Abstract
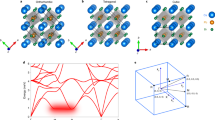
WE have completed an X-ray investigation of cæsium–antimony alloys which shows that the photoelectric surface material cæsium antimonide is a ‘normal valency’ intermetallic compound with a small range of homogeneity probably from Cs3Sb to Cs3+xSb1−x, where x, estimated from the observed variation of unit-cell dimensions, is of the order of 0.05. The atomic arrangement is pseudo body-centred cubic with a structure based upon the B32 sodium thallide type (NaTl). The cubic unit cell (a = 9.14–9.19 A.) contains sixteen atoms at special positions of space group Fd3m—O h 7. Eight equivalent sites at (0,0,0; 0,½,½; ½,0,½; ½,½,0) + 0,0,0; ¼,¼,¼ are occupied solely by cæsium atoms and eight other sites, at (0,0,0; 0,½,½; ½,0,½; ½,½,0) + ½,½,½; ¾,¾,¾, are occupied randomly by four cæsium and four antimony atoms. The structure may be described as consisting of two interpenetrating diamond-type lattices, one of cæsium atoms and the other of equal numbers of cæsium and antimony atoms. The semi-conducting properties of the material are explained by a filled Brillouin zone containing two electrons per atom. A full report of the investigation, together with a discussion of the cæsium antimonide structure and its correlation with other properties of the material, will be made elsewhere1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jack, K. H., and Wachtel, M. M., Proc. Roy. Soc. (in the press).
Waller, I., and James, R. W., Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 117, 214 (1927).
Lonsdale, K., and Grenville-Wells, H. J., Nature, 177, 986 (1956).
Weiss, R. J., DeMarco, J. J., Weremchuk, G., Corliss, L., and Hastings, J., Acta Cryst., 9, 42 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
JACK, K., WACHTEL, M. Structural Characterization of Cæsium Antimonide: Temperature Factors in Cubic Crystals. Nature 178, 1408–1409 (1956). https://doi.org/10.1038/1781408a0
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1781408a0
This article is cited by
-
The Cs-Sb (cesium-antimony) system
Journal of Phase Equilibria (1997)