Abstract
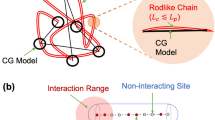
AN expression for the mean square radius of a randomly coiled long-chain polymer, that is, for the mean square distance of its constituent groups from their centre of mass, was first derived by Debye1. Debye's formula applies only to very long chains; the following simple derivation is valid for any unbranched chain, provided the correlation between two atoms depends only on the number of links separating them (this implies neglect of the excluded volume effect).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Debye, P., J. Chem. Phys., 14, 639 (1946).
Lagrange, J.-L., Oeuvres, 5, 535 (Paris, 1870). Cf. Lamb, H., “Statics”, 3rd edit., 166 (Cambridge, 1928).
Wall, F. T., J. Chem. Phys., 11, 67 (1943).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SACK, R. Mean Square Radius of randomly coiled Molecular Chains. Nature 171, 310 (1953). https://doi.org/10.1038/171310a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/171310a0