Abstract
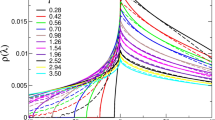
FOR the spectroscopic study of the light scattered in solids and fluids using interferometers of high resolving power, it is very important to be able to work with a light source giving sharp and intense spectral lines without accompanying hyperfine structure components or continuous spectrum. A zinc—mercury amalgam lamp in Pyrex glass has been developed in this laboratory by one of us (C. S. V.) Which gives the zinc triplet of lines 4680, 4722 and 4811 A., satisfying these requirements. It may be run continuously for days together without trouble, and is found to be a great advance on the ordinary mercury arcs for such investigations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raman, C. V., and Rao, B. V. R., NATURE, 139, 585 (1937); 141, 242 (1938).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RAMAN, C., VENKATESWARAN, C. Debye Heat Waves in Highly Viscous Liquids. Nature 142, 791 (1938). https://doi.org/10.1038/142791a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/142791a0
This article is cited by
-
Depolarisation of light scattered by liquids
Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences - Section A (1941)
-
Rigidity of Liquids
Nature (1939)