Abstract
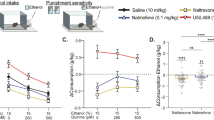
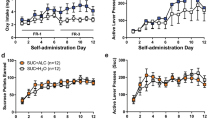
This study examined the effects of a nonselective opiate antagonist and antagonists selective for the μ1 versus δ opioid receptor on ethanol-seeking behavior induced by alcohol-related environmental stimuli in an animal model of relapse. Rats were trained to self-administer ethanol (10% w/v) or water on an FR 1 schedule in 30-min daily sessions. The availability of ethanol was signaled by an olfactory discriminative stimulus (S+). A different olfactory stimulus (S−) signaled water availability. In addition, each lever-response resulting in delivery of ethanol was paired with illumination of a visual cue for 5 s (SC+), whereas a 5-s white noise (SC−) was associated with water. The rats were then subjected to a 20-day extinction phase where lever presses had no programmed consequences. Reexposure to the S+/CS+ stimulus condition in the absence of further ethanol availability elicited strong recovery of responding. No effect was observed following presentation of S−/CS−. Subsequentely, ethanol-seeking behavior associated with the S+/CS+ stimulus condition was studied in rats treated with the nonselective opiate antagonist naltrexone (0.25–1 mg/kg, SC), the δ selective antagonist naltrindole (1–5 mg/kg, IP), and the μ1 selective antagonist naloxonazine (1–15 mg/kg, IP). Naltrexone (1 mg/kg) and naltrindole (5 mg/kg) selectively inhibited alcohol-seeking behavior. Naloxonazine (15 mg/kg) also reduced ethanol-seeking behavior but produced some nonselective behavioral suppression as well. The results provide evidence that selective blockade of either μ1 or δ opioid receptors inhibits ethanol-seeking behavior elicited by drug-related environmental stimuli. Moreover, the data suggest that drugs aimed at the δ opioid receptor may offer advantages in the treatment and prevention of relapse compared with agents that also block the μ1 receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Acquas E, Meloni M, Di Chiara G . (1993): Blockade of δ-opioid receptors in the nucleus accumbens prevents ethanol-induced stimulation of dopamine release. Eur J Pharmacol 230: 239–241
Altshuler HL, Phillips PE, Feinhandler DA . (1980): Alteration of ethanol self-administration by naltrexone. Life Sci 26: 679–688
Benjamin D, Grant ER, Pohorecky LA . (1993): Naltrexone reverses the ethanol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens in awake, freely moving rats. Brain Res 621: 137–140
Borg PJ, Taylor DA . (1997): Involvement of mu- and delta-opioid receptors in the effects of systemic and locally perfused morphine on extracellular levels of dopamine, DOPAC and HVA in the nucleus accumbens of the halothane- anaesthetized rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 355: 582–588
Childress AR, Hole AV, Ehrman RN, Robbins SJ, McLellan AT, O'Brien CP . (1993): Cue reactivity and cue reactivity interventions in drug dependence. NIDA Res Monogr 137: 73–95
Ciccocioppo R, Angeletti S, Weiss F . (2001): Long-lasting resistance to extinction of response reinstatement induced by ethanol-related stimuli: Role of genetic ethanol preference. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25: 1414–1419
Cruciani RA, Lutz RA, Munson PJ, Rodbard D . (1987): Naloxonazine effects on the interaction of enkephalin analogs with mu-1, mu and delta opioid binding sites in rat brain membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 242: 15–20
Cunningham CL, Prather LK . (1992): Conditioning trial duration affects ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Anim Learn Behav 20: 187–194
Davidson D, Amit Z . (1997): Naltrexone blocks acquisition of voluntary ethanol intake in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21: 677–683
Devine DP, Leone P, Pocock D, Wise RA . (1993): Differential involvement of ventral tegmental mu, delta and kappa opioid receptors in modulation of basal mesolimbic dopamine release: In vivo microdialysis studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266: 1236–1246
Di Chiara G, North RA . (1992): Neurobiology of opiate abuse. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13: 185–193
Dhawan BN, Cesselin F, Raghubir R, Reisine T, Bradley PB, Portoghese PS, Hamon M . (1996): International Union of Pharmacology. XII. Classification of opioid receptors. Pharmacol Rev 48: 567–592
Froehlich JC, Harts J, Lumeng L, Li TK . (1990): Naloxone attenuates voluntary ethanol intake in rats selectively bred for high ethanol preference. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35: 385–390
Froehlich JC, Zweifel M, Harts J, Lumeng L, Li TK . (1991): Importance of delta opioid receptors in maintaining high alcohol drinking. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 103: 467–472
Gonzales RA, Weiss F . (1998): Suppression of ethanol-reinforced behavior by naltrexone is associated with attenuation of ethanol-induced increase in dialysate dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 18: 10663–10671
Hart SL, Slusarczyk H, Smith TW . (1983): The involvement of opioid delta-receptors in stress induced antinociception in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 95: 283–285
Herz A . (1997): Endogenous opioid systems and alcohol addiction. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 129: 99–111
Honkanen A, Vilamo L, Wegelius K, Sarviharju M, Hyytia P, Korpi ER . (1996): Alcohol drinking is reduced by a mu 1-but not by a delta-opioid receptor antagonist in alcohol-preferring rats. Eur J Pharmacol 304: 7–13
Hubbell CL, Marglin SH, Spitalnic SJ, Abelson ML, Wild KD, Reid LD . . (1991): Opioidergic, serotonergic, and dopaminergic manipulations and rats′ intake of a sweetened alcoholic beverage. Alcohol 8: 355–367.
Hutchinson AC, Simpson GR, Randall JF, Zhang X, Calderon SN, Rice KC, Riley AL . (2000): Assessment of SNC 80 and naltrindole within a conditioned taste aversion design. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66: 779–787
Hyytiä P . (1993): Involvement of mu-opioid receptors in alcohol drinking by alcohol-preferring AA rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45: 697–701
Hyytiä P, Sinclair JD . (1993): Responding for oral ethanol after naloxone treatment by alcohol-preferring AA rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 17: 631–636
Johnson N, Pasternak GW . (1984): Binding of [3H]naloxonazine to rat brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol 26: 477–483
Katner SN, Magalong JG, Weiss F . (1999): Reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior by drug-associated discriminative stimuli after prolonged extinction in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 20: 471–479
Katner SN, Weiss F . (1999): Ethanol-associated olfactory stimuli reinstate ethanol-seeking behavior after extinction and modify extracellular dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23: 1751–1760
Kitchen I, Pinker SR . (1990): Antagonism of swim-stress-induced antinociception by the delta-opioid receptor antagonist naltrindole in adult and young rats. Br J Pharmacol 100: 685–688
Kornet M, Goosen C, Van Ree JM . (1991): Effect of naltrexone on alcohol consumption during chronic alcohol drinking and after a period of imposed abstinence in free-choice drinking rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 104: 367–376
Krishnan-Sarin S, Jing SL, Kurtz DL, Zweifel M, Portoghese PS, Li TK, Froehlich JC . (1995a): The delta opioid receptor antagonist naltrindole attenuates both alcohol and saccharin intake in rats selectively bred for alcohol preference. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 120: 177–185
Krishnan-Sarin S, Portoghese PS, Li TK, Froehlich JC . (1995b): The delta 2-opioid receptor antagonist naltriben selectively attenuates alcohol intake in rats bred for alcohol preference. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 52: 153–159
Krishnan-Sarin S, Wand GS, Li XW, Portoghese PS, Froehlich JC . (1998): Effect of mu opioid receptor blockade on alcohol intake in rats bred for high alcohol drinking. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59: 627–635
Ling GS, Simantov R, Clark JA, Pasternak GW . (1986): Naloxonazine actions in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 129: 33–38
Ludwig AM, Wikler A, Stark LH . (1974): The first drink. Psychobiological aspects of craving. Arch Gen Psychiatry 30: 539–547
Matsuzawa S, Suzuki T, Misawa M, Nagase H . (1998): Involvement of mu- and delta-opioid receptors in the ethanol-associated place preference in rats exposed to foot shock stress. Brain Res 803: 169–177
Matsuzawa S, Suzuki T, Misawa M, Nagase H . (1999): Different roles of mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptors in ethanol-associated place preference in rats exposed to conditioned fear stress. Eur J Pharmacol 368: 9–16
Middaugh LD, Bandy AL . (2000): Naltrexone effects on ethanol consumption and response to ethanol conditioned cues in C57BL/6 mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 151: 321–327
Monti PM, Rohsenow D J, Hutchison K E, Swift R M, Mueller T I, Colby S M, Brown RA, Gulliver SB, Gordon A, Abrams DB . (1999): . Naltrexone's effect on cue-elicited craving among alcoholics in treatment. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23: 1386–1394
O'Brien C, Childress AR, Ehrman R, Robbins S, McLellan AT . (1992): Conditioning mechanisms in drug dependence. Clin Neuropharmacol 15(Suppl 1, Pt A): 66A–67A
O'Brien CP, Volpicelli LA, Volpicelli JR . (1996): Naltrexone in the treatment of alcoholism: A clinical review. Alcohol 13: 35–39
O'Malley SS, Jaffe AJ, Chang G, Schottenfeld RS, Meyer RE, Rounsaville B . (1992): Naltrexone and coping skills therapy for alcohol dependence. A controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49: 881–887
Parker LA, Rennie M . (1992): Naltrexone-induced aversions: Assessment by place conditioning, taste reactivity, and taste avoidance paradigms. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41: 559–565
Portoghese PS, Sultana M, Nagase H, Takemori AE . (1988a): Application of the message-address concept in the design of highly potent and selective non-peptide delta opioid receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 31: 281–282
Portoghese PS, Sultana M, Takemori AE . (1988b): Naltrindole, a highly selective and potent non-peptide delta opioid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 146: 185–186
Robbins SJ, Ehrman RN . (1992): Designing studies of drug conditioning in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 106: 143–153
Robbins SJ, Ehrman RN, Childress AR, O'Brien CP . (1992): Using cue reactivity to screen medications for cocaine abuse: A test of amantadine hydrochloride. Addict Behav 17: 491–499
Roberts AJ, Heyser CJ, Koob GF . (1999): Operant self-administration of sweetened versus unsweetened ethanol: Effects on blood alcohol levels. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23: 1151–1157
Rogers H, Hayes AG, Birch PJ, Traynor JR, Lawrence AJ . (1990): The selectivity of the opioid antagonist, naltrindole, for delta-opioid receptors. J Pharm Pharmacol 42: 358–359
Rohsenow DJ, Monti PM, Hutchison KE, Swift RM, Colby SM, Kaplan GB . (2000): Naltrexone's effects on reactivity to alcohol cues among alcoholic men. J Abnorm Psychol 109: 738–742
Samson HH, Doyle TF . (1985): Oral ethanol self-administration in the rat: Effect of naloxone. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22: 91–99
Samson HH . (1986): Initiation of ethanol reinforcement using a sucrose-substitution procedure in food- and water-sated rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 10: 436–442
Staiger PK, White JM . (1991): Cue reactivity on alcohol abusers: Stimulus specificity and extinction of the response. Addict Behav 16: 211–221
Stevenson GW, Canadas F, Zhang X, Rice KC, Riley AL . (2000): Morphine discriminative control is mediated by the Mu opioid receptor. Assessment of delta opioid substitution and antagonism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66: 851–856
Tanda G, Di Chiara G . (1998): A dopamine-mu1 opioid link in the rat ventral tegmentum shared by palatable food (Fonzies) and non-psychostimulant drugs of abuse. Eur J Neurosci 10: 1179–1187
Volpicelli JR, Alterman AI, Hayashida M, O'Brien CP . (1992): Naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49: 876–880
Volpicelli JR, Watson NT, King AC, Sherman CE, O'Brien CP . (1995): Effect of naltrexone on alcohol “high” in alcoholics. Am J Psychiatry 152: 613–615
Weiss F, Mitchiner M, Bloom FE, Koob GF . (1990): Free-choice responding for ethanol versus water in alcohol preferring (P) and unselected Wistar rats is differentially modified by naloxone, bromocriptine, and methysergide. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 101: 178–186
Weiss F, Lorang MT, Bloom FE, Koob GF . (1993): Oral alcohol self-administration stimulates dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens: Genetic and motivational determinants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267: 250–258
Weiss F, Maldonado-Vlaar CS, Parsons LH, Kerr TM, Smith DL, Ben-Shahar O . (2000): Control of cocaine-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats: Effects on recovery of extinguished operant-responding and extracellular dopamine levels in amygdala and nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 4321–4326
Acknowledgements
This work is publication number 14027-NP from The Scripps Research Institute and was supported by NIAAA grant AA10531 (FW). The authors thank Miwe Arends for help with the preparation of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Please send reprint requests to: Friedbert Weiss, Ph.D., Department of Neuropharmacology (CVN-15), The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA. Fax: +1-858-784-7393, E-mail: bweiss@mail.scripps.edu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciccocioppo, R., Martin-Fardon, R. & Weiss, F. Effect of Selective Blockade of μ1 or δ Opioid Receptors on Reinstatement of Alcohol-Seeking Behavior by Drug-Associated Stimuli in Rats . Neuropsychopharmacol 27, 391–399 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00302-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00302-0
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Blocking μ-opioid receptors attenuates reinstatement of responding to an alcohol-predictive conditioned stimulus through actions in the ventral hippocampus
Neuropsychopharmacology (2023)
-
Alcohol availability during withdrawal gates the impact of alcohol vapor exposure on responses to alcohol cues
Psychopharmacology (2022)
-
The effects of nalmefene on the impulsive and reflective system in alcohol use disorder: A resting-state fMRI study
Psychopharmacology (2022)
-
Translational opportunities in animal and human models to study alcohol use disorder
Translational Psychiatry (2021)
-
Morphine and ethanol pretreatment effects on expression and extinction of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference and aversion in mice
Psychopharmacology (2021)