Abstract
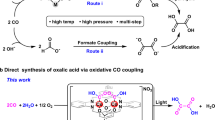
THE oxidation of α-diketones and α-keto-carboxylic acids by hydrogen peroxide involves the breaking of the carbon-carbon bond between the carbonyl carbon and the carbonyl or carboxyl groups1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holleman, Proc. K. Akad. Wetensch. Amsterdam, 6, 715 (1904).
Bunton, Minkoff, et al., Nature, 161, 172 (1948).
Haber and Wiess, Proc. Roy. Soc., A. 147, 333 (1934).
Fenton and Jones, J. Chem. Soc., 77, 71 (1900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BUNTON, C. Oxidation of α-Diketones andα-Keto-Acids by Hydrogen Peroxide. Nature 163, 444 (1949). https://doi.org/10.1038/163444a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/163444a0
This article is cited by
-
Oxidation of furfural to bio-based molecules with hydrogen peroxide via modified layered double hydroxides: the effect of gold nanoparticles on the selectivity
Journal of Porous Materials (2023)
-
Ethyl pyruvate protects against sepsis-associated encephalopathy through inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome
Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
The metabolic responses to hepatitis B virus infection shed new light on pathogenesis and targets for treatment
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Ethyl Pyruvate on Brain Energy Metabolism after Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: A 31P-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study
Neurochemical Research (2009)
-
Astrocytes Protect Against Copper-Catalysed Loss of Extracellular Glutathione
Neurochemical Research (2008)