Abstract
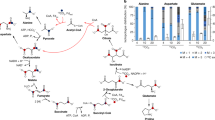
SOLUBLE enzyme preparations from Escherichia coli and Streptococcus fæcalis catalyse the dismutation of two molecules of pyruvate to acetyl phosphate, lactate and carbon dioxide when orthophosphate is present. Acetyl phosphate was determined by Lipmann's hydroxylamine reaction1. The system is almost inactive in the absence of added diphosphopyridine nucleotide (DPN). Maximum reaction-rates require, in addition to enzyme, substrate and pyridine nucleotide, the following components: orthophosphate, magnesium ions (Mg++) or manganese ions (Mn++), diphosphothiamine, a boiled extract of yeast, and lactic dehydrogenase. Coenzyme A is required for maximum yields of acetyl phosphate. The nature of the active factor in yeast extract is unknown; but it is not coenzyme A. It is possible that the compound may be a coenzyme form of the factor of O'Kane and Gunsalus2 required for oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate by S. fæcalis cells. In the absence of orthophosphate, the reaction-rate is sharply reduced and no acetyl phosphate accumulates. The dismutation can be formulated as follows: 
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipmann, F., and Tuttle, L. C., J. Biol. Chem., 159, 21 (1945).
O'Kane, D. J., and Gunsalus, I. C., J. Bact., 56, 499 (1948).
Stadtman, E. R., Fed. Proc., 9, 233 (1950).
Stern, J. R., Shapiro, B., and Ochoa, S., [Nature, 166, 403 (1950)].
Dolin, M. I., and Gunsalus, I. E. (unpublished experiments).
Ochoa, S., J. Biol. Chem., 155, 87 (1944).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KORKES, S., STERN, J., GUNSALUS, I. et al. Enzymatic Synthesis of Citrate from Pyruvate and Oxalacetate. Nature 166, 439–440 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1038/166439b0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/166439b0
This article is cited by
-
Lipoic acid
ChemTexts (2019)
-
Das coenzym a und seine biologischen funktionen
Ergebnisse der Physiologie Biologischen Chemie und Experimentellen Pharmakologie (1957)
-
Pathway for Glucose Oxidation in Asterococcus mycoides
Nature (1953)