Abstract
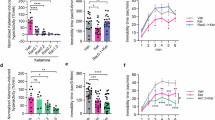
The effects of halothane and ketamine anesthesia on [11C]raclopride binding were assessed in the cat striatum at basal conditions and after drug- or depolarization-induced dopamine (DA) release using Positron Emission Tomography. At baseline, Scatchard analyses revealed that the higher [11C]raclopride binding found under halothane anesthesia was mainly attributable to a higher radioligand apparent affinity. Decreased [11C]raclopride binding was demonstrated following amphetamine under ketamine but not under halothane anesthesia. Under ketamine anesthesia transient DA overflows induced by direct stimulations of DA neurons through an intracerebral electrode induced transient changes in [11C]raclopride binding with a remarkable spatiotemporal accuracy. No effect was observed under halothane anesthesia. The failure to detect competition between DA and [11C]raclopride for binding on D2-receptors under halothane anesthesia might reflect, as already reported for other brain receptor systems, a halothane-promoted conversion of D2-receptors to a state of lower affinity for DA. It is suggested that the affinity state of receptors is a factor to be considered in in vivo ligand-activation studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Aronstam RS, Anthony BL, Dennison RL Jr . (1986): Halothane effects on muscarinic acetylcholine receptor complexes in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 35: 667–672
Baudry M, Martres MP, Schwartz JC . (1977): In vivo binding of 3H-pimozide in mouse striatum: effects of dopamine agonists and antagonists. Life Sci 21: 1163–1170
Bernstein KJ, Gangat Y, Verosky M, Vulliemoz Y, Triner L . (1981): Halothane effect on beta-adrenergic receptors in canine myocardium. Anesth Analg 60: 401–405
Bischoff S, Gunst F . (1997): Distinct binding patterns of [3H]raclopride and [3H]spiperone at dopamine D2 receptors in vivo in rat brain. Implications for pet studies. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 17: 419–431
Bohm M, Schmidt U, Schwinger RH, Bohm S, Erdmann E . (1993): Effects of halothane on beta-adrenoceptors and M-cholinoceptors in human myocardium: radioligand binding and functional studies. J Cardiov Pharmacol 21: 296–304
Breier A, Su TP, Saunders R, Carson RE, Kolachana BS, deBartolomeis A, Weinberger DR, Weisenfeld N, Malhotra AK, Eckelman WC, Pickar D . (1997): Schizophrenia is associated with elevated amphetamine-induced synaptic dopamine concentrations: evidence from a novel positron emission tomography method. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 2569–2574
Breier A, Adler CM, Weisenfeld N, Su TP, Elman I, Picken L, Malhotra AK, Pickar D . (1998): Effects of NMDA antagonism on striatal dopamine release in healthy subjects: application of a novel PET approach. Synapse 29: 142–147
Brix G, Zaers J, Adam LE, Bellemann ME, Ostertag H, Trojan H, Haberkorn U, Doll J, Oberdorfer F, Lorenz WJ . (1997): Performance evaluation of a whole-body PET scanner using the NEMA protocol. National Electrical Manufacturers Association. J Nucl Med 38: 1614–1623
Butcher SP, Fairbrother IS, Kelly JS, Arbuthnott GW . (1988): Amphetamine-induced dopamine release in the rat striatum: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem 50: 346–355
Carson RE, Channing MA, Vuong B-K, Watabe H Herscovitch, Eckelman WC . (2000): Amphetamine-induced dopamine release: duration of action assessed with [11C]raclopride in anesthetized monkeys. In Gjedde A, Hansen SB, Knudsen GM, Paulson OB (eds), Physiological Imaging of the Brain with PET. London, Academic Press, pp 205–209
Chergui K, Suaud-Chagny MF, Gonon F . (1994): Nonlinear relationship between impulse flow, dopamine release and dopamine elimination in the rat brain in vivo. Neuroscience 62: 641–645
Chugani DC, Ackermann RF, Phelps ME . (1988): In vivo [3H]spiperone binding: evidence for accumulation in corpus striatum by agonist-mediated receptor internalization. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8: 291–303
Dennison RL, Anthony BL, Narayanan TK, Aronstam RS . (1987): Effects of halothane on high affinity agonist binding and guanine nucleotide sensitivity of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors from brainstem rat. Neuropharmacol 26: 1201–1205
Dewey SL, Smith GS, Logan J, Brodie JD, Fowler JS, Wolf AP . (1993): Striatal binding of the PET ligand 11C-raclopride is altered by drugs that modify synaptic dopamine levels. Synapse 13: 350–356
Dewey SL, Smith GS, Logan J, Alexoff D, Ding YS, King P, Pappas N, Brodie JD, Ashby CR Jr . (1995): Serotonergic modulation of striatal dopamine measured with positron emission tomography (PET) and in vivo microdialysis. J Neuroscience 15: 821–829
Dugast C, Suaud-Chagny MF, Gonon F . (1994): Continuous in vivo monitoring of evoked dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens by amperometry. Neuroscience 62: 647–654
Eckenhoff MF, Eckenhoff RG . (1998): Quantitative autoradiography of halothane binding in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285: 371–376
Ehrin E, Gawell L, Högberg T, de Paulis T, Ström P . (1987): Synthesis of [Methoxy-3H]- and [Methoxy-11C]- labelled raclopride. Specific dopamine-D2 receptor ligands. J Labelled Compd Radiopharm 24: 931–940
Farde L, Eriksson L, Blomqvist G, Halldin C . (1989): Kinetic analysis of central [11C]raclopride binding to D2-dopamine receptors studied by PET - A comparison to the equilibrium analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 9: 696–708
Farde L, Wiesel FA, Stone-Elander S, Halldin C, Nordstrom AL, Hall H, Sedvall G . (1990): D2 dopamine receptors in neuroleptic-naïve schizophrenic patients. A positron emission tomography study with [11C]raclopride. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47: 213–219
Fink-Jensen A, Ingwersen SH, Nielsen PG, Hansen L, Nielsen EB, Hansen AJ . (1994): Halothane anesthesia enhances the effect of dopamine uptake inhibition on interstitial levels of striatal dopamine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 350: 239–244
Ford AP, Marsden CA . (1986): Influence of anaesthetics on rat striatal dopamine metabolism in vivo. Brain Res 379: 162–166
Freeman AS, Bunney BS . (1987): Activity of A9 and A10 dopaminergic neurons in unrestrained rats: further characterization and effects of apomorphine and cholecystokinin. Brain Res 405: 46–55
Gingrich JA, Caron MG . (1993): Recent advances in the molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Ann Rev Neurosci 16: 299–321
Ginovart N, Farde L, Halldin C, Swahn CG . (1997): Effect of reserpine-induced depletion of synaptic dopamine on [11C]raclopride binding to D2-dopamine receptors in the monkey brain. Synapse 25: 321–325
Gonon F, Navarre F, Buda M . (1984): In vivo monitoring of dopamine release in the rat brain with differential normal pulse voltammetry. Anal Chem 56: 573–575
Gonon F, Buda M . (1985): Regulation of dopamine release by impulse flow and by autoreceptors as studied by in vivo voltammetry in the rat striatum. Neuroscience 14: 765–774
Gonon F . (1988): Non linear relationship between impulse flow and dopamine released by rat midbrain dopaminergic neurons as studied by in vivo electrochemistry. Neuroscience 24: 19–28
Grace AA, Bunney BS . (1984): The control of firing pattern in nigral dopamine neurons: burst firing. J Neurosci 4: 2877–2890
Hall H, Wedel I, Halldin C, Kopp J, Farde L . (1990): Comparison of the in vitro receptor binding properties of N- [3H]methylspiperone and [3H]raclopride to rat and human brain membranes. J Neurochem 55: 2048–2057
Hartvig P, Torstenson R, Tedroff J, Watanabe Y, Fasth KJ, Bjurling P, Langstrom B . (1997): Amphetamine effects on dopamine release and synthesis rate studied in the Rhesus monkey brain by positron emission tomography. J Neural Transm 104: 329–339
Innis RB, Malison RT, al-Tikriti M, Hoffer PB, Sybirska EH, Seibyl JP, Zoghbi SS, Baldwin RM, Laruelle M, Smith EO, Charney DS, Heninger G, Elsworth JD, Roth JH . (1992): Amphetamine-stimulated dopamine release competes in vivo for [123I]IBZM binding to the D2 receptor in nonhuman primates. Synapse 10: 177–184
Irifune M, Fukuda T, Nomoto M, Sato T, Kamata Y, Nishikawa T, Mietani W, Yokoyama K, Sugiyama K, Kawahara M . (1997): Effects of ketamine on dopamine metabolism during anesthesia in discrete brain regions in mice: comparison with the effects during the recovery and subanesthetic phases. Brain Res 763: 281–284
Jasper HH, Ajmone-Marsan C . (1954): A Stereotaxic Atlas of the Diencephalon of the Cat. The National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa, Canada
Keita H, Henzel-Rouelle D, Dupont H, Desmonts JM, Mantz J . (1999): Halothane and isoflurane increase spontaneous but reduce the N-methyl-D- aspartate-evoked dopamine release in rat striatal slices: evidence for direct presynaptic effects. Anesthesiology 91: 1788–1797
Kegeles LS, Abi-Dargham A, Zea-Ponce Y, Rodenhiser-Hill J, Mann JJ, Van Heertum RL, Cooper T B, Carlsson A, Laruelle M . (2000): Modulation of amphetamine-induced striatal dopamine release by ketamine in humans: implications for schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 48: 627–640
Kobayashi K, Onoue O, Watanabe Y, Onoe H, Langström B . (1995): Difference in response of D2 receptor binding between 11C-N-methylspiperone and 11C-raclopride against anesthetics in rhesus monkey brain. J Neural Transm 100: 147–151
Koshikawa N, Tomiyama K, Omiya K, Kobayashi M . (1988): Ketamine anaesthesia has no effect on striatal dopamine metabolism in rats. Brain Res 444: 394–396
Kuhr WG, Ewing AG, Caudill WL, Wightman RM . (1984): Monitoring the stimulated release of dopamine with in vivo voltammetry. I: Characterization of the response observed in the caudate nucleus of the rat. J Neurochem 43: 560–569
Lammertsma AA, Hume SP . (1996): Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. Neuroimage 4: 153–158
Lannes B, Micheletti G, Warter J, Kempf E, Di Scala G . (1991): Behavioural, pharmacological and biochemical effects of acute and chronic administration of ketamine in the rat. Neurosci Lett 128: 177–181
Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, Van Dyck CH, Gil R, D'Souza CD, Erdos J, McCance E, Rosenblatt W, Fingado C, Zoghbi SS, Baldwin RM, Seibyl JP, Krystal JH, Charney DS, Innis RB . (1996): Single photon emission computerized tomography imaging of amphetamine-induced dopamine release in drug-free schizophrenic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 9235–9240
Laruelle M, Iyer RN, Al-Tikriti MS, Zea-Ponce Y, Malisson R, Zoghbi SS, Baldwin RM, Kung HF, Charney DS, Hoffer PB, Innis RB . (1997): Microdialysis and SPECT measurements of amphetamine-induced dopamine release in nonhuman primates. Synapse 25: 1–14
Laruelle M . (2000): Imaging synaptic neurotransmission with in vivo binding competition techniques: a critical review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20: 423–451
Leviel V, Cheramy A, Glowinski J . (1979): Role of the dendritic release of dopamine in the reciprocal control of the two nigro-striatal dopaminergic pathways. Nature 280: 236–239
Mantz J, Varlet C, Lecharny JB, Henzel D, Lenot P, Desmont JM . (1994): Effects of volatile anesthetics, thiopental, and ketamine on spontaneous and depolarization-evoked dopamine release from striatal synaptosomes in the rat. Anesthesiology 80: 352–363
Martin DC, Dennison RL, Introna RP, Aronstam RS . (1991): Influence of halothane on the interaction of serotonin1 and adenosine1 receptors with G protein in rat brain membranes. Biochem Pharmacol 42: 1313–1316
Micheletti G, Lannes B, Haby C, Borrelli E, Kempf E, Warter JM, Zwiller J . (1992): Chronic administration of NMDA antagonists induces D2 receptor synthesis in rat striatum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 14: 363–368
Miller DW, Abercrombie ED . (1996): Effects of MK-801 on spontaneous and amphetamine-stimulated dopamine release in striatum measured with in vivo microdialysis in awake rats. Brain Res Bull 40: 57–62
Miyano K, Tanifuji Y, Eger EI . (1993): The effect of halothane dose on striatal dopamine: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res 605: 342–344
Onoe H, Inoue O, Suzuki K, Tsukada H, Itoh T, Mataga N, Watanabe Y . (1994): Ketamine increases the striatal N-[11C]methylspiperone binding in vivo: positron emission tomography study using conscious rhesus monkey. Brain Res 663: 191–198
Osborne PG, O'Connor WT, Drew KL, Ungerstedt U . (1990): An in vivo microdialysis characterization of extracellular dopamine and GABA in dorsolateral striatum of awake freely moving and halothane anaesthetised rats. J Neurosci Methods 34: 99–105
Savaki HE, Girault JA, Spampinato U, Truong NA, Glowinski J, Besson MJ . (1986): Release of newly synthesized 3H-dopamine in the striatum: an adaptation of the push-pull cannula method to awake restrained and anesthetized rats. Brain Res Bull 16: 149–154
Schotten U, Schumacher C, Sigmund M, Rose H, Kammermeier H, Hanrath P . (1993): Beta-adrenoreceptor of isolated adult rat cardiomyocytes are not changed by halothane. Eur Heart J 14(Suppl): 299
Schotten U, Schumacher C, Sigmund M, Karlein C, Rose H, Kammermeier H, Sivarajan M, Hanrath P . (1998): Halothane, but not isoflurane, impairs the beta-adrenergic responsiveness in rat myocardium. Anesthesiology 88: 1330–1339
Seeman P, Guan HC, Niznik HB . (1989): Endogenous dopamine lowers the dopamine D2 receptor density as measured by [3H]raclopride: Implications for positron emission tomography of the human brain. Synapse 3: 96–97
Seeman P, Sunahara RK, Niznik HB . (1994): Receptor-receptor link in membranes revealed by ligand competition: example for dopamine D1 and D2 receptors. Synapse 17: 62–64
Sharp T, Zetterstrom T, Ljungberg T, Ungerstedt U . (1987): A direct comparison of amphetamine-induced behaviours and regional brain dopamine release in the rat using intracerebral dialysis. Brain Res 401: 322–330
Shiraishi M, Kamiyama Y, Huttemeier PC, Benveniste H . (1997): Extracellular glutamate and dopamine measured by microdialysis in the rat striatum during blockade of synaptic transmission in anesthetized and awake rats. Brain Res 759: 221–227
Sibley DR, de Lean A, Creese I . (1982): Anterior pituitary dopamine receptor. Demonstration of interconvertible high and low affinity states of the D2-dopamine receptor. J Biol Chem 257: 6351–6361
Smith GS, Schloesser R, Brodie JD, Dewey SL, Logan J, Vitkun SA, Simkowitz P, Hurley A, Cooper T, Volkow ND, Cancro R . (1998): Glutamate modulation of dopamine measured in vivo with positron emission tomography (PET) and 11C-raclopride in normal human subjects. Neuropsychopharmacol 18: 18–25
Spampinato U, Girault JA, Danguir J, Savaki HE, Glowinski J, Besson MJ . (1986): Apomorphine and haloperidol effects on striatal 3H-dopamine release in anesthetized, awake restrained and freely moving rats. Brain Res Bull 16: 161–166
Stahle L, Collin AK, Ungerstedt U . (1990): Effects of halothane anaesthesia on extracellular levels of dopamine, dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid in rat striatum: a microdialysis study. Arch Pharmacol 342: 136–140
Tsukada H, Nishiyama S, Kakiuchi T, Ohba H, Sato K, Harada N, Nakanishi S . (1999): Isoflurane anesthesia enhances the inhibitory effects of cocaine and GBR12909 on dopamine transporter: Pet studies in combination with microdialysis in the monkey brain. Brain Res 849: 85–96
Tsukada H, Harada N, Nishiyama S, Ohba H, Sato K, Fukumoto D, Kakiuchi T . (2000): Ketamine decreased striatal [11C]raclopride binding with no alterations in static dopamine concentrations in the striatal extracellular fluid in the monkey brain: multi-parametric PET studies combined with microdialysis analysis. Synapse 37: 95–103
Wreggett KA, Seeman P . (1984): Agonist high and low affinity states of the D2 dopamine receptor in calf brain. Partial conversion by guanine nucleotide. Mol Pharmacol 25: 10–17
Wikberg JE, Hede AR, Post C . (1987): Effects of halothane and other chlorinated hydrocarbons on alpha-2 adrenoreceptors in the mouse cortex. Pharmacol Toxicol 61: 271–277
Ylitalo P, Saarnivaara L, Ahtee L . (1976): Effect of ketamine anaesthesia on the content of monoamines and their metabolites in the rat brain. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 20: 216–220
Zetterstrom T, Sharp T, Ungerstedt U . (1986): Further evaluation of the mechanism by which amphetamine reduces striatal dopamine metabolism: a brain dialysis study. Eur J Pharmacol 132: 1–9
Zimmerman JB, Kennedy RT, Wightman RM . (1992): Evoked neuronal activity accompanied by transmitter release increases oxygen concentration in rat striatum in vivo but not in vitro. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12: 629–637
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants and fellowships (N.G.) from the Fondation de France and the France Parkinson foundations. The assistance of the members of the CERMEP group involved in the PET experiments is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ginovart, N., Hassoun, W., Le Cavorsin, M. et al. Effects of Amphetamine and Evoked Dopamine Release on [11C]raclopride Binding in Anesthetized Cats. Neuropsychopharmacol 27, 72–84 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00285-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00285-3
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Amphetamine challenge decreases yohimbine binding to α2 adrenoceptors in Landrace pig brain
Psychopharmacology (2012)
-
Ventral Striatal Dopamine Release in Response to Smoking a Regular vs a Denicotinized Cigarette
Neuropsychopharmacology (2009)
-
Effect of Increased Serotonin Levels on [18F]MPPF Binding in Rat Brain: Fenfluramine vs the Combination of Citalopram and Ketanserin
Neuropsychopharmacology (2005)
-
Imaging the Dopamine System with In Vivo [11C]raclopride Displacement Studies: Understanding the True Mechanism
Molecular Imaging and Biology (2005)