 221: 227–234
Sagar SM, Sharp FR, Curran T . (1988): Expression of c-fos protein in brain: Metabolic mapping at the cellular level. Science 240: 1328–1331
Schulteis G, Koob GF . (1996): Reinforcement processes in opiate addiction: A homeostatic model. Neurochem Res 21: 1437–1454
Schulz R, Herz A . (1977): Naloxone-precipitated withdrawal reveals sensitization to neurotransmitters in morphine tolerant/dependent rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 299: 95–99
Shaham Y, Rajabi H, Stewart J . (1996): Relapse to heroin-seeking in rats under opioid maintenance: The effects of stress, heroin priming, and withdrawal. J Neurosci 16: 1957–1963
Stinus L, Le Moal M, Koob GF . (1990): Nucleus accumbens and amygdala are possible substrates for the aversive stimulus effects of opiate withdrawal. Neurosci 37: 767–773
Stone EA, Zhang Y, Carr KD . (1995): Massive activation of c-fos in forebrain after mechanical stimulation of the locus coeruleus. Brain Res Bull 36: 77–80
Stone EA, Zhang Y, John SM, Bing G . (1991): c-Fos response to administration of catecholamines into brain by microdialysis. Neurosci Lett 133: 33–35
Stornetta RL, Norton FE, Guyenet PG . (1993): Autonomic areas of rat brain exhibit increased Fos-like immunoreactivity during opiate withdrawal in rats. Brain Res 624: 19–28
Terwilliger RZ, Beitner-Johnson D, Sevarino K, Crain S, Nestler EJ . (1991): A general role for adaptations in G-proteins and the cyclic AMP system in mediating the chronic actions of morphine and cocaine on neuronal function. Brain Res 548: 100–110
Titeler M, Seeman P . (1979): Selective labelling of different dopamine receptors by a new agonist 3H-ligand: 3H-N-propylnorapomorphine. Eur J Pharmacol 56: 291–292
White FJ, Wang RY . (1986): Electrophysiological evidence for the existence of both D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors in the rat nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 6: 274–280
Yuan XR, Madamba S, Siggins GR . (1992): Opioid peptides reduce synaptic transmission in the nucleus accumbens. Neurosci Lett 134: 223–228
Zahm DS, Brog JS . (1992): On the significance of subterritories in the “accumbens” part of the rat ventral striatum. Neurosciences 50: 751–767
Zhu Y, Walters C, Wilent B, Druhan J, Aston-Jones G . (1997): The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BST): A potential target site for noradrenergic actions in opiate withdrawal. Soc Neurosci Abstr 23: 1108
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Yan Zhu and Mr. Bryan Wilent for their excellent technical assistance on this project. The work was supported by PHS grants DA10088 to JPD and DA06214 to GAJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walters, C., Aston-Jones, G. & Druhan, J. Expression of Fos-related Antigens in the Nucleus Accumbens during Opiate Withdrawal and Their Attenuation by a D2 Dopamine Receptor Agonist. Neuropsychopharmacol 23, 307–315 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00113-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00113-5
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Opioid withdrawal: role in addiction and neural mechanisms
Psychopharmacology (2023)
-
Single nucleus transcriptomic analysis of rat nucleus accumbens reveals cell type-specific patterns of gene expression associated with volitional morphine intake
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Increased Dopamine Receptor Activity in the Nucleus Accumbens Shell Ameliorates Anxiety during Drug Withdrawal
Neuropsychopharmacology (2012)
-
Some effects of dopamine transporter and receptor ligands on discriminative stimulus, physiologic, and directly observable indices of opioid withdrawal in rhesus monkeys
Psychopharmacology (2009)
-
Noradrenergic transmission in the extended amygdala: role in increased drug-seeking and relapse during protracted drug abstinence
Brain Structure and Function (2008)