Abstract
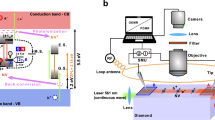
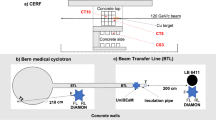
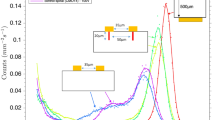
FIVE type 2 diamonds, whose ability to transmit ultra-violet radiation and whose response as counters of α-particles had already been examined, were irradiated by neutrons in B.E.P.O. at Harwell. Typical curves showing the variation in counting response (in terms of maximum pulse-height) with radiation dosage are shown in the graph. The general behaviour leaves no doubt that the counting response is progressively reduced with increasing neutron exposure. Similarly, photometric measurements showed that a uniform reduction occurred in the ultra-violet transmission.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Griffiths, J. H. E., Owen, J., and Ward, I. M., Nature, 173, 439 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BENNY, A., CHAMPION, F. Some Effects of Neutron Irradiation of Diamond. Nature 173, 1087 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1038/1731087a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1731087a0