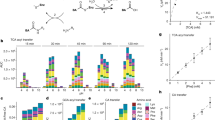
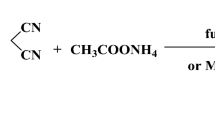Abstract
PREVIOUS communications1,2 have recorded the synthesis of antibacterial compounds derived from bile acids and sterols which contained basic groups, such as the amino-, amidino- and guanido-groups. In general, these derivatives were bacteriostatic for Gram-positive bacteria, but had little activity against Gram-negative organisms. Whereas surface tension measurements seemed to reveal a relationship between the bacteriostatic and surface activities of the bile acids and their anionic derivatives3, no such relationship was apparent in the properties of a series of the basic steroid compounds4. In an extension of these studies, we have synthesized and investigated several water-soluble, sulphur-containing, steroid derivatives.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett, J., Ryman, B. E., and Smith, F., J. Chem. Soc., 524, 526, 528 (1946).
James, S. P., Smith, F., Stacey, M., and Webb, M., J. Chem. Soc., 665 (1946).
Stacey, M., and Webb, M., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 134, 523 (1947).
Stacey, M., and Webb, M., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 134, 538 (1947).
Mylius, F., Ber., 20, 1968 (1887); cf. Hauptman, H., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 69, 562 (1947).
Cf. King, L. C., Dodson, R. M., and Subluskey, L. A., J. Amer. Cham. Soc., 70, 1176 (1948).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
JONES, A., SMITH, F. & WEBB, M. Sulphur-containing Steroid Derivatives. Nature 162, 857–858 (1948). https://doi.org/10.1038/162857b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/162857b0