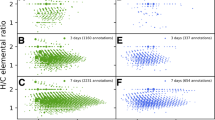
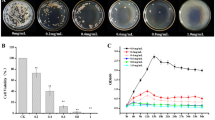
Abstract
NUMEROUS recent researches have directed our attention to the antimicrobial action of various aromatic amino or nitro compounds containing the following functional groups: sulphamide, R—SO2NH2; thio, R—S—R'; dithio, R—S—S—R'; sulphone, R—SO2—R'; thiophenol, R—SH; sulphinic acid, R—SO2H. By chemical analogy with the arsenic compounds in which the arsenoxide group shows in vitro a very high parasiticidal activity, we have been led to a study of the para-substituted aromatic sulphoxides.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GIRARD, A., RAY, A. & RICHARD, G. Antimicrobial Action of Some Aromatic Compounds. Nature 140, 283 (1937). https://doi.org/10.1038/140283a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/140283a0