Abstract
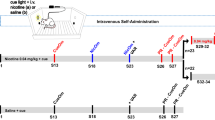
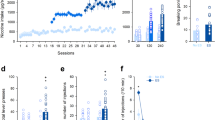
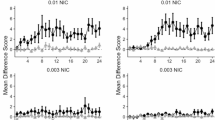
Consistent with human literature, previous studies identified attention-enhancing effects of nicotine in rats, using a 5-choice task. The present study addressed the influence of repeated exposure to nicotine on these effects. Over six weeks, the effects of nicotine (0.0, 0.05 and 0.2 mg/kg) given ten min before sessions were tested each week. In addition, rats were injected daily two hours after sessions. In the first week, when these post-session injections were of saline for all rats, pre-session nicotine had profound rate-disruptive effects at the larger dose. In weeks 2–6, when half the rats received post-session injections of saline and the other half of nicotine (0.4 mg/kg), the disruptive effects of pre-session nicotine had disappeared and it enhanced attentional performance on all response indices. These effects did not differ significantly between post-session treatment groups or weeks, although they appeared less pronounced in the last two weeks. When tested under modified task parameters in weeks 9 and 10, nicotine (0.1 mg/kg) robustly enhanced performance in both groups despite continuing daily post-session administration of nicotine or saline. These studies provide evidence that, following tolerance to initial disruptive effects, the nicotine-induced attentional enhancement is stable across lengthy periods of chronic exposure. This is important for potential therapeutic applications of the drug and indicates that these effects can be a continuous motive for smoking behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Benwell ME, Balfour DJ . (1992): The effects of acute and repeated nicotine treatment on nucleus accumbens dopamine and locomotor activity. Br J Pharmacol 105: 849–856
Bizarro L, Stolerman IP . (2001): Different effects of nicotine and motivational level on performance in the rat five-choice serial reaction time task. Behav Pharmacol 12(Suppl 1):S9
Benwell ME, Balfour DJ, Birrell CE . (1995): Desensitization of the nicotine-induced mesolimbic dopamine responses during constant infusion with nicotine. Br J Pharmacol 114: 454–460
Blondel A, Simon H, Sanger DJ, Moser P . (1999): The effect of repeated nicotine administration on the performance of drug-naive rats in a five-choice serial reaction time task. Behav Pharmacol 10: 665–673
Cadoni C, Di Chiara G . (2000): Differential changes in accumbens shell and core dopamine in behavioral sensitization to nicotine. Eur J Pharmacol 387: R23–R25
Caggiula AR, Epstein LH, Stiller R . (1989): Changing environmental cues reduces tolerance to nicotine-induced anorexia. Psychopharmacology (Berl)99: 389–392
Carli M, Robbins TW, Evenden JL, Everitt BJ . (1983): Effects of lesions to ascending noradrenergic neurones on performance of a 5-choice serial reaction task in rats; implications for theories of dorsal noradrenergic bundle function based on selective attention and arousal. Behav Brain Res 9: 361–380
Clarke PB, Kumar R . (1983): The effects of nicotine on locomotor activity in non-tolerant and tolerant rats. Br J Pharmacol 78: 329–337
Di Chiara G . (2000): Role of dopamine in the behavioural actions of nicotine related to addiction. Eur J Pharmacol 393: 295–314
Foulds J, Stapleton J, Swettenham J, Bell N, McSorley K, Russell MA . (1996): Cognitive performance effects of subcutaneous nicotine in smokers and never-smokers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 127: 31–38
Grottick AJ, Higgins GA . (2000): Effect of subtype selective nicotinic compounds on attention as assessed by the five-choice serial reaction time task. Behav Brain Res 117: 197–208
Hahn B, Shoaib M, Stolerman IP . (2002): Nicotine-induced enhancement of attention in the five-choice serial reaction time task: the influence of task-demands. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 162: 129–137
Heishman SJ . (1998): What aspects of human performance are truly enhanced by nicotine? Addiction 93: 317–320
Heishman SJ, Henningfield JE . (2000): Tolerance to repeated nicotine administration on performance, subjective, and physiological responses in nonsmokers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152: 321–333
Irvine EE, Cheeta S, File SE . (1999): Time-course of changes in the social interaction test of anxiety following acute and chronic administration of nicotine. Behav Pharmacol 10: 691–697
Irvine EE, Cheeta S, File SE . (2001): Tolerance to nicotine's effects in the elevated plus-maze and increased anxiety during withdrawal. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 68: 319–325
Jones GM, Sahakian BJ, Levy R, Warburton DM, Gray JA . (1992): Effects of acute subcutaneous nicotine on attention, information processing and short-term memory in Alzheimer's disease. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 108: 485–494
Ksir C, Hakan R, Hall DP Jr, Kellar KJ . (1985): Exposure to nicotine enhances the behavioral stimulant effect of nicotine and increases binding of [3H]acetylcholine to nicotinic receptors. Neuropharmacology 24: 527–531
Ksir C, Hakan RL, Kellar KJ . (1987): Chronic nicotine and locomotor activity: influences of exposure dose and test dose. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 92: 25–29
Levin ED . (1992): Nicotinic systems and cognitive function. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 108: 417–431
Levin ED, Conners CK, Sparrow E, Hinton SC, Erhardt D, Meck WH, Rose JE, March J . (1996a): Nicotine effects on adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 123: 55–63
Levin ED, Morgan MM, Galvez C, Ellison GD . (1987): Chronic nicotine and withdrawal effects on body weight and food and water consumption in female rats. Physiol Behav 39: 441–444
Levin ED, Wilson W, Rose JE, McEvoy J . (1996b): Nicotine-haloperidol interactions and cognitive performance in schizophrenics. Neuropsychopharmacology 15: 429–436
Levin ED, Conners CK, Silva D, Hinton SC, Meck WH, March J, Rose JE . (1998): Transdermal nicotine effects on attention. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 140: 135–141
Levin ED, Simon BB . (1998): Nicotinic acetylcholine involvement in cognitive function in animals. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 138: 217–230
Marks MJ, Burch JB, Collins AC . (1983): Effects of chronic nicotine infusion on tolerance development and nicotinic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226: 817–825
Marks MJ, Stitzel JA, Collins AC . (1985): Time course study of the effects of chronic nicotine infusion on drug response and brain receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 235: 619–628
Marks MJ, Grady SR, Collins AC . (1993): Downregulation of nicotinic receptor function after chronic nicotine infusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266: 1268–1276
Marshall DL, Redfern PH, Wonnacott S . (1997): Presynaptic nicotinic modulation of dopamine release in the three ascending pathways studied by in vivo microdialysis: comparison of naive and chronic nicotine-treated rats. J Neurochem 68: 1511–1519
Miller DK, Wilkins LH, Bardo MT, Crooks PA, Dwoskin LP . (2001): Once weekly administration of nicotine produces long-lasting locomotor sensitization in rats via a nicotinic receptor-mediated mechanism. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 156: 469–476
Mirza NR, Stolerman IP . (1998): Nicotine enhances sustained attention in the rat under specific task conditions. Psychopharmacology 138: 266–274
Nelsen JM, Goldstein L . (1972): Improvement of performance on an attention task with chronic nicotine treatment in rats. Psychopharmacologia 26: 347–360
Nelsen JM, Goldstein L . (1973): Chronic nicotine treatment in rats. 1. Acquisition and performance of an attention task. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 5: 681–693
Olale F, Gerzanich V, Kuryatov A, Wang F, Lindstrom J . (1997): Chronic nicotine exposure differentially affects the function of human alpha3, alpha4, and alpha7 neuronal nicotinic receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283: 675–683
Perkins KA, Grobe JE, Fonte C, Goettler J, Caggiula AR, Reynolds WA, Stiller RL, Scierka A, Jacob RG . (1994): Chronic and acute tolerance to subjective, behavioral and cardiovascular effects of nicotine in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270: 628–638
Sahakian B, Jones G, Levy R, Gray J, Warburton D . (1989): The effects of nicotine on attention, information processing, and short- term memory in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type. Br J Psychiatry 154: 797–800
Sanderson EM, Drasdo AL, McCrea K, Wonnacott S . (1993): Upregulation of nicotinic receptors following continuous infusion of nicotine is brain-region-specific. Brain Res 617: 349–352
Schwartz RD, Kellar KJ . (1985): In vivo regulation of [3H]acetylcholine recognition sites in brain by nicotinic cholinergic drugs. J Neurochem 45: 427–433
Stolerman IP, Mirza NR, Shoaib M . (1995): Nicotine psychopharmacology: addiction, cognition and neuroadaptation. Med Res Rev 15: 47–72
Stolerman IP . (1999): Inter-species consistency in the behavioural pharmacology of nicotine dependence. Behav Pharmacol 10: 559–580
Wang F, Nelson ME, Kuryatov A, Olale F, Cooper J, Keyser K, Lindstrom J . (1998): Chronic nicotine treatment up-regulates human alpha3 beta2 but not alpha3 beta4 acetylcholine receptors stably transfected in human embryonic kidney cells. J Biol Chem 273: 28721–28732
Wesnes K, Warburton DM . (1984): Effects of scopolamine and nicotine on human rapid information processing performance. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 82: 147–150
White HK, Levin ED . (1999): Four-week nicotine skin patch treatment effects on cognitive performance in Alzheimer's disease. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 143: 158–165
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the MRC. We thank Terry Hewett for technical assistance, Dr. Mohammed Shoaib for valuable discussions, and Dr. Sabine Landau for assistance with statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hahn, B., Stolerman, I. Nicotine-induced Attentional Enhancement in Rats: Effects of Chronic Exposure to Nicotine. Neuropsychopharmacol 27, 712–722 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00348-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(02)00348-2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Convergent observations of MK-801-induced impairment in rat 5C-CPT performance across laboratories: reversal with a D1 but not nicotinic agonist
Psychopharmacology (2021)
-
Cross-species evidence that nicotine widens the attentional window
Psychopharmacology (2021)
-
Dyskinesia in an unmedicated adolescent with a 5-year history of tobacco use: a case report
Journal of Medical Case Reports (2016)
-
Strain dependency of the effects of nicotine and mecamylamine in a rat model of attention
Psychopharmacology (2016)
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in attention circuitry: the role of layer VI neurons of prefrontal cortex
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2014)