Abstract
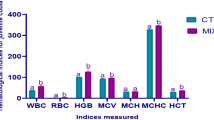
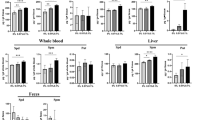
The effect of l-ascorbic acid in increasing the number of red blood corpuscles has been studied in various laboratory animals1 but hitherto not in mice. The present investigation was made to ascertain the action of the vitamin on the latter animal, taking into consideration, at the same time, the fact that there are many dietetic factors which affect the blood picture. Thus besides being properly fed on a diet consisting of cabbage and a mixture of cereal flour (8 parts) and whole milk powder (2 parts), the animals were given a salt mixture of iron, copper and cobalt (42, 55, 0.03 p.p.m. respectively2) and cod liver oil.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, Y. T., Chen, J. M., and Shen, T., Arch. Biochem., 3, 235 (1943). Aszodi, Z., Biochem. Z., 291, 34 (1937). Slonimski, P. W., Arch. Exp. Zellforsch. Gewebezücht, 22, 101 (1938). D'Alessandro, B., Minerva Med. 7 11, 273 (1939).
Hauk, A. E. H., Thomas, A. W., and Sherman, H. C., J. Nutrition, 31, 609 (1946).
Mather, K., "Statistical Analysis in Biology" (1943).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CHEN, JM. Induced Polycythæmia by l-Ascorbic Acid in Albino Mice. Nature 160, 681 (1947). https://doi.org/10.1038/160681a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/160681a0