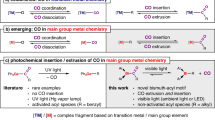
Abstract
THE recent observation of Arthur1, who found that the CO/(CO + CO2) ratio in the products of combustion of carbon in air at 800° C. was greatly increased by addition of chlorine or its compounds, is extended by results obtained in these laboratories during the past six months. We have worked at 800°–1,000° C. with undried gases, and find that:
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur, Nature, 157, 733 (1946).
Cf. Semenoff, “Chemical Kinetics and Chain Reactions” (Oxford University Press).
Cf. Hinshelwood, “Kinetics of Chemical Change in Gaseous Systems” (Oxford University Press).
Chukhanov, J. Tech. Phys. U.S.S.R., 5, 511 (1938). (See Fuel, 18, 292.)
Karshavina, Tech. Phys. U.S.S.R. (Eng.), 633 (1938). (See Fuel, 19, 220.)
Bangham and Bennett, Fuel, 19, 95.
Hiles and Mott, Fuel, 23, 134 and 154.
Thring, Trans. Farad. Soc., 42, 366 (1946).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BRIDGER, G. Combustion of Carbon and Carbon Monoxide. Nature 158, 236 (1946). https://doi.org/10.1038/158236b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/158236b0