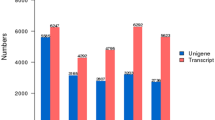
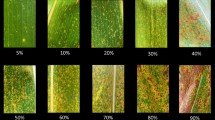
Abstract
THE maize rust fungus Puccinia polysora was first described in 1897 by Underwood in Alabama on Tripsacum, a plant allied to maize; it was later also found on Erianthus, a species of grass related to the sugar-cane. In 1941, Cummins detected the fungus for the first time on maize in the United States, but a careful review of herbarium material collected earlier from different parts of the Continent and deposited as the common maize rust, P. sorghi Schw., brought out that many of the specimens had indeed been attacked by P. polysora.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ORIAN, G. Occurrence of Puccinia polysora Underwood in the Indian Ocean Area. Nature 173, 505 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1038/173505a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/173505a0
This article is cited by
-
Southern corn rust caused by Puccinia polysora Underw: a review
Phytopathology Research (2021)
-
De novo transcriptome assembly, polymorphic SSR markers development and population genetics analyses for southern corn rust (Puccinia polysora)
Scientific Reports (2021)