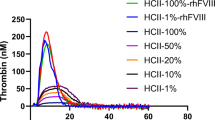
Abstract
BOTH heparin1 and histamine2 are now known to be concentrated in the tissue mast cells, and it might thus be expected that the release of histamine caused by damage to the mast cells would be accompanied by the release of heparin and a consequent increase in the clotting,time of blood. So far this dual effect has been observed in only one species, the dog, in which an intravenous injection of peptone or of a chemical histamine liberator such as compound 48/80 can release sufficient heparin to render the blood incoagulable. In the rat, however, although compound 48/80 releases histamine from the numerous mast cells in the subcutaneous connective tissue, the clotting time of the rat's blood remains unchanged. We have therefore attempted to discover what happens to the heparin in the rat following a maximal release of histamine by compound 48/80.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jorpes, J. E., “Heparin in the Treatment of Thrombosis” (2nd ed., Oxf. Univ. Press, London, 1946).
Riley, J. F., and West, G. B., J. Physiol., 120, 528 (1953).
Cass, R., Riley, J. F., West, G. B., Head, K. W., and Stroud, S. W., Nature, 174, 318 (1954).
Snellman, O., Jensen, R., and Sylvén, B., Nature, 161, 639 (1948).
Charles, A. F., and Scott, D. A., Biol. Chem., 102, 426 (1933).
Riley, J. F., and West, G. B., J. Path. Bact., 69, 269 (1955).
Fawcett, D. W., J. Exp. Med., 100, 217 (1954).
Riley, J. F., Lancet, i, 841 (1954).
Fischer, A., Biol. Rev., 22, 178 (1947).
Mota, I., Beraldo, W. T., and Junqueira, L. C. U., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 83, 455 (1953).
Paton, W. D. M., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 6, 499 (1951).
Adams, S. S., J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 9, 580 (1953).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RILEY, J., SHEPHERD, D., WEST, G. et al. Function of Heparin. Nature 176, 1123 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1038/1761123a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1761123a0
This article is cited by
-
Zur Physiologie der Mastzellen als Tr�ger des Heparins und Histamins
Klinische Wochenschrift (1956)