Abstract
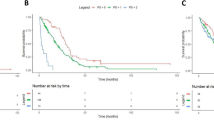
The MMT4 study was designed to explore an intensive chemotherapy regimen (MMT4–89) and the role of high-dose melphalan (MMT4–91) in children with metastatic soft tissue sarcoma, including extraosseous peripheral neuroectodermal tumor (PNET). Thirty-one patients with PNET were treated between 1989 and 1995 (11 according to MMT4–89 and 20 according to MMT4–91). Chemotherapy consisted of four CEVAIE cycles, each including three 3-week courses: CEV (carboplatin 500 mg/m2, epirubicin 150 mg/m2, vincristine 1.5 mg/m2), IVA ifosfamide 9 g/m2, actinomycin 1.5 mg/m2, vincristine 1.5 mg/m2), IVE (ifosfamide 9 g/m2, etoposide 600 mg/m2, vincristine 1.5 mg/m2). In MMT4–91 the fourth CEVAIE was replaced with melphalan 200 mg/m2 with stem cell rescue. The CEV combination was evaluated as a window study. Surgery followed the second cycle. Radiotherapy was administered to post-surgical residual disease. The response rate was 55% after CEV, rising to 80% after the first CEVAIE. Twenty-five patients achieved complete remission (CR). Overall, the 5-year EFS was 22.6%: 36.4% and 15% for patients treated according to MMT4–89 and MMT4–91, respectively (P = 0.3). Local control was achieved in 77% of irradiated patients vs 45% of non-irradiated. Age >10 years was associated with significantly poorer outcome (P = 0.04). In conclusion, despite the high CR rate, intensive chemotherapy with or without high-dose melphalan appeared to have little impact on the survival of patients with metastatic extraosseus PNET.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gururangan S, Marina NM, Luo X et al. Treatment of children with peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor or extraosseous Ewing's tumor with Ewing's-directed therapy J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1998 20: 55 61
Terrier P, Henry-Amar M, Triche TJ et al. Is neuro-ectodermal differentiation of Ewing's sarcoma of bone associated with an unfavourable prognosis? Eur J Cancer 1995 31A: 307 314
Miser JS, Kinsella TJ, Triche TJ et al. Treatment of peripheral neuroepithelioma in children and young adults J Clin Oncol 1987 5: 1752 1758
Marina NM, Pappo AS, Parham DM . Chemotherapy dose-intensification for pediatric patients with Ewing's family of tumors and desmoplastic small round-cell tumors: a feasibility study at St Jude Children's Research Hospital J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 180 190
Koscielniak E, Harms D, Henze G et al. Results of treatment for soft tissue sarcoma in childhood and adolescence: a final report of the German Cooperative Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study CWS-86 J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 3706 3719
Cecchetto G, Antoniello LM, Guglielmi M for ICS RMS-88 et al. Localized peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors and extraosseous Ewing's sarcomas: the experience of the Italian Cooperative Study RMS-88 Med Ped Oncol 1996 4: 339 (Abstr. 209)
Raney RB, Asmar L, Newton WA Jr . Ewing's sarcoma of soft tissues in childhood: a report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study, 1972 to 1991 J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 574 582
Philips M, Pinkerton CR . Pilot study of a rapid etoposide–cisplatin regimen in paediatric soft tissue sarcoma Eur J Cancer 1992 28: 399 403
Doz F, Pinkerton CR . What is the place of carboplatin in paediatric oncology? Eur J Cancer 1994 30A: 194 201
Carli M, Colombatti R, Oberlin O et al. High-dose melphalan with autologous stem-cell rescue in metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 2796 2803
Frascella E, Pritchard-Jones K, Modak S et al. Response of previously untreated metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma to combination chemotherapy with carboplatin, epirubicin and vincristine Eur J Cancer 1996 32A: 821 825
Koscielniak E, Rodary C, Flamant F et al. Metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma and histologically similar tumors in childhood: a retrospective European multicentre analysis Med Pediatr Oncol 1992 20: 209 214
Kushner BH, Meyers PA, Gerald WL et al. Very high-dose short-term chemotherapy for poor-risk peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors, including Ewing's sarcoma, in children and young adults J Clin Oncol 1995 13: 2796 2804
Felgenhauer J, Hawkins D, Pendergrass T . Very intensive, short-term chemotherapy for children and adolescents with metastatic sarcomas Med Pediatr Oncol 2000 34: 29 38
Horowitz ME, Kinsella TJ, Wexler LH et al. Total-body irradiation and autologous bone marrow transplant in the treatment of high-risk Ewing's sarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma J Clin Oncol 1993 11: 1911 1918
Matthay KK, Villablanca JG, Seeger RC et al. Treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma with intensive chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous bone marrow transplantation, and 13-cis-retinoic acid. Children's Cancer Group New Engl J Med 1999 341: 165 173
Blay JY, Bouhour D, Ray-Coquard I et al. High-dose chemotherapy with autologous hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for advanced soft tissue sarcoma in adults J Clin Oncol 2000 18: 3643 3650
Pinkerton CR, Groot-Loonen J, Barrett J et al. Rapid VAC high dose melphalan regimen: a novel chemotherapy approach for childhood soft tissue sarcomas Br J Cancer 1991 64: 381 385
Ladenstein R, Lasset C, Pinkerton R et al. Impact of megatherapy in children with high-risk Ewing's tumours in complete remission: a report from the EBMT Solid Tumour Registry Bone Marrow Transplant 1995 15: 697 705
Carli M, Colombatti, Pinkerton R et al. prognostic factors in children with metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma: results of the European Intergroup Studies MMT89 and MMT91 Proc SIOP Med Pediatr Oncol 1997 29: 324 (Abstr. 32)
Anderson JR, Ruby E, Link M et al. Identification of a favorable subset of patients with metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1997 16: 510 (Abstr. 1836)
Burdach S, van Kaick B, Laws HJ et al. Allogeneic and autologous stem cell transplantation in advanced Ewing tumors Ann Oncol 2000 11: 1451 1462
Cotterill SJ, Ahrens S, Paulussen M et al. Prognostic factors in Ewing's tumor of bone: analysis of 975 patients from the European Intergroup Cooperative Ewing's Sarcoma Study Group J Clin Oncol 2000 18: 3108 3114
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ilaria Zanetti and Joan Malings for data managing and secretarial assistance. This research has been partially supported by a grant from the Fondazione Città della Speranza.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bisogno, G., Carli, M., Stevens, M. et al. Intensive chemotherapy for children and young adults with metastatic primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the soft tissue. Bone Marrow Transplant 30, 297–302 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1703617
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1703617