Summary:
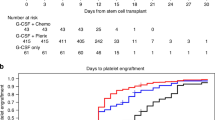
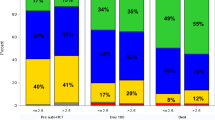
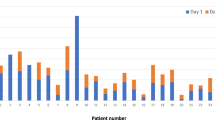
The purpose of the study was to examine the yield of CD34+ cells, response rates, and toxicity of high-dose cyclophosphamide with or without etoposide in patients with multiple myeloma. In total, 77 myeloma patients received either cyclophosphamide 4.5 g/m2 (n=28) alone or with etoposide 2 g/m2 (n=49) in a nonrandomized manner, followed by G-CSF 10 μg/kg/day for the purpose of stem cell mobilization. The effects of various factors on CD34+ cell yield, response rate and engraftment were explored. A median of 22.39 × 106 CD34+ cells/kg were collected on the first day of leukapheresis (range 0.59–114.71 × 106/kg) in 71 (92%) of patients. Greater marrow plasma cell infiltration (P=0.02) or prior radiation therapy (P=0.02) adversely affected CD34+ cell yield. In total, 45% of patients receiving cyclophosphamide and 56% of those receiving cyclophosphamide/etoposide had at least a minimum response by EBMT criteria. In all, 25% of patients who received cyclophosphamide alone vs 75.5% of patients who received combined chemotherapy required hospitalization mainly for treatment of neutropenic fever. Cyclophosphamide alone is associated with impressive CD34+ cell yields and clear antimyeloma activity. The addition of etoposide resulted in increased toxicity without significant improvement in CD34+ cell yield or response rates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attal M, Harousseau JL, Stoppa AM et al. A prospective, randomized trial of autologous bone marrow transplantation and chemotherapy in multiple myeloma. Intergroupe Francais du Myelome. N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 91–97.
Attal M, Harousseau JL . Randomized trial experience of the Intergroupe Francophone du Myelome. Semin Hematol 2001; 38: 226–230.
Barlogie B, Jagannath S, Desikan KR et al. Total therapy with tandem transplants for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood 1999; 93: 55–65.
Barbui AM, Galli M, Dotti G et al. Negative selection of peripheral blood stem cells to support a tandem autologous transplantation programme in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 2002; 116: 202–210.
Olavarria E, Kanfer EJ . Selection and use of chemotherapy with hematopoietic growth factors for mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells. Curr Opin Hematol 2000; 7: 191–196.
Blade J, Samson D, Reece D et al. Criteria for evaluating disease response and progression in patients with multiple myeloma treated by high-dose therapy and haemopoietic stem cell transplantation. Myeloma Subcommittee of the EBMT. European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplant. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 1115–1123.
Fermand JP, Ravaud P, Chevret S et al. High-dose therapy and autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma: up-front or rescue treatment? Results of a multicenter sequential randomized clinical trial. Blood 1998; 92: 3131–3136.
Schmitz N, Linch DC, Dreger P et al. Randomised trial of filgrastim-mobilised peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation versus autologous bone-marrow transplantation in lymphoma patients. Lancet 1996; 347: 353–357.
Narayanasami U, Kanteti R, Morelli J et al. Randomized trial of filgrastim versus chemotherapy and filgrastim mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells for rescue in autologous transplantation. Blood 2001; 98: 2059–2064.
Meisenberg B, Brehm T, Schmeckel A et al. A combination of low-dose cyclophosphamide and colony-stimulating factors is more cost-effective than granulocyte-colony-stimulating factors alone in mobilizing peripheral blood stem and progenitor cells. Transfusion 1998; 38: 209–215.
Koc ON, Gerson SL, Cooper BW et al. Randomized cross-over trial of progenitor-cell mobilization: high-dose cyclophosphamide plus granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) versus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus G-CSF. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 1824–1830.
Demirer T, Buckner CD, Gooley T et al. Factors influencing collection of peripheral blood stem cells in patients with multiple myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 937–941.
Goldschmidt H, Hegenbart U, Wallmeier M et al. Factors influencing collection of peripheral blood progenitor cells following high-dose cyclophosphamide and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 1997; 98: 736–744.
Goldschmidt H, Hegenbart U, Haas R, Hunstein W . Mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells with high-dose cyclophosphamide (4 or 7 g/m2) and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with multiple myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 691–697.
Tricot G, Jagannath S, Vesole D et al. Peripheral blood stem cell transplants for multiple myeloma: identification of favorable variables for rapid engraftment in 225 patients. Blood 1995; 85: 588–596.
Prince HM, Imrie K, Sutherland DR et al. Peripheral blood progenitor cell collections in multiple myeloma: predictors and management of inadequate collections. Br J Haematol 1996; 93: 142–145.
Dimopoulos MA, Delasalle KB, Champlin R, Alexanian R . Cyclophosphamide and etoposide therapy with GM-CSF for VAD-resistant multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 1993; 83: 240–244.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Kathleen Ruehle for assistance with data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gojo, I., Guo, C., Sarkodee-Adoo, C. et al. High-dose cyclophosphamide with or without etoposide for mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells in patients with multiple myeloma: efficacy and toxicity. Bone Marrow Transplant 34, 69–76 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704529
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704529
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bendamustine, etoposide and dexamethasone to mobilize peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells for autologous transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2016)
-
International myeloma working group (IMWG) consensus statement and guidelines regarding the current status of stem cell collection and high-dose therapy for multiple myeloma and the role of plerixafor (AMD 3100)
Leukemia (2009)
-
Ifosfamide, epirubicin, and etoposide (IEV) mobilize peripheral blood stem cells more efficiently than cyclophosphamide/etoposide
Annals of Hematology (2007)
-
Autologous stem cell transplantation followed by consolidation chemotherapy for patients with multiple myeloma
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2006)
-
Peripheral blood stem cell mobilization by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor alone and engraftment kinetics following autologous transplantation in children and adolescents with solid tumor
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2006)