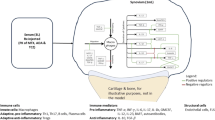
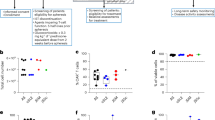
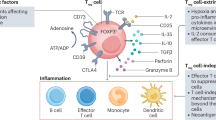
Summary:
Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) can be performed in a variety of refractory autoimmune diseases. A retrospective multicenter analysis is presented to evaluate safety and efficacy of ASCT for refractory juvenile idiopathic arthritis. In all, 18 of the 34 patients (53%) with a follow-up of 12 to 60 months achieved a drug-free complete remission. There were three cases (9%) of transplant-related mortality and two cases of disease-related mortality (6%). Infectious complications were seen frequently. We propose adjustments in future protocols to reduce this mortality in this high-risk patient group.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Bekkum DW . Stem cell transplantation for autoimmune disorders. Preclinical experiments. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2004; 17: 201–222.
Marmont AM . Stem cell transplantation for autoimmune disorders. Coincidental autoimmune disease in patients transplanted for conventional indications. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2004; 17: 223–232.
Wallace CA, Sherry DD . Trial of intravenous pulse cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone in the treatment of severe systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1997; 40: 1852–1855.
Lovell DJ, Giannini EH, Reiff A et al. Etanercept in children with polyarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 763–769.
Yokota S . Interleukin 6 as a therapeutic target in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003; 15: 581–586.
Quartier P, Taupin P, Bourdeaut F et al. Efficacy of etanercept for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis according to the onset type. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 1093–1101.
Petty RE . Prognosis in children with rheumatic diseases: justification for consideration of new therapies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999; 38: 739–742.
Spiegel LR, Schneider R, Lang BA et al. Early predictors of poor functional outcome in systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: a multicenter cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 2000; 43: 2402–2409.
Giannini EH, Ruperto N, Ravelli A et al. Preliminary definition of improvement in juvenile arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1997; 40: 1202–1209.
Ruperto N, Ravelli A, Falcini F et al. Performance of the preliminary definition of improvement in juvenile chronic arthritis patients treated with methotrexate. Italian Pediatric Rheumatology Study Group. Ann Rheum Dis 1998; 57: 38–41.
De Kleer IM, Brinkman DM, Ferster A et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for refractory juvenile idiopathic arthritis: analysis of clinical efficacy mortality and transplant related morbidity. Ann Rheum Dis 2004; 63: 1318–1326.
Wulffraat NM, Brinkman D, Ferster A et al. Long-term follow-up of autologous stem cell transplantation for refractory juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32 (Suppl. 1): S61–S64.
Ramanan AV, Schneider R . Macrophage activation syndrome – what's in a name!. J Rheumatol 2003; 30: 2513–2516.
Ravelli A, De Benedetti F, Viola S, Martini A . Macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis successfully treated with cyclosporine. J Pediatr 1996; 128: 275–278.
Stephan JL, Kone-Paut I, Galambrun C et al. Reactive haemophagocytic syndrome in children with inflammatory disorders. A retrospective study of 24 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001; 40: 1285–1292.
Silverman ED, Miller III JJ, Bernstein B, Shafai T . Consumption coagulopathy associated with systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Pediatr 1983; 103: 872–876.
Hertzberger-ten Cate R, Cats A . Toxicity of sulfasalazine in systemic juvenile chronic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1991; 9: 85–88.
Prahalad S, Bove KE, Dickens D et al. Etanercept in the treatment of macrophage activation syndrome. J Rheumatol 2001; 28: 2120–2124.
Ravelli A, Caria MC, Buratti S et al. Methotrexate as a possible trigger of macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 2001; 28: 865–867.
Grom AA, Villanueva J, Lee S et al. Natural killer cell dysfunction in patients with systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and macrophage activation syndrome. J Pediatr 2003; 142: 292–296.
Wulffraat NM, Rijkers GT, Elst EF et al. Reduced perforin expression in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis is restored by autologous stem cell transplantation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003; 42: 375–379.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wulffraat, N., Vastert, B. & Tyndall, A. Treatment of refractory autoimmune diseases with autologous stem cell transplantation: focus on juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Bone Marrow Transplant 35 (Suppl 1), S27–S29 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704840
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704840
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: diagnosis, management, and outcome
Nature Clinical Practice Rheumatology (2006)
-
Update on the medical treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Current Rheumatology Reports (2006)