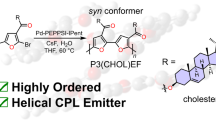
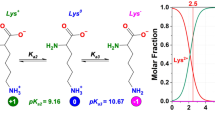
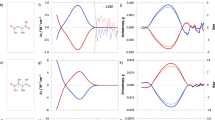
Abstract
THE Liebermann-Burchard reaction1 is extensively used for the characterization of polynuclear compounds (steroids, polyterpenoids, etc.). Applying this reaction to some of these compounds and simpler ones, according to the conditions described by Nath, Chakravorty and Chowdhury2, with enough chloroform to give a homogeneous medium, colloidal solutions are obtained. With cholesterol, Î-amyrenol, abietic acid, limonene, cyclohexanone and linalool, the solutions are strongly coloured and show a strong Tyndall effect and Brownian movement by the ultramicroscope.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liebermann, C., Ber., 18, 1804 (1885). Burchard, O., Diss. Rostock (1899).
Nath, M. C., Chakravorty, M. K., and Chowdhury, S. R., Nature, 157, 103 (1946).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
COELHO, F., ALVES, F. Liebermann-Burchard Reaction. Nature 157, 803 (1946). https://doi.org/10.1038/157803a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/157803a0
This article is cited by
-
Zur Cholesterinbestimmung im Hautfett
Archiv f�r Dermatologie und Syphilis (1951)