Abstract
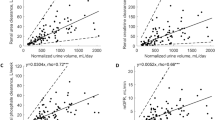
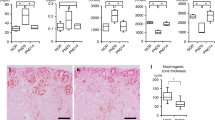
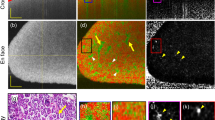
OBSERVATIONS have been made on the role of the renal innervation in kidney function. A dog's kidney was transplanted to the inguinal region by end-to-end anastomosis of the renal vessels to the femoral; the bladder and distal ureteral orifices were exteriorized. Convalescence was uneventful and both kidneys gave every tested physiological evidence of normal function. During antidiuretic, that is, normal, urine flows, the rate of urine flow and of glomerular filtration is greater in the transplanted kidney than in the untransplanted kidney of the same animal. Following administration of a large quantity of water or of a small dose of adrenalin, the above differences become strikingly reversed; this strongly suggests that the transplanted kidney has continued to be effectively denervated. It was demonstrated that phenol red, water and chloride secretion are practically identical in both kidneys per unit volume of glomerular filtrate. Cogent evidence is presented indicating that adrenalin normally acts indirectly on the vas efferens of the glomerular vascular tufts, that is, only by way of the renal nerve supply, and that “pituitrin” acts directly on the tubules. The work will shortly be published in full.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MALUF, N., CLARKE, R. & THOMPSON, K. Role of the Renal Innervation in Kidney Function. Nature 144, 292 (1939). https://doi.org/10.1038/144292a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/144292a0